CHAPTER 1
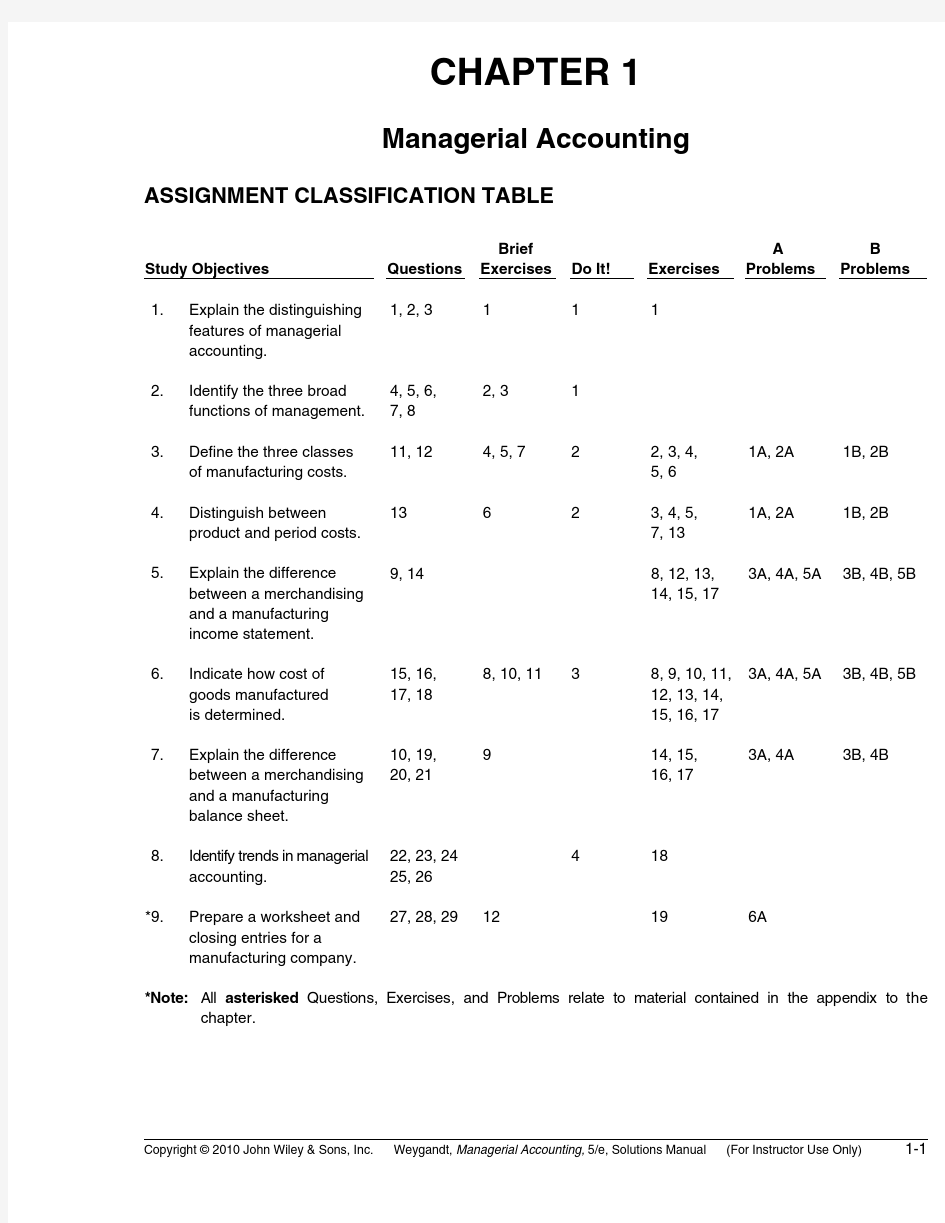
Managerial Accounting ASSIGNMENT CLASSIFICATION TABLE
Study Objectives Questions
Brief
Exercises Do It!Exercises
A
Problems
B
Problems
1.Explain the distinguishing
features of managerial
accounting.
1, 2, 3111
2.Identify the three broad
functions of management.4, 5, 6,
7, 8
2, 31
3.Define the three classes
of manufacturing costs.11, 124, 5, 722, 3, 4,
5, 6
1A, 2A1B, 2B
4.Distinguish between
product and period costs.13623, 4, 5,
7, 13
1A, 2A1B, 2B
5.Explain the difference
between a merchandising
and a manufacturing
income statement.9, 148, 12, 13,
14, 15, 17
3A, 4A, 5A3B, 4B, 5B
6.Indicate how cost of
goods manufactured
is determined.15, 16,
17, 18
8, 10, 1138, 9, 10, 11,
12, 13, 14,
15, 16, 17
3A, 4A, 5A3B, 4B, 5B
7.Explain the difference
between a merchandising
and a manufacturing
balance sheet.10, 19,
20, 21
914, 15,
16, 17
3A, 4A3B, 4B
8.Identify trends in managerial
accounting.22, 23, 24
25, 26
418
*9.Prepare a worksheet and
closing entries for a
manufacturing company.
27, 28, 2912196A
*Note:All asterisked Questions, Exercises, and Problems relate to material contained in the appendix to the chapter.
Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-1
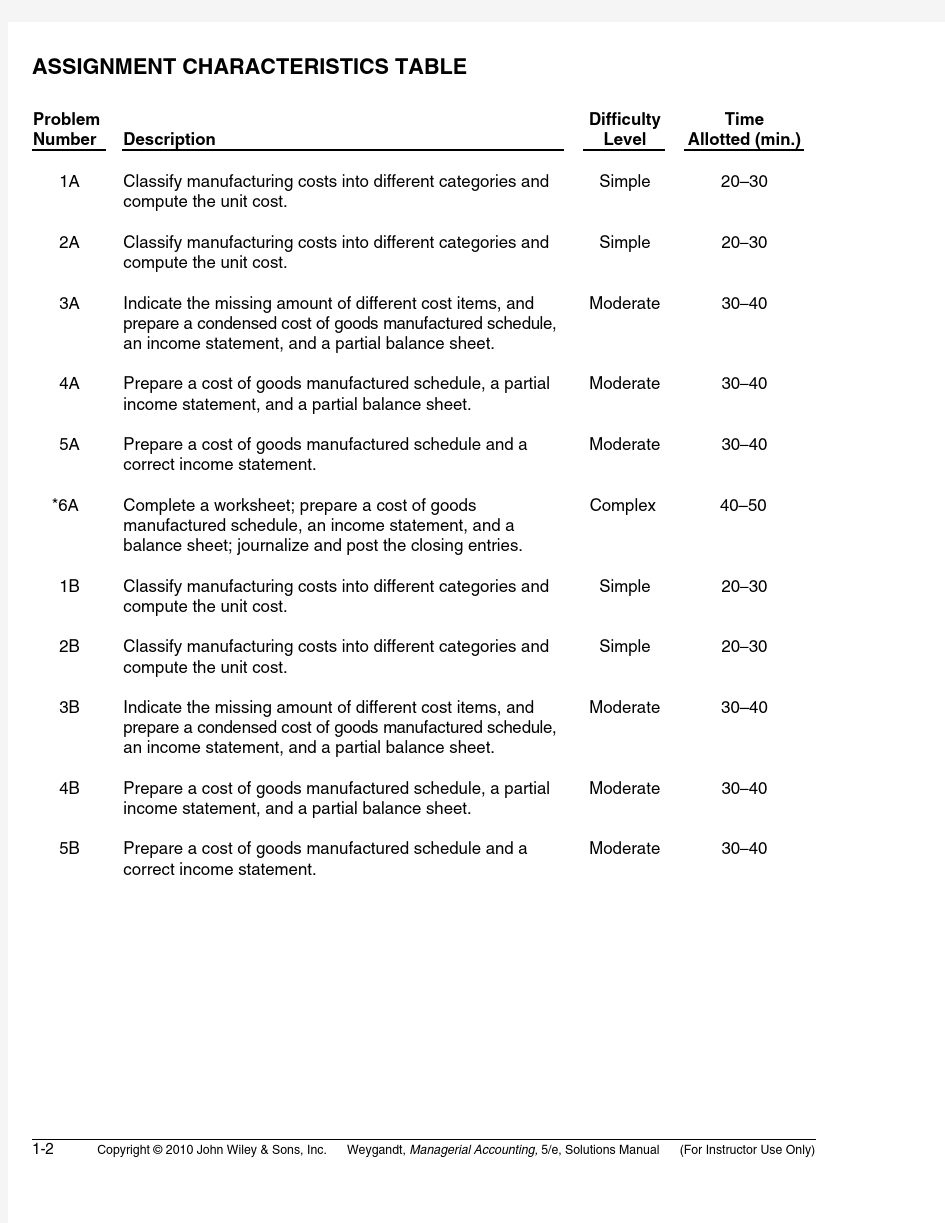
ASSIGNMENT CHARACTERISTICS TABLE
Problem
Number Description Difficulty
Level
Time
Allotted (min.)
