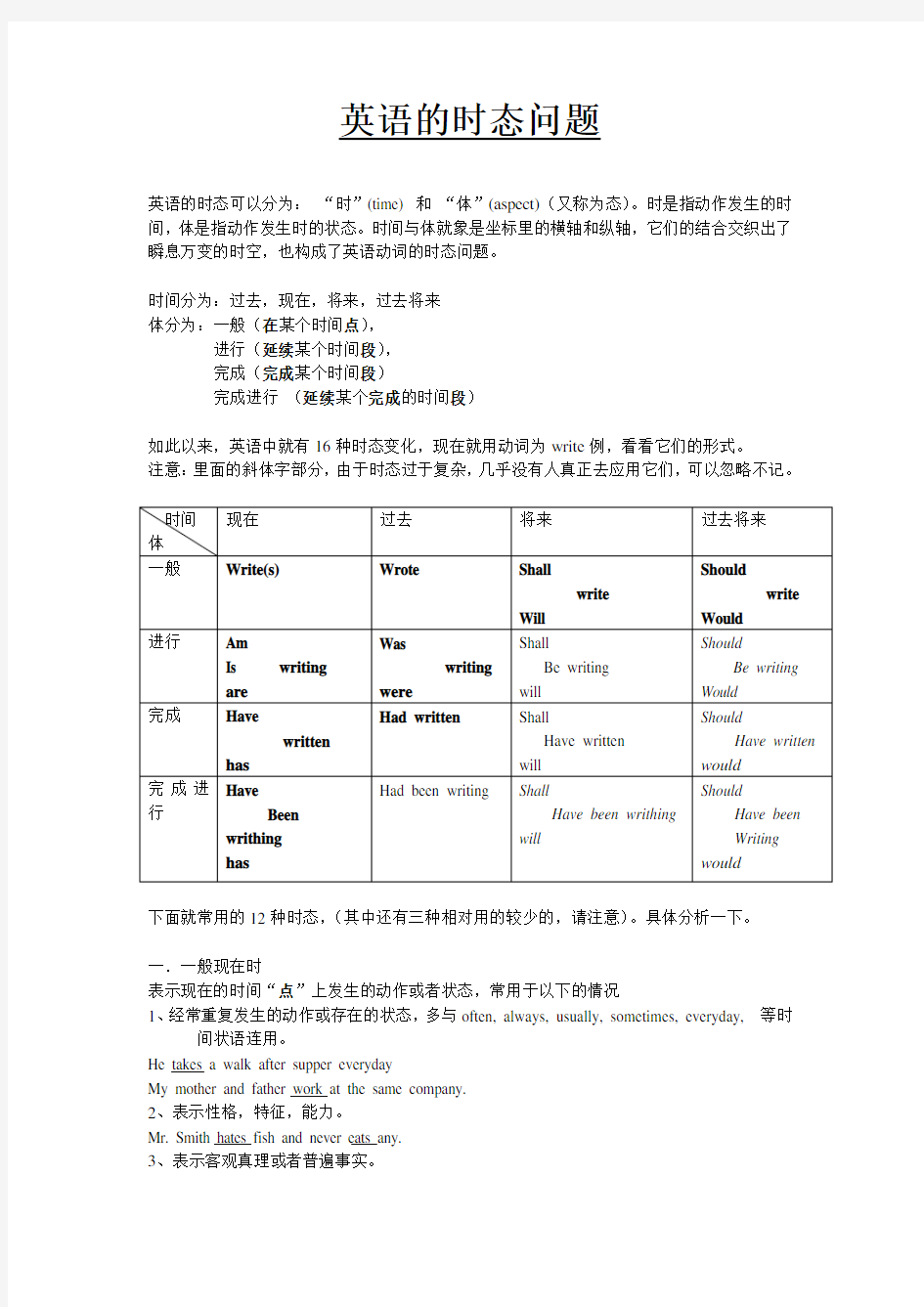

英语的时态问题
英语的时态可以分为:“时”(time) 和“体”(aspect)(又称为态)。时是指动作发生的时间,体是指动作发生时的状态。时间与体就象是坐标里的横轴和纵轴,它们的结合交织出了瞬息万变的时空,也构成了英语动词的时态问题。
时间分为:过去,现在,将来,过去将来
体分为:一般(在某个时间点),
进行(延续某个时间段),
完成(完成某个时间段)
完成进行(延续某个完成的时间段)
如此以来,英语中就有16种时态变化,现在就用动词为write例,看看它们的形式。
注意:里面的斜体字部分,由于时态过于复杂,几乎没有人真正去应用它们,可以忽略不记。
下面就常用的12种时态,(其中还有三种相对用的较少的,请注意)。具体分析一下。
一.一般现在时
表示现在的时间“点”上发生的动作或者状态,常用于以下的情况
1、经常重复发生的动作或存在的状态,多与often, always, usually, sometimes, everyday, 等时
间状语连用。
He takes a walk after supper everyday
My mother and father work at the same company.
2、表示性格,特征,能力。
Mr. Smith hates fish and never eats any.
3、表示客观真理或者普遍事实。
The sun rises in the east.
二.一般过去时
表示过去某时发生的动作或者状态,常和表示过去某个时间“点”的时间状语(yesterday, last week, 3 years ago, in 1987)连用
She bought a car last week.