1A Classify manufacturing costs into different categories and
compute the unit cost.
Simple20–30
2A Classify manufacturing costs into different categories and
compute the unit cost.
Simple20–30
3A Indicate the missing amount of different cost items, and
prepare a condensed cost of goods manufactured schedule,
an income statement, and a partial balance sheet.
Moderate30–40
4A Prepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule, a partial
income statement, and a partial balance sheet.
Moderate30–40
5A Prepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule and a
correct income statement.
Moderate30–40
*6A Complete a worksheet; prepare a cost of goods
manufactured schedule, an income statement, and a
balance sheet; journalize and post the closing entries.
Complex40–50
1B Classify manufacturing costs into different categories and
compute the unit cost.
Simple20–30
2B Classify manufacturing costs into different categories and
compute the unit cost.
Simple20–30
3B Indicate the missing amount of different cost items, and
prepare a condensed cost of goods manufactured schedule,
an income statement, and a partial balance sheet.
Moderate30–40
4B Prepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule, a partial
income statement, and a partial balance sheet.
Moderate30–40
5B Prepare a cost of goods manufactured schedule and a
correct income statement.
Moderate30–40
1-2Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
BLOOM’S TAXONOMY TABLE
Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual
(For Instructor Use Only)
1-3
C o r r e l a t i o n C h a r t b e t w e e n B l o o m ’s T a x o n o m y , S t u d y O b j e c t i v e s a n d E n d -o f -C h a p t e r E x e r c i s e s a n d P r o b l e m s
S t u d y O b j e c t i v e K n o w l e d g e C o m p r e h e n s i o n A p p l i c a t i o n A n a l y s i s S y n t h e s i s E v a l u a t i o n
*1.E x p l a i n t h e d i s t i n g u i s h i n g f e a t u r e s o f m a n a g e r i a l a c c o u n t i n g .
Q 1-1Q 1-2Q 1-3B E 1-1D I 1-1E 1-1*2.I d e n t i f y t h e t h r e e b r o a d f u n c t i o n s o f m a n a g e m e n t .
Q 1-4Q 1-5Q 1-6Q 1-7Q 1-8B E 1-2B E 1-3D I 1-1*3.D e f i n e t h e t h r e e c l a s s e s o f m a n u f a c t u r i n g c o s t s .Q 1-11Q 1-12B E 1-4B E 1-5B E 1-7D I 1-2E 1-2E 1-3E 1-4E 1-5E 1-6
P 1-1A P 1-2A P 1-1B
P 1-2B
*4.D i s t i n g u i s h b e t w e e n p r o d u c t a n d p e r i o d c o s t s .
Q 1-13B E 1-6D I 1-2E 1-3E 1-4E 1-5E 1-7E 1-13P 1-1A P 1-2A P 1-1B P 1-2B
*5.E x p l a i n t h e d i f f e r e n c e b e t w e e n a m e r c h a n d i s i n g a n d a m a n u f a c t u r i n g i n c o m e s t a t e m e n t .Q 1-9Q 1-14E 1-15
E 1-8E 1-12E 1-13E 1-14E 1-17P 1-4A P 1-4B P 1-3A P 1-5A P 1-3B P 1-5B
*6.I n d i c a t e h o w c o s t o f g o o d s m a n u f a c t u r e d i s d e t e r m i n e d .
E 1-15
Q 1-15Q 1-16Q 1-17Q 1-18B E 1-8B E 1-10B E 1-11D I 1-3E 1-8E 1-9E 1-10E 1-11E 1-12E 1-13
E 1-14E 1-16E 1-17P 1-4A P 1-4B E 1-10E 1-11P 1-3A P 1-5A P 1-3B P 1-5B
*7.E x p l a i n t h e d i f f e r e n c e b e t w e e n a m e r c h a n d i s i n g a n d a m a n u f a c t u r i n g b a l a n c e s h e e t .Q 1-19Q 1-10Q 1-20Q 1-21E 1-15B E 1-9E 1-14E 1-16E 1-17P 1-4A P 1-4B
P 1-3A P 1-3B *8.I d e n t i f y t r e n d s i n m a n a g e r i a l a c c o u n t i n g .
Q 1-22Q 1-23Q 1-24Q 1-25Q 1-26D I 1-4E 1-18*9.P r e p a r e a w o r k s h e e t a n d c l o s i n g e n t r i e s f o r a m a n u f a c t u r i n g c o m p a n y
Q 1-28
Q 1-27Q 1-29B E 1-12E 1-19P 1-6A B r o a d e n i n g Y o u r P e r s p e c t i v e
R e a l -W o r l d F o c u s
D e c i s i o n M a k i n g A c r o s s t h e O r g a n i z a t i o n M a n a g e r i a l A n a l y s i s
E x p l o r i n g t h e W e b C o m m u n i c a t i o n
E t h i c s C a s e A l l A b o u t Y o u
ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS
1.(a)Disagree. Managerial accounting is a field of accounting that provides economic and financial
information for managers and other internal users.
(b)Mary is incorrect. Managerial accounting applies to all types of businesses—service, merchandising,
and manufacturing.
2.(a)Financial accounting is concerned primarily with external users such as stockholders, creditors,
and regulators. In contrast, managerial accounting is concerned primarily with internal users such
as officers and managers.
(b)Financial statements are the end product of financial accounting. The statements are prepared
quarterly and annually. In managerial accounting, internal reports may be prepared as frequently
as needed.
(c)The purpose of financial accounting is to provide general-purpose information for all users.
The purpose of managerial accounting is to provide special-purpose information for specific
decisions.
3.Differences in the content of the reports are as follows:
Financial Managerial
?Pertains to business as a whole and is highly aggregated.
?Limited to double-entry accounting and cost data.
?Generally accepted accounting principles.?Pertains to subunits of the business and may be very detailed.
?Extends beyond double-entry accounting system to any relevant data.?Standard is relevance to decisions.
In financial accounting, financial statements are verified annually through an independent audit by certified public accountants. There are no independent audits of internal reports issued by managerial accountants.
4.Budgets are prepared by companies to provide future direction. Because the budget is also used
as an evaluation tool, some managers try to game the budgeting process by underestimating their division’s predicted performance so that it will be easier to meet their performance targets.
On the other hand, if the budget is set at unattainable levels, managers sometimes take unethical actions to meet targets to receive higher compensation or in some cases to keep their jobs.
5.Karen should know that the management of an organization performs three broad functions:
(1)Planning requires management to look ahead and to establish objectives.
(2)Directing involves coordinating the diverse activities and human resources of a company to
produce a smooth-running operation.
(3)Controlling is the process of keeping the company’s activities on track.
6.Disagree. Decision making is not a separate management function. Rather, decision making involves
the exercise of good judgment in performing the three management functions explained in the answer to question five above.
7.Employees with line positions are directly involved in the company’s primary revenue generating
operating activities. Examples would include plant managers and supervisors, and the vice president of operations. In contrast, employees with staff positions are not directly involved in revenue-generating operating activities, but rather serve in a support capacity to line employees. Examples include employees in finance, legal, and human resources.
1-4Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
Questions Chapter 1 (Continued)
8.CEOs and CFOs must now certify that financial statements give a fair presentation of the company’s
operating results and its financial condition and that the company maintains an adequate system of internal controls. In addition, the composition of the board of directors and audit committees receives more scrutiny, and penalties for misconduct have increased.
9.The differences between income statements are in the computation of the cost of goods sold as
follows:
Manufacturing company:Beginning finished goods inventory plus cost of goods manufactured minus ending finished goods inventory = cost of goods sold.
Merchandising company:Beginning merchandise inventory plus cost of goods purchased minus ending merchandise inventory = cost of goods sold.
10.The difference in balance sheets pertains to the presentation of inventories in the current asset
section. In a merchandising company, only merchandise inventory is shown. In a manufacturing company, three inventory accounts are shown: finished goods, work in process, and raw materials.
11.Manufacturing costs are classified as either direct materials, direct labor, or manufacturing overhead.
12.No, Matt is not correct. The distinction between direct and indirect materials is based on two criteria:
(1) physical association and (2) the convenience of making the physical association. Materials which
can not be easily associated with the finished product are considered indirect materials.
13.Product costs, or inventoriable costs, are costs that are a necessary and integral part of producing
the finished product. Period costs are costs that are identified with a specific time period rather than with a salable product. These costs relate to nonmanufacturing costs and therefore are not inventoriable costs.
14. A merchandising company has beginning merchandise inventory, cost of goods purchased, and
ending merchandise inventory. A manufacturing company has beginning finished goods inventory, cost of goods manufactured, and ending finished goods inventory.
15.(a)X = total cost of work in process.
(b)X = cost of goods manufactured.
16.Raw materials inventory, beginning......................................................................................$ 12,000
Raw materials purchases.......................................................................................................170,000 Total raw materials available for use....................................................................................182,000 Raw materials inventory, ending........................................................................................... 15,000 Direct materials used....................................................................................................$167,000 17.Direct materials used...............................................................................................................$240,000
Direct labor used......................................................................................................................200,000 Total manufacturing overhead...............................................................................................180,000 Total manufacturing costs............................................................................................$620,000
18.(a)Total cost of work in process ($26,000 + $620,000)..............................................$646,000
(b)Cost of goods manufactured ($646,000 – $32,000)...............................................$614,000
19.The order of listing is finished goods inventory, work in process inventory, and raw materials inventory.
Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-5
Questions Chapter 1 (Continued)
20.The products differ in how each are consumed by the customer. Service companies consume
immediately; the product is not put into inventory. Meals at a restaurant are the best example where they are consumed immediately by the customer. There could be a long lead time before the product is consumed in a manufacturing environment.
21.Yes, product costing techniques apply equally well to manufacturers and service companies. Each
need to keep track of the cost of services in order to know whether it is generating a profit. The techniques shown in this chapter, to accumulate manufacturing costs to determine manufacturing inventory, are equally useful for determining the cost of services.
22.The value chain refers to all activities associated with providing a product or service. For a manufac-
turer, these include research and development, product design, acquisition of raw materials, production, sales and marketing, delivery, customer relations, and subsequent service.
23.An enterprise resource planning (ERP) system is an integrated software system that provides a
comprehensive, centralized resource for information. Its primary benefits are that it replaces the many individual systems typically used for receivables, payables, inventory, human resources, etc. Also, it can be used to get information from, and provide information to, the company’s customers and suppliers.
24.In a just-in-time inventory system the company has no extra inventory stored. Consequently, if
some units that are produced are defective, the company will not have enough units to deliver to customers.
25.The balanced scorecard is called “balanced” because it strives to not over emphasize any one
performance measure, but rather uses both financial and non-financial measures to evaluate all aspects of a company’s operations in an integrated fashion.
26.Activity-based costing is an approach used to allocate overhead based on each product’s relative
use of activities in making the product. Activity-based costing is beneficial because it results in more accurate product costing and in more careful scrutiny of all activities in the value chain.
*27.The accounting cycle for a manufacturing company is the same as for a merchandising company when a periodic inventory system is used.
*28.The account balances carried into the cost of goods manufactured columns are beginning and ending work in process and raw materials inventories, raw materials purchases, direct labor, indirect labor, factory repairs, factory utilities, factory depreciation, and factory insurance.
*29.(a)The closing entry for the two inventories is:
Dec. 31Work in Process Inventory................................................................XX
Raw Materials Inventory....................................................................XX
Manufacturing Summary..........................................................XX
(b)The closing entry for manufacturing summary is:
Dec. 31Income Summary................................................................................XX
Manufacturing Summary..........................................................XX
1-6Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
SOLUTIONS TO BRIEF EXERCISES
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-1
Financial Accounting Managerial Accounting Primary users External users Internal users
Types of reports Financial statements Internal reports Frequency of reports Quarterly and annually As frequently as needed Purpose of reports General-purpose Special-purpose information
for specific decisions Content of reports Generally accepted
Relevance to decisions
accounting principles
No independent audits Verification Annual audit by certified
public accountant
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-2
One implication of SOX was to clarify top management’s responsibility for the company’s financial statements. CEOs and CFOs must now certify that financial statements give a fair presentation of the company’s operating results and its financial condition. In addition, top managers must certify that the company maintains an adequate system of internal controls to safeguard the company’s assets and ensure accurate financial reports. Also, more attention is now paid to the composition of the company’s board of directors. In particular, the audit committee of the board of directors must be comprised entirely of independent members (that is, non-employees) and must contain at least one financial expert. Finally, to increase the likelihood of compliance with these and other new rules, the penalties for misconduct were substantially increased.
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-3
(a) 1.Planning.
(b) 2.Directing.
(c) 3.Controlling.
Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-7
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-4
(a)DM Frames and tires used in manufacturing bicycles.
(b) DL Wages paid to production workers.
(c)M O Insurance on factory equipment and machinery.
(d)M O Depreciation on factory equipment.
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-5
(a)Direct materials.
(b)Direct materials.
(c)Direct labor.
(d)Manufacturing overhead.
(e)Manufacturing overhead.
(f)Direct materials.
(g)Direct materials.
(h)Manufacturing overhead.
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-6
(a)Product.
(b)Period.
(c)Period.
(d)Period.
(e)Product.
(f)Product.
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-7
Product Costs
Direct Materials Direct
Labor
Factory
Overhead
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)X
X
X
X
1-8Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-8
(a)Direct materials used......................................................................$180,000
Direct labor.........................................................................................229,000 Total manufacturing overhead....................................................208,000 Total manufacturing costs...................................................$617,000 (b)Beginning work in process...........................................................$ 25,000
Total manufacturing costs............................................................617,000 Total cost of work in process..............................................$642,000 BRIEF EXERCISE 1-9
DIAZ COMPANY
Balance Sheet
December 31, 2011
Current assets
Cash................................................................................$ 62,000 Accounts receivable..................................................200,000 Inventories
Finished goods..................................................$71,000
Work in process.................................................87,000
Raw materials.....................................................73,000 231,000 Prepaid expenses....................................................... 38,000 Total current assets.................................$531,000 BRIEF EXERCISE 1-10
Direct Materials Used
Direct
Labor Used
Factory
Overhead
Total
Manufacturing
Costs
(1)
(2)
(3)$81,000
$144,000
$136,000
Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-9
BRIEF EXERCISE 1-11
Total Manufacturing
Costs
Work in
Process
(January 1)
Work in
Process
(December 31)
Cost of Goods
Manufactured
(1)
(2)
(3)$136,000
$123,000
$58,000
$174,000
*BRIEF EXERCISE 1-12
Account Work Sheet Column
Finished Goods Inventory Work in Process Inventory Raw Materials Purchases Direct Labor Income statement (DR)
Cost of goods manufactured (DR) Cost of goods manufactured (DR) Cost of goods manufactured (DR)
SOLUTIONS FOR DO IT! REVIEW EXERCISES
DO IT! 1-1
1.False
2.False
3.False
4.True
5.True
6.True
DO IT! 1-2
Period costs:
Advertising
Salaries of sales representatives
1-10Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
DO IT! 1-2 (Continued)
Product costs:
Blank CDs (DM)
Depreciation of CD image burner (MO)
Salary of factory manager (MO)
Factory supplies used (MO)
Paper inserts for CD cases (DM)
CD plastic cases (DM)
Salaries of factory maintenance employees (MO)
Salaries of employees who burn music onto CDs (DL)
DO IT! 1-3
ROLEN MANUFACTURING COMPANY
Cost of Goods Manufactured Schedule
For the Month Ended April 30
Work in process, April 1.......................................$ 5,000 Direct materials........................................................