He came to help me at that time.
三.一般将来时
表示将来的时间“点”上发生的动作或者状态。
The train will arrive soon.
We shall know the news tomorrow.
四.过去将来时
过去某个时间“点”上将要发生的动作或状态。
I asked her where she would spend her holiday.
I told my father that I should go home next Monday.
五.现在进行时
表示现在的时间“段”上正在延续进行的动作或者状态。
I’m doing some washing.
What are you doing?
六.过去进行时
在过去某一个时间“段”正在延续进行的动作。
I was working in my office at eight o’clock yesterday evening.
He was making a phone call when I saw him.
七.将来进行时
在将来某个时间“段”正在发生的动作,一般表示一种猜测和未来的计划,一般不太常用。What will you be doing at 3 o’clock tomorrow afternoon?
(明天下午三点你将在做什么哪)
八.现在完成时
表示动作在一个时间“段”的完成,而且这个时间段是从过去某一点延续到现在的。经常跟时间状语since 1987,for 10 hours , by the last year相连。
My brother has been ill for 3 days.
I have not seen her since 1991.
九.过去完成时
在过去的某个时间“段”里动作的完成,从过去的一点再到过去的另一点。或者称为过去的过去。
He said that he had written her a letter.
Helen rang me up after I had gone to sleep.
十.将来完成进行时
表示在将来某一时间以前已经完成的动作,一般不太常用。
I’ll have done all the work by next day.
十一。现在完成进行时
表示从过去某一个时间开始一直延续到现在的动作,它强调在这个已经完成的时间“段”,动作持续的进行,常有感情色彩。
I have been looking for you everywhere for the whole morning.
我找了你整整一天了。(有抱怨的感情色彩)
十二。过去完成进行时
正个时间段都是发生在过去的,是过去的一点延续到过去的另一点,并且强调动作的持续进行,带感情色彩,但一般不常用。
He told me he had been teaching for more than 20 years.
最后提醒一下:
某些与时态规律不太一致的规则。
表示一般将来的意思的,除了一般将来时态外,还可以用以下的几种形式表达。过去将来同样可以运用。
1、一般现在时
am (is ,are) + to do
The girls are to go to school next week.
2、现在完成时
am (is ,are) + doing
We are going to visit the Museum of Chinese History tomorrow.
在这里,我们重点讲一下以下常用时态:
一、一般现在时
一般现在时主要用来表示:
1. 表示一种永久性的、不涉及特定的时间的一般性陈述和客观存在。
e.g. I) He smokes too much.
II) It seldom snows here.
2. 用于说明自然规律、客观真理、科学事实,格言、谚语等也属于词类等。
e.g. I) The earth moves round the sun.
II) Actions speak louder than words. 行动胜于雄辩。
3. 动作动词的一般现在时可以表示现阶段重复发生的一系列事件。这时常和sometimes, often, usually, frequently, every day/week/month/year, daily, monthly, once a year, twice a day, five times a month等表示频度的副词(短语)连用。
e.g. I) Teenagers often spend hours shopping, especially on weekends.
II) We always care for each other and care for each other.
4. 如果动作动词所指的是一个在讲话时开始并结束的单一行为,则意味着该事件很少
或没有持续性,通常只用于行为语、特殊感叹句或对快速体育运动等的实况报导。
e.g. I) Here comes the winner.
II) I declare the meeting open. 我宣布会议开始。
5. 表示将来时间。在由when,if,after,before,as soon as,even if,in case,though,till,until,unless,so long as等引导的时间状语从句或条件状语从句中,一般现在时可以用来表示将来时间。
e.g.I) You’d better take an umbrella in case (万一) it rains.
II) So long as (只要) you work hard, you’ll surely succeed.
6. 一般现在时可以用来表示一个按规定、计划、或安排要发生的情况。但这只限于少
数动词,如begin, come, go, leave, sail, start, arrive, return, end, stop, depart, open, close等。
e.g. I) The plane takes off at 11 a.m.
II) School begins the day after tomorrow.
III) Is there a film on tonight?
7. 在I hope, I bet等后面的that-分句中可用一般现在时表示将来概念。
e.g.I) I bet Houston Rocket beats Miami Heats this afternoon.
II) I hope the storm passes quickly.
8. 在see (to it), make sure, make certain等后面的that-分句中可用一般现在时表示将来概念。
e.g. I) Please see (to it) that windows are closed before you leave.
II) Be sure that you don’t work too hard.
9. 用于讲故事,叙述文、新闻报导或图片说明等中,以增加描述的生动性和真实感。
e.g. He sits down, shivers (颤抖) a little. The clock outside strikes twelve.
二、一般将来时
一般将来时主要用来表示:
1. 将要发生的动作或情况。
e.g. I) When shall we have an oral test (口试)?
II) He will start to work in June.
2. 习惯动作或未来的倾向。
e.g. I) Wherever he goes, he will take an umbrella with him.
II) Only in this way will we succeed. 只有这样我们才能成功。
3. 表示将要发生的动作,除了一般将来时外,还有一些其他结构和时态。
a) be going + 不定式 (表示打算、准备做的事或即将发生或肯定要发生的事)
e.g. I) Look at those clouds! It’s going to rain. 看那些乌云,天快下雨了。
II) I am going to leave for Paris with my classmates next week.
b) be about + 不定式 (表示正要、刚要发生的事情)
e.g. I) The train is about to leave.
II) We are just in time. The curtain is about to go up. 我们来得很及时,电影刚好拉开序幕。
c) be + 不定式 (表示按日程将要发生的动作)
e.g. I) There is to be a test in the fifth week.
II) I am to meet my friend at the railway station this afternoon.
d) 动词现在时 (见现在进行时2)
e) 一般现在时 (见一般现在时5、6、7、8)
f) 动词将来进行时,可用来表示不含意图的将来概念。
e.g. I) Machines will be doing many jobs that people do today.
II) We will be staying in Beijing for three days.
三、一般过去时
一般过去时主要用来表示:
1. 表示事件或状态必定发生在过去,从其完成到现在之间有一段间隔。过去时间可以
由状语表示,如yesterday,an hour ago,in 1972,last year等。
e.g. I) In 1972, Father’s Day became a national holiday in the United States.
II) Jane was here a moment ago.
2. 动作动词的一般过去时可以表示在过去一段时间里重复发生的一系列事件。这时常
和sometimes, often, usually, frequently, every day/week/month/year, daily, monthly, once a year, twice a day, five times a month等表示频度的副词(短语)连用。
e.g. I) Ken never smoked.
II) I went to the cinema three times last week.
3. 在时间和条件状语从句中,一般过去时可以替代过去将来时。
e.g. I) Father promised to buy me a MP3 if he got a pay raise.
II) I couldn’t watch that exciting game before my homework was finished.
谓语动词的时态(二)
四、现在完成时
1. 现在完成时只要用来表示:
a) 开始于过去而延续至今的动作(有可能继续延续下去)或重复性的事件。
e.g. I) Advertising has become a very specialized activity in modern times. 广告在现代社会中已成为一项非常专业化的活动。
II) She has lived here since 1997.
b) 动作的结果到现在时刻仍然存在,常与recently, just, already, yet, before, in the past few years, up to now, so far, this year, for, since等时间状语连用。
e.g. I) So far we have learned a lot about different tenses.
II) In the past few decades (十年) great changes have taken place in Hangzhou.
2. 现在完成时和一般过去时的比较:
a) 意义上的区别
两种时态的动作都发生在过去,现在完成时强调动作现在的结果;过去时着眼过去的动作或状态本身。试比较:
e.g. I) I have read this book. (说明我了解书的内容。)
II) I read this book yesterday. (叙述昨天做的一件事,与现在无关。)
c) 特殊用法
i) 在“This/ It is the first (second, third, last, etc.) time …”后用现在完成时。
e.g. It is the first time that I have traveled by train.
ii) 在“It is/ has been a long time since …”后用过去时。
e.g. It has been 10 years since I graduated from my university.
iii) 在“This is + 最高级形容词 + 名词”后的从句中用现在完成时。
e.g. He is the most interesting person I have ever met.
五、将来完成时
将来完成时由shall (will) have加过去分词构成,主要表示将来某时已经发生的事情。如果句子中有“by + 将来的某一时间”或when, before等时间状语时,可以用将来完成时。
e.g. I) I shall have finished my homework before lunch.
II) By the end of next month, he will have lived here fore three years.
III) When we get there, they will probably have left.
IV) Hurry up, or the train will have left by the time we get to the station.
六、过去完成时
1. 过去完成时的用法
过去完成时主要表示先于过去某一时间的事件或状态,即“过去的过去”。这一事件或状态可以在过去某一时间以前已经完成,也可能从“过去的过去”某一时间一直延续到过去某一时间(甚至还可能延续下去,但与现在时间无关)。
a) 过去完成时常和after, before, by, till, when, until等引入的状语连用。
e.g. I) I began collecting stamps in February and by November I had collected more than 2000.
II) When I woke up it had already stopped raining.
III) She didn’t go to bed until she ha d finished her homework.
b) 在很多情况下没有明显的时间状语,时间由上下文表示出来。
e.g.I) He went to see his boss and told him what had happened.
II) They returned earlier than we had expected.
c) 过去完成时的几种特殊用法
i) 和before连用,表示“还没……就”。
e.g. I) She cried before I had realized what was happening. 我还没有意识到发生什么事情她就哭了起来。
II) They set out before I had told them the address.
ii) “It/This/That was the first/second/third time that …” 结构中的从句,要求用过去完成时态。
e.g. I) It was the first time they had tried foreign food.
II) It was the first time that he had finished his composition in 30 minutes.
iii) 在“no sooner … than …”和“hardly/scarcely … when …”的结构中,主句中用过去完成时,从句中用一般过去时。
e.g. I) I had hardly closed my eyes when the telephone rang.
II) No sooner had we begun than we were told to stop.
iv) 与expect, hope, intend, mean, plan, suppose, think, want等动词连用时,表示过去的希望、预期、意图或愿望等没有实现。
e.g.I) I had planned to visit you, but I just couldn’t find time.
II) He had hoped to help you, but he was ill.
2. 过去完成时和一般过去时的比较:
过去完成时表示过去某一时刻,或某个动作前发生的事,即过去的过去,它着眼于显示过去发生的几个动作的先后。一般过去时只叙述过去某时刻或某时刻后发生的动作,但不强调时间顺序。
e.g. I) When he got home, his wife had already prepared the dinner. (他回家前饭已做好。)
II) When he got home, he saw a letter on his desk. (他回家后看到桌上有一封信。)
七、现在进行时
现在进行时主要用来表示:
1. 现在或现在这一阶段正在进行的动作。
e.g. I) They are making preparations for it.