Raw materials, April 1......................................$ 10,000
Raw materials purchases................................ 98,000
Total raw materials available for use..........108,000
Less: Raw materials, April 30....................... 14,000
Direct materials used........................................$ 94,000
Direct labor................................................................60,000 Manufacturing overhead....................................... 180,000
Total manufacturing costs................................... 334,000 Total cost of work in process.............................$339,000 Less: Work in process, April 31........................ 3,500 Cost of goods manufactured..............................$335,500 DO IT! 1-4
1.f
2.a
3.c
4.d
5.e
6.b
Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-11
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES
EXERCISE 1-1
1.False. Financial accounting focuses on providing information to external
users.
2.True.
3.False. Preparation of budgets is part of managerial accounting.
4.False. Managerial accounting applies to service, merchandising and
manufacturing companies.
5.True.
6.False. Managerial accounting reports are prepared as frequently as
needed.
7.True.
8.True.
9.False. Financial accounting reports must comply with Generally Accepted
Accounting Principles.
10.False. Managerial accountants are expected to behave ethically, and there
is a code of ethical standards for managerial accountants.
EXERCISE 1-2
1.(b)Direct labor.*
2.(c)Manufacturing overhead.
3.(c) Manufacturing overhead.
4.(c) Manufacturing overhead.
5.(a)Direct materials.
6.(b)Direct labor.
7.(c)Manufacturing overhead.
8.(c) Manufacturing overhead.
9.(c)Manufacturing overhead.
10.(a)Direct materials.
*or sometimes (c), depending on the circumstances
1-12Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
EXERCISE 1-3
(a)Materials used in product........DM Advertising expense.................Period
Depreciation on plant.............MOH Property taxes on plant...............MOH Property taxes on store......Period Delivery expense........................Period
Sales commissions....................Period Labor costs of assembly
line workers................................DL Salaries paid to sales clerks.....Period Factory supplies used...........MOH
(b)Product costs are recorded as a part of the cost of inventory because
they are an integral part of the cost of producing the product. Product costs are not expensed until the goods are sold. Period costs are recognized as an expense when incurred.
EXERCISE 1-4
(a)Factory utilities....................................................................................$ 11,500
Depreciation on factory equipment.............................................. 12,650 Indirect factory labor......................................................................... 48,900 Indirect materials................................................................................80,800 Factory manager’s salary................................................................. 8,000 Property taxes on factory building............................................... 2,500 Factory repairs..................................................................................... 2,000 Manufacturing overhead...................................................................$166,350
(b)Direct materials....................................................................................$137,600
Direct labor............................................................................................ 69,100 Manufacturing overhead...................................................................166,350 Product costs.......................................................................................$373,050
(c)Depreciation on delivery trucks....................................................$ 3,800
Sales salaries......................................................................................46,400 Repairs to office equipment........................................................... 1,300 Advertising........................................................................................... 18,000 Office supplies used......................................................................... 2,640 Period costs.........................................................................................$ 72,140
Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-13
EXERCISE 1-5
1. 2.(c)
(c)
3.
4.
(a)
(c)
5.
6.
(b)*
(d)
7.
8.
(a)
(b)
9.
10.
(c)
(c)
*or sometimes (c), depending on the circumstances.
EXERCISE 1-6
1.(b)
2.(c)
3.(a)
4.(c)
5.(c)
6.(c)
7.(c)
8.(c)
9.(c)
10.(c)
EXERCISE 1-7
(a)Delivery service (product) costs:
Indirect materials$ 5,400
Depreciation on delivery equipment11,200
Dispatcher’s salary5,000
Gas and oil for delivery trucks2,200
Drivers’ salaries11,000
Delivery equipment repairs 300
Total$35,100
(b)Period costs:
Property taxes on office building$ 870
CEO’s salary12,000
Advertising1,600
Office supplies650
Office utilities990
Repairs on office equipment 180
Total$16,290
1-14Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
EXERCISE 1-8
(a)Work-in-process, 1/1.....................................$ 12,000
Direct materials used....................................$100,000
Direct labor.......................................................110,000
Manufacturing overhead
Depreciation on plant...........................$60,000
Factory supplies used..........................23,000
Property taxes on plant....................... 14,000
Total manufacturing overhead.................. 97,000
Total manufacturing costs.......................... 307,000 Total cost of work-in-process....................319,000 Less: ending work-in-process................... 15,500 Cost of goods manufactured.....................$303,500 (b)Finished goods, 1/1.......................................$ 60,000
Cost of goods manufactured .................... 303,500 Cost of goods available for sale...............363,500 Finished goods, 12/31.................................. 55,600 Cost of goods sold........................................$307,900 EXERCISE 1-9
Total raw materials available for use:
Direct materials used..................................................................$190,000 Add: Raw materials inventory (12/31)................................. 12,500 Total raw materials available for use.....................................$202,500 Raw materials inventory (1/1):
Direct materials used..................................................................$190,000 Add: Raw materials inventory (12/31).................................12,500 Less: Raw materials purchases.............................................(158,000) Raw materials inventory (1/1)...................................................$ 44,500 Total cost of work in process:
Cost of goods manufactured...................................................$510,000 Add: Work in process (12/31).................................................. 81,000 Total cost of work in process...................................................$591,000 Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-15