II) He is showing a foreign guest round the city.
2. 一个在最近按计划或安排要进行的动作。但这只限于少数动词,如go, come, leave, start, arrive, return, work, sleep, stay, do, play等。
e.g. I) We are leaving on Friday.
II) I am seeing the doctor today.
3. 有时用来代替一般现在时,表示一个经常性动作或状态,通常是为了表示一种感情(如赞叹、厌烦等)。
e.g. I) He is constantly complaining about his teacher. 他老是抱怨他的老师。
II) How are you feeling today?
III) He is always boasting. 他老爱说大话。
be间或可以用在进行时态,表示一时的表现。
e.g. I) The boy is being difficult. 这男孩正在闹别扭。(可能他平时很听话的。)
II) Frank is being a good boy today. 弗兰克今天很乖。(可能他平时并不乖。)
八、过去进行时
过去进行体和现在进行体的用法相仿,只是时间向过去推移而已。过去进行时表示过去某时或某断时期正在进行的动作。
e.g. I) What were you doing when I called?
II) What were you doing last night at 10 o’clock?
九、将来进行时
将来进行时表示将来某时或某时期正在进行的动作。
e.g.I) I don’t know what my wife will be doing when I return home.
II) When I prepare for the college entrance examination (高考), my sister will be taking her vacation (度假) at the seaside.
十、现在完成进行时
现在完成进行时可以用来表示:
1. 表示现在某时刻之前一直在进行着的动作,这个动作可能已经完成,也可能仍在进行。
e.g. I) How long has it been raining?
II) I have been working on my paper for five years.
2. 有些延续动词如live, study, teach, work等的现在完成时与现在完成进行时的区别不大,都表示延续一段时间的动作,现在完成时更强调动作的延续性。
e.g.I) I have lived here for ten years. = I have been living here for ten years.
II) How long have you taught English here? = How long have you been teaching English here?
但是,多数延续性动词的现在完成时与现在完成进行时表达的意义有所不同。
e.g. He has been writing this morning and has written four letters.
十一、过去完成进行时
过去完成进行时的主要用法与现在完成进行时的用法相仿,只是时间推移到了过去。
e.g. I) They had been waiting for half an hour before the bus came.
II) The fire had been burning for over a week.
十二、将来完成进行时
将来完成进行时将来某时刻前一直进行的动作。
e.g. I) By next year he will have been teaching English for 30 years.
II) In an hour you will have been surfing the net (上网) for 5 hours today.
1) After searching for half an hour, she realized that her glasses____on the table all the time. D
A) were lain B) had been lain
C) are lying D) had been lying
2) By the time you get to Beijing tomorrow, I____for Shanghai. A
A) shall have left B) will leave
C) am leaving D)have already left
3) I bought a new house last year, but I____my old house yet, so at the moment I have two houses. B
A) didn't sell B) have not sold
C) had not sold D) don't sell
4) Ever since the family moved to the suburbs last year, they____better health. B
A) could have enjoyed B) have enjoyed
C) have been enjoyed D)are enjoying
5) I decided to go to the library as soon as I____.C
A) finish what I did
B) finished what I did
C) finished what I was doing
D)would finish what I was doing
6)Julia hadn't reached the restaurant when Jim____there. A
A)got B) has got C) had got D) had been
7) Even though they____for twenty years, the two neighbors are not on good terms. D
A) have been lived side by side
B) had been living side by side
C) have been side by side living
D) have been living side by side
8) When the final grades were posted, Max____that he had passed the physics exam after all. B
A) discovers B) discovered
C) had discovered D) has discovered
9)I____you the book as soon as possible, I promise you. B
A) would send B) will send
C) sent D) send
10) We____down when she____plates of food for us. D
A) had hardly sat, had bought
B) hardly sat, bought
C) hardly sat, had bought
D) had hardly sat, bought
11) When I called you this morning, nobody answered the phone.____? D
A)where have you been B) where have you been to
C) where did you go D) where were you
12) As my mother____here before, I went to meet her at the railway station. A
A)had never been B) has never been
C) had been never D) never was
13) Our team____every match so far this year, but we still have three more games to play. B
A) was winning B) has won
C) had won D) wins
14) He____for three years. B
A)has joined the army
B) has been in the army
C) has been serving in the army
D) joined the army
15) The growth of part time and flexible working patterns, and of training and retraining schemes, ____more women to take advantage of employment opportunities. D
A) have allowed B) allow
C) allowing D) allows
16) The car____at the present speed until it reaches the foot of the mountain at about ten o'clock tonight. C
A) would go B) went
C) will be going D) goes
17) The company____a rise in salary for ages, but nothing has happened yet. C
A) is promised B) is promising
C) has been promising D) promised
18) No sooner had he sat down than the telephone____. C
A) rings B) was ringing
C) rang D) hand rung
19) I hope the time is not far off that they shall____for the betterment of the working class. B
A) make to fight B) be made to fight
C) be fought D) fought
20) Mr. James____a city bus for over twenty-five years before retirement. C
A) is driving B) drove
C) has driven D) drives
21) I____a radio talk on Shakespeare when my uncle came home and started shouting at the top of his voice. C
A) was hearing B) heard
C) was listening to D) listened to
22) He____novels, whenever his wife goes shopping. B
A) is reading B) reads
C) has read D) has been reading
23)I am not sure whether tomorrow he____the meeting or not, as he has not been here lately. C
A) attend B) attends
C)will attend D) attended
24)I____that she will pass the final examination. A
A) expect B) have expected
C) had expected D) was expected
25) They thought it____fun to take the car. B
A) can be B) would be
C) will be D) has been
26)She reminded me that Bangkok____the capital of Thailand. A
A)is B)was
C)had been D)have been
27)“Let's hurry. The president is coming.”“Oh, I am afraid that we____.” D
A) already miss him B) had already missed him
C) will miss him already D) have already missed him
28) She was told the examination____on Friday. B
A) will be given B)would be given
C) to be given D) is given
29)They believed that by using computers the production of their factory____. C
A) will already increase
B) would greatly increase
C) would be increased greatly
D) will have been greatly increased
30)You won't know if it fits you before you____it on. C
A) will try
B) are trying
C) try
D) have tried
31)We____your terms carefully but____to say that we cannot accept them. C
A) are studying…regret
B) have studied…are regretting
C) have studied…regret
D) have been studying…have regretted
32) James has just arrived, but I didn't know he____until yesterday. B
A) will come B) was coming
C) had been coming D) came
33) By the time you arrive tonight, I____for several hours. D
A) had studied B) have been studied
C) had been studying D) will have been studying
34)According to the timetable, the train for Shanghai____at seven o'clock in the evening. A
A) leaves B) has left
C) was left D) will leave
35)I can't find my dictionary. I wonder whether Mary____it now. B
A) have B) has
C) is having D) had
36) Mr. Harris said that he____to the supermarket before going home. C
A) will go B) had gone
C) would go D) is to go
37)It was not until then that I came to know that knowledge____only from practice. D
A) had B) has come
C) came D) comes
38)You____the difficulties when I finish telling you the whole story. C
A) will be seen B) will have seen
C) will see D) see
39) She is studying medical science now, but she____a lawyer. A
A) used to be B) would be
C) formerly were D) had been
40) It is reported that by the end of this month, the output of cement in the factory____by about 10%.(CET-4 1996,1) A
A) will have risen B) has risen
C) will be risen D) has been rising
41)My train arrives in New York at eight o'clock. The plane I would like to take from there____by then. (CET-4 1998,6) A
A) will have left B) would leave
C) had left D) has left
时态部分练习题
1)D 2)A 3)B 4)B 5)C 6)A 7)D 8)B 9)B 10)D 11)D 12)A 13)B 14)B 15)D 16)C 17)C 18)C 19)B 20)C 21)C 22)B 23)C 24)A 25)B 26)A 27)D 28)B 29)C 30)C 31)C 32)B 33)D 34)A 35)B 36)C 37)D 38)C 39)A 40)A 41)A
大学英语语法 学习提纲 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种: 名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. 2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。如:who, she, you, it . 3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly. 7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before . 10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如: I’m Miss Green.(我是格林小姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名词、 代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。如: He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间 接宾语。间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给 我写了一封信) 有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾 语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信) 5、定语修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、代词、数词等担任。如: Shanghai is a big city .(上海是个大城市)
14. 倒装 倒装句之全部倒装 全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有: 1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, com e, go, lie, run。 There goes the bell. Then came the chairman. Here is your letter. 2) 表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。 Out rushed a missile from under the bomber. Ahead sat an old woman. 注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。 Here he comes. Away they went. 倒装句之全部倒装 全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有: 1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, come, go, lie, run。 There goes the bell. Then came the chairman. Here is your letter. 2) 表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。 Out rushed a missile from under the bomber. Ahead sat an old woman. 注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。 Here he comes. Away they went. 倒装句之部分倒装
大学英语语法1——基础时态 时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 1. 一般现在时 用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 Mr. Lee told his students the early bird (catch) the worm. E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?)