EXERCISE 1-9 (Continued)
Total manufacturing costs:
Total cost of work in process.......................................................$591,000 Less: Work in process (1/1)..........................................................(210,000) Total manufacturing costs............................................................$381,000 Direct labor:
Total manufacturing costs............................................................$381,000 Less: Total overhead.......................................................................(122,000) Direct materials used..........................................................(190,000) Direct labor.........................................................................................$ 69,000 EXERCISE 1-10
A + $57,000 + $46,500 = $185,650$242,500 – $11,000 = F
A = $82,150 F = $231,500
$185,650 + B = $221,500$130,000 + G + $102,000 = $253,700 B = $35,850G = $21,700
$221,500 – C = $185,275$253,700 + H = $337,000
C = $36,225H = $83,300
$58,400 + $86,000 + $81,600 = D$337,000 – $70,000 = I
D = $226,000I = $267,000
$226,000 + $16,500 = E
E = $242,500
Additional explanation to EXERCISE 1-10 solution:
Case A
(a)Total manufacturing costs.............................................................$185,650
Less: Manufacturing overhead.....................................................(46,500) Direct labor..............................................................................(57,000) Direct materials used.......................................................................$ 82,150 1-16Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
EXERCISE 1-10 (Continued)
(b)Total cost of work in process........................................................$221,500
Less: Total manufacturing costs................................................. (185,650) Work in process (1/1/11).................................................................$ 35,850 (c)Total cost of work in process........................................................$221,500
Less: Cost of goods manufactured............................................. (185,275) Work in process (12/31/11).............................................................$ 36,225 Case B
(d)Direct materials used.......................................................................$ 58,400
Direct labor.......................................................................................... 86,000 Manufacturing overhead................................................................. 81,600 Total manufacturing costs.............................................................$226,000 (e)Total manufacturing costs.............................................................$226,000
Work in process (1/1/11).................................................................16,500 Total cost of work in process........................................................$242,500 (f)Total cost of work in process........................................................$242,500
Less: Work in process (12/31/11).................................................(11,000) Cost of goods manufactured........................................................$231,500 Case C
(g)Total manufacturing costs.............................................................$253,700
Less: Manufacturing overhead....................................................(102,000) Direct materials used.......................................................... (130,000) Direct labor...........................................................................................$ 21,700 (h)Total cost of work in process........................................................$337,000
Less: Total manufacturing costs................................................. (253,700) Work in process (1/1/11).................................................................$ 83,300 (i)Total cost of work in process........................................................$337,000
Less: Work in process (12/31/11).................................................(70,000) Cost of goods manufactured........................................................$267,000 Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-17
EXERCISE 1-11
(a)(a)$127,000 + $140,000 + $77,000 = $344,000
(b)$344,000 + $33,000 – $360,000 = $17,000
(c)$450,000 – ($200,000 + $132,000) = $118,000
(d)$40,000 + $470,000 – $450,000 = $60,000
(e)$245,000 – ($80,000 + $100,000) = $65,000
(f)$245,000 + $60,000 – $80,000 = $225,000
(g)$288,000 – ($70,000 + $75,000) = $143,000
(h)$288,000 + $45,000 – $270,000 = $63,000
(b)MABRY COMPANY
Cost of Goods Manufactured Schedule
For the Year Ended December 31, 2011
Work in process, January 1.....................................$ 33,000 Direct materials............................................................$127,000
Direct labor....................................................................140,000
Manufacturing overhead........................................... 77,000
Total manufacturing costs............................... 344,000 Total cost of work in process..................................377,000 Less: Work in process inventory,
December 31.................................................... 17,000 Cost of goods manufactured...................................$360,000 1-18Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
EXERCISE 1-12
(a)VARGAS CORPORATION
Cost of Goods Manufactured Schedule
For the Month Ended June 30, 2011
Work in process, June 1..................................$ 3,000 Direct materials used........................................$20,000
Direct labor...........................................................30,000
Manufacturing overhead
Indirect labor...............................................$4,500
Factory manager’s salary.......................3,000
Indirect materials.......................................2,200
Maintenance, factory equipment..........1,800
Depreciation, factory equipment..........1,400
Factory utilities (400)
Total manufacturing overhead.......13,300 Total manufacturing costs..............................63,300 Total cost of work in process.........................66,300 Less: Work in process, June 30................... 3,800 Cost of goods manufactured.........................$62,500 (b)VARGAS CORPORATION
Income Statement (Partial)
For the Month Ended June 30, 2011
Net sales............................................................................$87,100 Cost of goods sold
Finished goods inventory, June 1...................$ 5,000
Cost of goods manufactured [from (a)]............62,500
Cost of goods available for sale.......................67,500
Finished goods inventory, June 30................. 7,500
Cost of goods sold......................................60,000 Gross profit......................................................................$27,100 Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)1-19
EXERCISE 1-13
(a)
WOYAK CONSULTING
Schedule of Cost of Contract Services Provided