例:If traffic problems will not be solved soon, driving in cities will become impossible. 2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 表示按计划安排即将发生的动作。 例如:She is leaving for Beijing.她要去北京。 My father is coming to see me this Saturday.这个星期六我爸爸要来看我。My wife is always criticizing me.我的妻子总是批评我。 现在进行时与频度副词always、continually、constantly、forever等连用,常表示不满或抱怨情绪等。 注意: The food that Cathy is cooking in the kitchen _____ delicious. A. is smelling B. smells C. has smelled D. will smell 感官动词,如smell, taste, sound , feel等 A study of the motion of objects is necessary if we are understanding their behaviors and learn to control them. 表示感情、拥有关系、状态或思想的动词,如agree、believe, belong, contain, hate, hear(听到), like, love, mind, notice, possess, see, seem, understand, want等。 3. 现在完成时(have done)
英语共有十六个时态、四个体。(注:四个体为——一般、进行、完成、完成进行。) 英语中的四个体相当于法语、西班牙语以及所有印欧语系罗曼语族中的式,如:直陈式,命令式等。 (1)一般现在时 基本形式(以do为例): 第三人称单数:does(主语为非第三人称单数); 肯定句:主语+动词原形+其他; He works for us. 否定句:主语+don…t/doesn't+动词原形+其他; He doesn't work for us. 一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他。 肯定回答:Yes,(+主语+do/does). 否定回答:No,(+主语+don't/doesn't.) 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句语 Does he work for us? Yes, he does. No, he doesn't What does he do for us? He works for us. (2)一般过去时 be动词+行为动词的过去式 否定句式:在行为动词前加didn…t,同时还原行为动词,或was/were+not; was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词 例如:Did he work for us? He didn't work for us. He worked for us. (3)一般将来时 am/are/is+going to+do 或 will/shall+do am/is/are/about to + do am/is/are to + do; 一般将来时的表达方法 be going to +动词原形 be +不定式,be to+动词原形,be about to +动词原形
动词时态 一、一般现在时 1.定义:表示经常发生的情况、有规律出现的情况、总是发生的事和事实真理。 2.时间状语:Always,usually,often,sometimes,every week (day,year,month…),once a week(day,year,month…),on Sundays(on Mondays …). 3.基本结构:主语+ do/does +其他;(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式)。 4.否定形式:主语+ am/is/are + not + 其他(此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词)。 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 6.例句:(1)It seldom snows here.这里很少下雪。 (2)He is always ready to help others.他总是乐于帮助别人。 (3)Action speaks louder than words.事实胜于雄辩。 二、一般过去时 1.定义:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2.时间状语:ago,yesterday,the day before yesterday,last week,last(year,night,month…),in 1989,just now,at the age of 5,one day,long ago,once upon a time. 3.基本结构:主语+ 动词的过去式或be的过去式+名词。 4.否定形式:主语+ was/were + not + 其他(在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词)。 5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。 6.例句:(1)She often came to help us in those days.那些天她经常来帮助我们。 (2)I didn't know you were so busy.我不知道你是这么忙。 三、一般将来时 1.定义:表示将要发生的动作、打算、计划或准备做某事。 2.时间状语:Tomorrow,soon,in a few minutes,the day after tomorrow,etc. 3.基本结构:(1)主语+ am/is/are + going to + do sth (2)主语+ will/shall + do + do sth 4.否定句:在系动词is/am/are或情态动词will/shall后加not 5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首。{首字母大写} 6.例句:(1)They are going to have a competition with us in studies. 他们将有一场比赛和我们一起研究。 (2)It is going to rain.天要下雨了。 四、一般过去将来时 1.定义:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。 2.时间状语:The next day (morning \,year…),the following month(week…),etc. 3.基本结构:主语+ was/were + going to + do + 其它;主语+ would/should + do +其它 4.否定形式:主语+ was/were + not + going to + do; 主语+ would/should + not + do.
课程教案 ——时态专题 模块一:现在进行时 Warm-up 请观察下列句子,并寻找其中的规律: 1.I'm drawing pictures. 2.I'm reading a book in the library. 3.She is jumping. 4.It's eating bananas. 5.They're climbing trees. 6.He is swimming. Presentation I. 现在进行时的定义:现在进行时一般表示正在进行的动作或事情,也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。 II. 请看下列例子: I am reading a book in the classroom. Mary is swimming in the sea. They are eating lunch now. 主语是实际的人/物/代词be动词要和主语一致动词的现在分词地点状语/时间状语通常 在句末 III.现在进行时的句型结构及举例: 句式句型结构及例子 肯定式主语+ be (am / is / are) + 动词的分词形式+ 其他Lucy is watching TV now. 否定式主语+ be (am / is / are) + not+ 动词的分词形式+ 其他I am not reading a book in the classroom. 一般疑问句式Be (am / is / are) +主语+ 动词的分词形式+ 其他—Are you having a picnic? —No, we aren’t. —Are they eating the honey? —Yes, they are. 疑问词+ be (am / is / are) +主语+ 动词的分词形式?
在句子中起名词作用的句子叫名词从句(Noun Clauses)。名词从句的功能相当于名词词组, 它在复合句中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语、介词宾语等,因此根据它在句中不同的语法功能,名词从句又可分别称为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。 一、引导名词性从句的连接词 引导名词性从句的连接词可分为三类: 连词:that(无任何词意) whether,if(均表示“是否”表明从句内容的不确定性) as if ,as though(均表示“好像”,“似乎”) 以上在从句中均不充当任何成分 连接代词:what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whose, which.whichever,whomever 连接副词:when, where, how, why 不可省略的连词: 1. 介词后的连词 2. 引导主语从句和同位语从句的连词不可省略。 That she was chosen made us very happy. We heard the news that our team had won. 比较: whether与if 均为"是否"的意思。但在下列情况下,whether 不能被if 取代: 1. whether引导主语从句并在句首 2. 引导表语从句 3. whether从句作介词宾语 4. 从句后有"or not" Whether he will come is not clear. 大部分连接词引导的主语从句都可以置于句末,用it充当形式主语。 It is not important who will go. It is still unknown which team will win the match. 二. 主语从句 作句子主语的从句叫主语从句。主语从句通常由从属连词that,whether,if和连接代词what,who,which,whatever,whoever以及连接副词how,when,whe re,why等词引导。that在句中无词义,只起连接作用;连接代词和连接副词在句中既保留自己的疑问含义、又起连接作用,在从句中充当从句的成分。例如:What he wants to tell us is not clear. 他要跟我们说什么,还不清楚。 Who will win the match is still unknown. 谁能赢得这场比赛还不得而知。
初中英语语法八大时态总结 初中英语时态是英语学习中一个至关重要的内容,同学们在实际运用时,往往对时态总是倍感棘手,为了让大家能更深刻地记住英语语法中的各种时态,下面是小编为您收集整理的初中英语语法八大时态总结,供大家参考! 初中英语语法八大时态总结 一、一般现在时: 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语:always,usually,often,sometimes,everyweek(day,year,month),onceaweek,onSundays,etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加dont,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesnt,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 二、一般过去时: 概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 时间状语:ago,yesterday,thedaybeforeyesterday,
lastweek(year,night,month),in1989,justnow,attheageof5,oneday,longlongago,onceuponatime,etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didnt,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词。 三、现在进行时: 概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。 时间状语:now,atthistime,thesedays,etc. 基本结构:am/is/are+doing 否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing. 一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。 四、过去进行时: 概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。 时间状语:atthistimeyesterday,atthattime或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。 基本结构:was/were+doing 否定形式:was/were+not+doing. 一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。 五、现在完成时:
大学英语语法与练习——u n i t14倒装
14. 倒装 14.1 倒装句之全部倒装 全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有: 1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, com e, go, lie, run。 There goes the bell. Then came the chairman. Here is your letter. 2) 表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。 Out rushed a missile from under the bomber. Ahead sat an old woman. 注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。 Here he comes.Away they went. 14.1 倒装句之全部倒装 全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有: 1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, come, go, lie, run。 There goes the bell. Then came the chairman.
Here is your letter. 2) 表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。 Out rushed a missile from under the bomber. Ahead sat an old woman. 注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。 Here he comes. Away they went. 14.2 倒装句之部分倒装 部分倒装是指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态倒装至主语之前。如果句中的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do, does或did,并将其置于主语之前。 1)句首为否定或半否定的词语,如no, not, never, seldom, little, hardly, at no time, in no way, n ot until… 等。 Never have I seen such a performance. Nowhere will you find the answer to this question. Not until the child fell asleep did the mother leave the room. 当Not until引出主从复合句,主句倒装,从句不倒装。 注意:如否定词不在句首不倒装。 I have never seen such a performance. The mother didn't leave the room until the child fell asleep. 典型例题
英语语法大全之种时态 TPMK standardization office【 TPMK5AB- TPMK08- TPMK2C- TPMK18】
师大附小 英语语法大全小学教育 Jwwang 2017-8-16
目录 一、什么是时态? (1) 1.1 时间的定义 (1) 1.2 状态的定义 (1) 二、动词的十二类时态 (2) 2.1 一般式 (2) 2.1.1 一般现在时(DO) (2) 2.1.2 一般过去时(DID) (2) 2.1.3 一般将来时(WILL DO) (2) 2.2 进行式 (3) 2.2.1 现在进行时(AM/IS/ARE DOING) (3) 2.2.2 过去进行时(WAS/WERE DOING) (3) 2.2.3 将来进行时(WILL BE DOING) (3) 2.3 完成式 (4) 2.3.1 现在完成时(HAVE/HAS DONE) (4) 2.3.2 过去完成时(HAD DONE) (4) 2.3.3 将来完成时(WILL HAVE DONE) (5) 2.4 完成进行式 (5) 2.4.1 现在完成进行时(HAVE/HAS BEEN DOING) (5) 2.4.2 过去完成进行时(HAD BEEN DOING) (6) 2.4.3 将来完成进行时(WILL HAVE BEEN DOING) (6) 2.5 过去将来时 (7) 2.5.1 一般过去将来时(WOULD DO) (8) 2.5.2 过去将来进行时(WOULD BE DOING) (8) 2.5.3 过去将来完成时(WOULD HAVE DONE) (8) 2.5.4 过去将来完成进行时(WOULD HAVE BEEN DOING) (8)
大学英语语法 (CET--4) 学习提纲 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种: 名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. 2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。如:who, she, you, it . 3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly. 7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before . 10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。 如:I’m Miss Green.(我是格林小姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名 词、代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。如: He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接 宾语。间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给我写了 一封信) 有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾 语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信) 5、定语修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、代词、数词等担任。如: Shanghai is a big city .(上海是个大城市) 6、状语用来修饰动词、形容词、副词,通常由副词担任。如:He works hard .(他工作努力) 7、宾语补足语用来说明宾语怎么样或干什么,通常由形容词或动词充当。如:They usually keep their classroom clean.(他们通常让教室保持清洁)/ He often helps me do my lessons.(他常常帮我做功课)/ The teacher wanted me to learn French all by myself.(老师要我自学法语) ☆同位语通常紧跟在名词、代词后面,进一步说明它的情况。如:Where is your classmate Tom ?(你的同学汤姆在哪里?)