For the Month Ended August 31, 2011
Supplies used (direct materials)..........................................$ 1,200 Salaries of professionals (direct labor).............................12,600 Service overhead:
Utilities for contract operations.....................................$1,400
Contract equipment depreciation (900)
Insurance on contract operations (800)
Janitorial services for professional offices (400)
Total overhead.............................................................. 3,500 Cost of contract services provided...............................$17,300 (b)The costs not included in the cost of contract services provided would
all be classified as period costs. As such, they would be reported on the income statement under administrative expenses.
EXERCISE 1-14
(a)Work-in-process, 1/1...................................$ 13,500
Direct materials
Materials inventory, 1/1......................$ 21,000
Materials purchased............................ 150,000
Materials available for use................171,000
Less: Materials inventory, 12/31..... 30,000
Direct materials used..................................$141,000
Direct labor.....................................................200,000
Manufacturing overhead............................ 180,000
Total manufacturing costs........................ 521,000 Total cost of work-in-process..................534,500 Less: Work-in-process, 12/31................... 17,200 Cost of goods manufactured....................$517,300 (b)Sales.................................................................$900,000
Cost of goods sold
Finished goods, 1/1.............................$ 27,000
Cost of goods manufactured .......... 517,300
Cost of goods available for sale.....544,300
Finished goods, 12/31........................ 21,000
Cost of goods sold....................... 523,300 Gross profit....................................................$376,700 1-20Copyright ? 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Weygandt, Managerial Accounting, 5/e, Solutions Manual (For Instructor Use Only)
财务专业术语中英文对照表 英文中文说明 Account Accounting system 会计系统 American Accounting Association 美国会计协会 American Institute of CPAs 美国注册会计师协会 Audit 审计 Balance sheet 资产负债表 Bookkeepking 簿记 Cash flow prospects 现金流量预测 Certificate in Internal Auditing 部审计证书 Certificate in Management Accounting 管理会计证书 Certificate Public Accountant注册会计师 Cost accounting 成本会计 External users 外部使用者 Financial accounting 财务会计 Financial Accounting Standards Board 财务会计准则委员会 Financial forecast 财务预测 Generally accepted accounting principles 公认会计原则 General-purpose information 通用目的信息 Government Accounting Office 政府会计办公室 Income statement 损益表 Institute of Internal Auditors 部审计师协会 Institute of Management Accountants 管理会计师协会 Integrity 整合性 Internal auditing 部审计 Internal control structure 部控制结构 Internal Revenue Service 国收入署 Internal users部使用者 Management accounting 管理会计 Return of investment 投资回报 Return on investment 投资报酬 Securities and Exchange Commission 证券交易委员会
各种花卉的英文名 iris蝴蝶花 cockscomb鸡冠花 honeysuckle金银花chrysanthemum菊花 carnation康乃馨 orchid兰花 canna美人蕉 jasmine茉莉花 daffodil水仙花 peony牡丹 begonia秋海棠 cactus仙人掌 christmas flower圣诞花/一品红poppy罂粟 tulip郁金香 chinese rose月季 violet紫罗兰 peach flower桃花 aloe芦荟 mimosa含羞草 dandelion蒲公英
plum bolssom梅花中国水仙 new year lily 石榴 pomegranate 月桂victor's laurel 报春花 polyanthus 木棉 cotton tree 紫丁香 lilac 吊钟 lady's eardrops 紫荆 Chinese redbud 百合 lily 紫罗兰 wall flower 桃花 peach 紫藤 wisteria 杜鹃 azalea 铃兰 lily-of-the-valley 牡丹 tree peony 银杏 ginkgo 芍药 peony 蝴蝶兰 moth orchid 辛夷 violet magnolia 蟹爪仙人掌 Christmas cactus 玫瑰 rose 郁金香 tulip
茶花 common camellia 千日红 common globe-amaranth 非洲堇 African violet 栀子花 cape jasmine 木槿 rose of Sharon 风信子 hyacinth 百子莲 African lily 牵牛花 morning glory 君子兰 kefir lily 荷包花 lady's pocketbook 含笑花 banana shrub 非洲菊 African daisy 含羞草 sensitive plant 茉莉 Arabian jasmine 猪笼草 pitcher plant 凌霄花 creeper 树兰 orchid tree 康乃馨coronation 鸡冠花 cockscomb 荷花lotus 鸢萝 cypress vine 菩提 botree
会计术语中英对照 文稿归稿存档编号:[KKUY-KKIO69-OTM243-OLUI129-G00I-FDQS58-
一、会计与会计理论 会计 accounting 决策人 Decision Maker 投资人 Investor 股东 Shareholder 债权人 Creditor 财务会计 Financial Accounting 管理会计 Management Accounting 成本会计 Cost Accounting 私业会计 Private Accounting 公众会计 Public Accounting 注册会计师 CPA Certified Public Accountant 国际会计准则委员会 IASC 美国注册会计师协会 AICPA 财务会计准则委员会 FASB 管理会计协会 IMA 美国会计学会 AAA 税务稽核署 IRS 独资企业 Proprietorship 合伙人企业 Partnership 公司 Corporation 会计目标 Accounting Objectives 会计假设 Accounting Assumptions 会计要素 Accounting Elements 会计原则 Accounting Principles 会计实务过程 Accounting Procedures 财务报表 Financial Statements 财务分析Financial Analysis 会计主体假设 Separate-entity Assumption 货币计量假设 Unit-of-measure Assumption 持续经营假设 Continuity(Going-concern) Assumption 会计分期假设 Time-period Assumption 资产 Asset 负债 Liability 业主权益 Owner's Equity 收入 Revenue 费用 Expense
财会常见名词英汉对照表 (1)会计与会计理论 会计accounting 决策人Decision Maker 投资人Investor 股东Shareholder 债权人Creditor 财务会计Financial Accounting 管理会计Management Accounting 成本会计Cost Accounting 私业会计Private Accounting 公众会计Public Accounting 注册会计师CPA Certified Public Accountant 国际会计准则委员会IASC 美国注册会计师协会AICPA 财务会计准则委员会FASB 管理会计协会IMA 美国会计学会AAA 税务稽核署IRS 独资企业Proprietorship 合伙人企业Partnership 公司Corporation
会计目标Accounting Objectives 会计假设Accounting Assumptions 会计要素Accounting Elements 会计原则Accounting Principles 会计实务过程Accounting Procedures 财务报表Financial Statements 财务分析Financial Analysis 会计主体假设Separate-entity Assumption 货币计量假设Unit-of-measure Assumption 持续经营假设Continuity(Going-concern) Assumption 会计分期假设Time-period Assumption 资产Asset 负债Liability 业主权益Owner's Equity 收入Revenue 费用Expense 收益Income 亏损Loss 历史成本原则Cost Principle 收入实现原则Revenue Principle 配比原则Matching Principle 全面披露原则Full-disclosure (Reporting) Principle
会计方面专业术语的xx acceptance承兑 account账户 accountant会计员 accounting会计 accounting system会计制度 accounts payable应付账款 accounts receivable应收账款 accumulated profits累积利益 adjusting entry调整记录 adjustment调整 administration expense管理费用 advances预付 advertising expense广告费 agency代理 agent代理人 agreementxx allotments分配数 allowance津贴 amalgamation合并 amortization摊销
amortized cost应摊成本 annuities年金 applied cost已分配成本 applied expense已分配费用 applied manufacturing expense己分配制造费用apportioned charge摊派费用 appreciation涨价 article of association公司章程 assessment课税 assets资产 attorney fee律师费 audit审计 auditor审计员 average平均数 average cost平均成本 bad debt坏账 balance余额 balance sheet资产负债表 bank account银行账户 bank balance银行结存 bank charge银行手续费
bank deposit银行存款 bank discount银行贴现bank draft银行汇票 bank loan银行借款 bank overdraft银行透支bankers acceptance银行承兑bankruptcy破产 bearer持票人 beneficiary受益人 bequest遗产 bill票据 bill of exchange汇票 bill of lading提单 bills discounted贴现票据bills payable应付票据 bills receivable应收票据board of directors董事会bonds债券 bonus红利 book value账面价值bookkeeper簿记员
植物花卉中英文对照、花卉英文名大全 金橘--------------kumquat 米仔兰(米兰)--------- milan tree 变叶木-------------croton 一品红-------------poinsettia 扶桑--------------Chinese hibiscus 吊灯花-------------fringed hibiscus 马拉巴栗(发财树)------- Guiana chestnut 山茶--------------camellia 云南山茶------------Yunnan camellia 金花茶-------------golden camellia 瑞香--------------daphne 结香--------------paper bush 倒挂金钟------------fuchsia 八角金盘------------Japan fatsia 常春藤-------------ivy 鹅掌柴-------------umbrella tree 杜鹃花-------------rhododendron 茉莉花-------------jasmine 桂花--------------sweet osmanthus 夹竹桃-------------sweet-scented oleander 黄花夹竹桃-----------lucky-nut-thevetia 鸡蛋花-------------frangipani 龙吐珠-------------bleeding-heart glorybower 夜香树(木本夜来香)------night jasmine 鸳鸯茉莉------------broadleaf raintree 栀子花-------------cape jasmine 蝴蝶兰-------------moth orchid 卡特兰-------------cattleya 石斛--------------dendrobium 兜兰--------------lady slipper 兰花--------------orchid 春兰--------------goering cymbidium
会计专业专业术语中英文对照 一、会计与会计理论 会计 accounting 决策人 Decision Maker 投资人 Investor 股东 Shareholder 债权人 Creditor 财务会计 Financial Accounting 管理会计 Management Accounting 成本会计 Cost Accounting 私业会计 Private Accounting 公众会计 Public Accounting 注册会计师 CPA Certified Public Accountant 国际会计准则委员会 IASC 美国注册会计师协会 AICPA 财务会计准则委员会 FASB 管理会计协会 IMA 美国会计学会 AAA 税务稽核署 IRS 独资企业 Proprietorship 合伙人企业 Partnership 公司 Corporation
会计目标 Accounting Objectives 会计假设 Accounting Assumptions 会计要素 Accounting Elements 会计原则 Accounting Principles 会计实务过程 Accounting Procedures 财务报表 Financial Statements 财务分析Financial Analysis 会计主体假设 Separate-entity Assumption 货币计量假设 Unit-of-measure Assumption 持续经营假设 Continuity(Going-concern) Assumption 会计分期假设 Time-period Assumption 资产 Asset 负债 Liability 业主权益 Owner's Equity 收入 Revenue 费用 Expense 收益 Income 亏损 Loss 历史成本原则 Cost Principle 收入实现原则 Revenue Principle 配比原则 Matching Principle
iris 蝴蝶花hon eysuckle 金银花 chrysanthemum 菊花 carnation 康乃馨 orchid 兰花 canna 美人蕉 jasmine 茉莉花 daffodil 水仙花 peony 牡丹 begonia 秋海棠 cactus 仙人掌 christmas flower 圣诞花/一品红 poppy 罂粟 tulip 郁金香 chi nese rose 月 季 violet 紫罗兰 peach flower 桃花 aloe 芦荟 mimosa 含羞草 dandelion 蒲公英 plum bolssom 梅花中国水仙new year lily
石榴pomegranate 月桂victor's laurel 报春花polyanthus 木棉cotton tree 紫丁香lilac 吊钟lady's eardrops 紫荆Chinese redbud 百合lily 紫罗兰wall flower 桃花peach 紫藤wisteria 杜鹃azalea 铃兰lily-of-the-valley 牡丹tree peony 银杏ginkgo 芍药peony 蝴蝶兰moth orchid 辛夷violet magnolia 蟹爪仙人掌Christmas cactus 玫瑰rose 郁金香tulip
非洲堇African violet 栀子花cape jasmine 木槿rose of Sharon 风信子hyacinth 百子莲African lily 牵牛花morning glory 君子兰kefir lily 荷包花lady's pocketbook 含笑花bana shrub 非洲菊African daisy 含羞草sensitive plant 茉莉Arabian jasmine 猪笼草pitcher plant 凌霄花creeper 树兰orchid tree 康乃馨coronation 荷花lotus 鸢萝cypress vine 菩提botree 大理花dahlia
Accounting system 会计系统 American Accounting Association 美国会计协会American Institute of CPAs 美国注册会计师协会 Audit 审计 Balance sheet 资产负债表 Bookkeepking 簿记 Cash flow prospects 现金流量预测 Certificate in Internal Auditing 内部审计证书 Certificate in Management Accounting 管理会计证书Certificate Public Accountant注册会计师 Cost accounting 成本会计 External users 外部使用者 Financial accounting 财务会计 Financial Accounting Standards Board 财务会计准则委员会Financial forecast 财务预测 Generally accepted accounting principles 公认会计原则General-purpose information 通用目的信息Government Accounting Office 政府会计办公室 Income statement 损益表 Institute of Internal Auditors 内部审计师协会 Institute of Management Accountants 管理会计师协会Integrity 整合性 Internal auditing 内部审计 Internal control structure 内部控制结构 Internal Revenue Service 国内收入署 Internal users 内部使用者 Management accounting 管理会计 Return of investment 投资回报 Return on investment 投资报酬 Securities and Exchange Commission 证券交易委员会Statement of cash flow 现金流量表 Statement of financial position 财务状况表 Tax accounting 税务会计 Accounting equation 会计等式 Articulation 勾稽关系 Assets 资产 Business entity 企业个体 Capital stock 股本 Corporation 公司 Cost principle 成本原则 Creditor 债权人 Deflation 通货紧缩 Disclosure 批露 Expenses 费用
会计方面专业术语的英文翻译 acceptance 承兑 account 账户 accountant 会计员 accounting 会计 accounting system 会计制度 accounts payable 应付账款 accounts receivable 应收账款 accumulated profits 累积利益 adjusting entry 调整记录 adjustment 调整 administration expense 管理费用 advances 预付 advertising expense 广告费 agency 代理 agent 代理人 agreement 契约 allotments 分配数 allowance 津贴 amalgamation 合并 amortization 摊销 amortized cost 应摊成本 annuities 年金 applied cost 已分配成本 applied expense 已分配费用 applied manufacturing expense 己分配制造费用apportioned charge 摊派费用 appreciation 涨价 article of association 公司章程 assessment 课税 assets 资产 attorney fee 律师费 audit 审计 auditor 审计员 average 平均数 average cost 平均成本 bad debt 坏账 balance 余额
balance sheet 资产负债表 bank account 银行账户 bank balance 银行结存 bank charge 银行手续费 bank deposit 银行存款 bank discount 银行贴现 bank draft 银行汇票 bank loan 银行借款 bank overdraft 银行透支 bankers acceptance 银行承兑 bankruptcy 破产 bearer 持票人 beneficiary 受益人 bequest 遗产 bill 票据 bill of exchange 汇票 bill of lading 提单 bills discounted 贴现票据 bills payable 应付票据 bills receivable 应收票据 board of directors 董事会 bonds 债券 bonus 红利 book value 账面价值 bookkeeper 簿记员 bookkeeping 簿记 branch office general ledger 支店往来账户broker 经纪人 brought down 接前 brought forward 接上页 budget 预算 by-product 副产品 by-product sales 副产品销售 capital 股本 capital income 资本收益 capital outlay 资本支出 capital stock 股本 capital stock certificate 股票 carried down 移后 carried forward 移下页 cash 现金 cash account 现金账户 cash in bank 存银行现金 cash on delivery 交货收款
常见花的英文单词 中国水仙new year lily 石榴pomegranate 月桂victor's laurel 报春花polyanthus 木棉cotton tree 紫丁香lilac 吊钟lady's eardrops 紫荆Chinese redbud 百合lily 紫罗兰wall flower 桃花peach 紫藤wisteria 杜鹃azalea 铃兰lily-of-the-valley 牡丹tree peony 银杏ginkgo 芍药peony 蝴蝶兰moth orchid 辛夷violet magnolia 蟹爪仙人掌Christmas cactus 玫瑰rose 郁金香tulip 茶花common camellia 千日红common globe-amaranth 非洲堇African violet 栀子花cape jasmine 木槿rose of Sharon 风信子hyacinth 百子莲African lily 牵牛花morning glory 君子兰kefir lily 荷包花lady's pocketbook 含笑花banana shrub 非洲菊African daisy 含羞草sensitive plant 茉莉Arabian jasmine 猪笼草pitcher plant 凌霄花creeper 树兰orchid tree 康乃馨coronation 鸡冠花cockscomb
荷花lotus 鸢萝cypress vine 菩提botree 大理花dahlia 圣诞百合Christmas bell 一串红scarlet sage 紫薇crape myrtle 勿忘我forget-me-not 睡莲water lily 文心兰dancing lady 吊兰spider plant 白头翁pappy anemone 向日葵sunflower 矢车菊cornflower 竹bamboo 金鱼草snapdragon 夹竹桃oleander 金盏花pot marigold 月季花china rose 金银花honeysuckle 长春花old maid 金莲花garden nasturtium 秋海棠begonia 非洲凤仙African touch-me-not 美人蕉canna 曼陀罗angel's trumpet 晚香玉tuberose 梅花flowering apricot 野姜花ginger lily 圣诞红common poinsettia 菊花chrysanthemum 虞美人Iceland poppy 昙花epiphyllum 鸢尾iris 龙胆royal blue 腊梅winter sweet 麒麟花crown of thorns 木芙蓉cotton rose 九重葛paper flower 火鹤花flamingo flower 三色堇tricolor viola 嘉德丽亚兰cattleya
一、会计与会计理论 会计accounting 决策人Decision Maker 投资人Investor 股东Shareholder 债权人Creditor 财务会计Financial Accounting 管理会计Management Accounting 成本会计Cost Accounting 私业会计Private Accounting 公众会计Public Accounting 注册会计师CPA Certified Public Accountant 国际会计准则委员会IASC 美国注册会计师协会AICPA 财务会计准则委员会FASB 管理会计协会IMA 美国会计学会AAA 税务稽核署IRS 独资企业Proprietorship 合伙人企业Partnership 公司Corporation 会计目标Accounting Objectives 会计假设Accounting Assumptions 会计要素Accounting Elements 会计原则Accounting Principles 会计实务过程Accounting Procedures 财务报表Financial Statements 财务分析Financial Analysis 会计主体假设Separate-entity Assumption 货币计量假设Unit-of-measure Assumption 持续经营假设Continuity(Going-concern) Assumption 会计分期假设Time-period Assumption 资产Asset 负债Liability 业主权益Owner's Equity 收入Revenue 费用Expense 收益Income
亚洲常见花卉英文译名Abutilon pictum / Thomsonii风铃花 Abutilon Hybriden金铃花 Acacia dealbata银栲皮树 Acaena / New Zealand burr无瓣蔷薇(纽西兰球果属植物) Acanthus叶蓟属植物 Acer palmatum掌叶槭 Achillea / Yarrow丽纹锯草(蓍草属植物) Achimenes / Cupid's bower / hot water plant长筒花Actinidia狝猴桃<--攀缘植物 Adenium obesum沙漠玫瑰(天宝花) Adiantum capilus-veneris / True maidenhair fern铁线蕨Aegopodium podagraia 'Variegata'斑叶羊角芹 African daisy非洲菊 Agapanthus / African lily百子莲 Agastache藿香 Agave龙舌兰属植物 Ageratum houstonianum紫花霍香蓟 Agrostemma githago / Corn cockle麦仙翁 Ajuga reptans匍筋骨草 Akebia木通(别名:巧克力藤蔓) <--攀缘植物
Alcea rosea / Hollyhock蜀葵 Alchemilla / Lady's mantle斗篷草 Allium葱属 Aloe芦荟属植物 Alyssum香荠属植物 Amaranthus苋属植物 Ampelopsis山葡萄<--攀缘植物 Ampelopsis brevipedunculata蛇白蔹 Anchusa capensis / Alkanet非洲勿忘草Androsace carnea / Rock jasmine铜钱花Anethu, graveolens / Dill莳萝 Annual phlox福禄考 Antennaria dioica山荻 Anthemis西洋甘菊 Anthemis punctata subsp cupaniana春黄菊Antirrhinum majus / Snapdragon金鱼草 Arabis / Rock cress南芥菜(岩水芹) Aralia elata黃斑高? Arbutus野草莓樹 Arctotis Fastuosa / Monarch of the veldt南非雛菊Arenaria balearica蚤綴
一些有用的会计术语 A: A share A股;甲类股份 abatement of tax 减税;减扣免税额 ABN AMRO Bank N.V. 荷兰银行 above-the-line expenditure 线上项目支出;经常预算支出above-the-line receipt 线上项目收入;经常预算收入ABSA Asia Limited 南非联合亚洲有限公司 absolute change 绝对数值变更 absolute expenditure 实际开支 absolute guideline figure 绝对准则数字 absolute interest 绝对权益 absolute order of discharge 绝对破产解除令 absolute profit margin 绝对利润幅度 absolute value 实值;绝对值 absolutely vested interest 绝对既得权益 absorbed cost 已吸收成本;已分摊成本 absorption 吸收;分摊;合并 absorption rate 吸收率;摊配率;分摊率 ACB Finance Limited 亚洲商业财务有限公司acceptable form of reciprocity 合理的互惠条件acceptable rate 适当利率;适当汇率
acceptance agreement 承兑协议 acceptance for honour 参加承兑 acceptor 承兑人;接受人;受票人 acceptor for honour 参加承兑人 accident insurance 意外保险 Accident Insurance Association of Hong Kong 香港意外保险公会accident insurance scheme 意外保险计划 accident year basis 意外年度基准 accommodation 通融;贷款 accommodation bill 通融票据;空头票据 accommodation party 汇票代发人 account balance 帐户余额;帐户结余 account book 帐簿 account collected in advance 预收款项 account current book 往来帐簿 account of after-acquired property 事后取得的财产报告account of defaulter 拖欠帐目 account payable 应付帐款 account payee only [A/C payee only] 只可转帐;存入收款人帐户account receivable 应收帐款 account receivable report 应收帐款报表 account statement 结单;帐单;会计财务报表 account title 帐户名称;会计科目
A (1)ABC 作业基础成本计算 A (2)absorbed overhead 已汲取制造费用 A (3)absorption costing 汲取成本计算 A (4)account 帐户,报表 A (5)accounting postulate 会计假设 A (6)accounting series release 会计公告文件 A (7)accounting valuation 会计计价 A (8)account sale 承销清单 A (9)accountability concept 经营责任概念 A (10)accountancy 会计职业 A (11)accountant 会计师 A (12)accounting 会计 A (13)agency cost 代理成本 A (14)accounting bases 会计基础 A (15)accounting manual 会计手册 A (16)accounting period 会计期间 A (17)accounting policies 会计方针 A (18)accounting rate of return 会计酬劳率 A (19)accounting reference date 会计参照日 A (20)accounting reference period 会计参照期间A (21)accrual concept 应计概念 A (22)accrual expenses 应计费用
A (23)acid test ration 速动比率(酸性测试比率) A (24)acquisition 购置 A (25)acquisition accounting 收购会计 A (26)activity based accounting 作业基础成本计算A (27)adjusting events 调整事项 A (28)administrative expenses 行政治理费 A (29)advice note 发货通知 A (30)amortization 摊销 A (31)analytical review 分析性检查 A (32)annual equivalent cost 年度等量成本法 A (33)annual report and accounts 年度报告和报表A (34)appraisal cost 检验成本 A (35)appropriation account 盈余分配帐户 A (36)articles of association 公司章程细则 A (37)assets 资产 A (38)assets cover 资产保障 A (39)asset value per share 每股资产价值 A (40)associated company 联营公司 A (41)attainable standard 可达标准 A (42)attributable profit 可归属利润 A (43)audit 审计 A (44)audit report 审计报告
AICPA财务英语中英文对照表 A account 账户 account payable 应付账款 accounting system 会计系统 Accounting Principle Board (APB) (美国)会计准则委员会 accrual basis 权责发生制(应计制) accumulated depreciation 累计折旧 account FORMat 账户格式 accrue 应计 accounting cycle 会计循环 accounts receivable 应收账款 accounts receivable turnover 应收账款周转率 accelerated depreciation 加速折旧 adjusting entries 调整分录 adjustment 调整 aging of accounts receivable 应收账款账龄分析法 allowance for bad debts 坏账准备 allowance for doubtful accounts 坏账准备 allowance for uncollectible 坏账准备 allowance method 备抵法 allowance for depreciation 折旧备抵账户 amortization 摊销 annual report 年度报告 annuity 年金 assets 资产
audit 审计 auditor’s opinion 审计意见书 auditor 审计师 audit committee 审计委员会 average collection period 平均收账期AICPA 美国注册会计师协会 APB Opinions 会计准则委员会意见书B balance 余额 bad debt recoveries 坏账收回 bad debts 坏账 bad debts expense 坏账费用 balance sheet 资产负债表 balance sheet equation 资产负债表等式basket purchase 一揽子采购 betterment 改造投资,改造工程投资bearer instrument 不记名票据 bonds 债券 book of original entry 原始分录账簿 book value 账面价值 C capital 资本 capital stock certificate 股本证明书 cash basis 收付实现制(现金收付制)cash dividends 现金股利 cash flow statement 现金流量表 carrying amount 账面价值 carrying value 账面价值 callable bonds 可赎债券,可提前兑回债券
流动资产CURRENT ASSETS: 现金Cash on hand 银行存款Cash in bank 有价证券Marketable securitiea 应收票据Notes receivable 应收帐款Accounts receivable 坏帐准备Provision for bad debts 预付帐款Advances to suppliers 其他应收款Other receivables 待摊费用Deferred and prepaid expenses 存货Inventories 存货变现损失准备Provision for loss on realization of inventory 一年内到期的长期债券投资Long-term investments maturing within one year 其他流动资产Other current assets 长期投资Long-term in vestments 一年以上的应收款项Receivables collectable after one year 固定资产:FIXED ASSETS: 固定资产原价Fixed assets-cost 累计折旧Accumulated depreciation 固定资产净值Fixed assets-net value 固定资产清理Disposal of fixed assets 在建工程Construction in progress 无形资产INTANGIBLE ASSETS: 场地使用权Land occupancy right 工业产权及专有技术Proprietary technology and patents 其他无形资产Other intangibles assets 其他资产:OTHER ASSETS 开办费Organization expenses 筹建期间汇兑损失Exchange loss during start-up peried 递延投资损失Deferred loss on investments 递延税款借项Deferred taxes debit 其他递延支出Other deferred expenses 待转销汇兑损失Unamortized cxehange loss 流动负债CURRENT LIABILITIES: 短期借款Short term loans 应付票据Notes payable 应付帐款Accounts payable 应付工资Accrued payroll 应交税金Taxes payable 应付利润Dividends payable 预收货款Advances from customers 其他应付款Other payables
一、资产类 Assets 流动资产 Current assets 货币资金 Cash and cash equivalents 1001现金 Cash 1002 银行存款 Cash in bank 1009 其他货币资金 Other cash and cash equivalents '100901 外埠存款 Other city Cash in bank '100902 银行本票 Cashier's cheque '100903 银行汇票 Bank draft '100904 信用卡 Credit card '100905 信用证保证金 L/C Guarantee deposits '100906 存出投资款 Refundable deposits 1101 短期投资 Short-term investments '110101 股票 Short-term investments - stock '110102 债券 Short-term investments - corporate bonds '110103 基金 Short-term investments - corporate funds '110110 其他 Short-term investments - other 1102 短期投资跌价准备 Short-term investments falling price reserves 应收款 Account receivable 1111 应收票据 Note receivable 银行承兑汇票 Bank acceptance 商业承兑汇票 Trade acceptance 1121 应收股利 Dividend receivable 1122 应收利息 Interest receivable 1131 应收账款 Account receivable 1133 其他应收款 Other notes receivable 1141 坏账准备 Bad debt reserves 1151 预付账款 Advance money 1161 应收补贴款 Cover deficit by state subsidies of receivable 库存资产 Inventories 1201 物资采购 Supplies purchasing 1211 原材料 Raw materials 1221 包装物 Wrappage 1231 低值易耗品 Low-value consumption goods 1232 材料成本差异 Materials cost variance 1241 自制半成品 Semi-Finished goods 1243 库存商品 Finished goods 1244 商品进销差价 Differences between purchasing and selling price 1251 委托加工物资 Work in process - outsourced 1261 委托代销商品 Trust to and sell the goods on a commission basis 1271 受托代销商品 Commissioned and sell the goods on a commission basis 1281 存货跌价准备 Inventory falling price reserves 1291 分期收款发出商品 Collect money and send out the goods by stages