英语的时态问题 英语的时态可以分为:“时”(time) 和“体”(aspect)(又称为态)。时是指动作发生的时间,体是指动作发生时的状态。时间与体就象是坐标里的横轴和纵轴,它们的结合交织出了瞬息万变的时空,也构成了英语动词的时态问题。 时间分为:过去,现在,将来,过去将来 体分为:一般(在某个时间点), 进行(延续某个时间段), 完成(完成某个时间段) 完成进行(延续某个完成的时间段) 如此以来,英语中就有16种时态变化,现在就用动词为write例,看看它们的形式。 注意:里面的斜体字部分,由于时态过于复杂,几乎没有人真正去应用它们,可以忽略不记。 下面就常用的12种时态,(其中还有三种相对用的较少的,请注意)。具体分析一下。 一.一般现在时 表示现在的时间“点”上发生的动作或者状态,常用于以下的情况 1、经常重复发生的动作或存在的状态,多与often, always, usually, sometimes, everyday, 等时 间状语连用。 He takes a walk after supper everyday My mother and father work at the same company. 2、表示性格,特征,能力。 Mr. Smith hates fish and never eats any. 3、表示客观真理或者普遍事实。
The sun rises in the east. 二.一般过去时 表示过去某时发生的动作或者状态,常和表示过去某个时间“点”的时间状语(yesterday, last week, 3 years ago, in 1987)连用 She bought a car last week. He came to help me at that time. 三.一般将来时 表示将来的时间“点”上发生的动作或者状态。 The train will arrive soon. We shall know the news tomorrow. 四.过去将来时 过去某个时间“点”上将要发生的动作或状态。 I asked her where she would spend her holiday. I told my father that I should go home next Monday. 五.现在进行时 表示现在的时间“段”上正在延续进行的动作或者状态。 I’m doing some washing. What are you doing? 六.过去进行时 在过去某一个时间“段”正在延续进行的动作。 I was working in my office at eight o’clock yesterday evening. He was making a phone call when I saw him. 七.将来进行时 在将来某个时间“段”正在发生的动作,一般表示一种猜测和未来的计划,一般不太常用。What will you be doing at 3 o’clock tomorrow afternoon? (明天下午三点你将在做什么哪) 八.现在完成时 表示动作在一个时间“段”的完成,而且这个时间段是从过去某一点延续到现在的。经常跟时间状语since 1987,for 10 hours , by the last year相连。 My brother has been ill for 3 days. I have not seen her since 1991. 九.过去完成时 在过去的某个时间“段”里动作的完成,从过去的一点再到过去的另一点。或者称为过去的过去。 He said that he had written her a letter. Helen rang me up after I had gone to sleep.
Unit1 Ways of Learning Part II Reading Task Comprehension Content Question Pair Work 1.They were studying arts education in Chinese kindergartens and elementary schools in Nanjing. 2.Their 18-month-old son Benjamin was fond of trying to place the key into the slot of the key box during their stay at the Jinling Hotel. 3.They would come over to watch Benjamin and then try to teach him how to do it properly. 4.Because he realized that this anecdote was directly relevant to their assigned tasks in China: to investigate early childhood education and to throw light on Chinese attitudes toward creativity. 5.Most of them displayed the same attitude as the staff at the Jinling Hotel. 6.He emphasized that the most important thing is to teach the child that on can solve a problem effectively by oneself. 7.He means that this incident pointed to important differences in educational and artistic practices between China and the USA. 8.The manner in which the Chinese staff saw the need to teach the child by guiding his hand in the characteristic of a broader attitude to education, one that stands in contrast to the Western preference for leaving the child to explore and learn unaided. 9.One example is of children at the age of 5 or 6 painting flowers, fish and animals skillfully and confidently; in a second example, calligraphers 9 and 10 years old were producing works; and in a third, young artists work on perfecting their craft for several hours a day. 10.Americans think that unless creativity has been acquired early, it may never emerge, and skills can be picked up later. Chinese think that if skills are not acquired early, they may never be acquired, and there is no hurry to promote creativity. 11.This is mainly due to the difference in their way of thinking. 12.The author makes the suggestion that we should strike a better balance between the poles of creativity and basic skills. Text Organization Working On Your Own 1.
一般现在时 1.表示现在习惯或经常反复发生的动作。常与always, usually, often, sometimes, every day (week, month)等连用。 He plays football twice a week.他每周踢两次足球。 I sometimes go to work on foot.我有时步行去上班。 2.表示现在的事实或状态。 It’s cold today.今天很冷。 You look tired now.你现在看起来很疲乏。 3. 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。 I don't want so much. Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well. 比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup. I am doing my homework now. 第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。再如:Now watch me, I switch on the current and stand back. 第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。 4.表示格言或警句中。 Pride goes before a fall.骄者必败。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。 例:Columbus proved that the earth is round.. 5.表示客观事实或普遍其理。 It’s far from the earth to the sun.地球与太阳间的距离很远。 Five and three makes eight.五加三得八。 5.表示已预先安排或计划好将来确定会发生的动作。 但主要用于go, come, leave, start, return, arrive等瞬间动词。 The train from London arrives at 7:00.从伦敦来的火车7:00到站。 He leaves on business the day after tomorrow.他后天出差。 6.在时间、让步及条件状语从句中表示将来的动作。 I’ll call you as soon as I get there.我一到那里就打电话给你。 I’ll come if he invites me.他如果邀请我我就来。 7.在以here, there开头的句子里,表示正在发生的动作。 Her comes the bus!汽车来了! There goes the bell!铃响了! 当主语是代词时,代词必须放在动词之前。如: There he comes!他来了! 8.某些表示心理状态和感觉的动词,如feel, love, hope, want, understand等表示现在发生的具体行为。 I feel pain in my head.我头疼。 I don’t understand what you mean.我不理解你的意思。 此时只用一般现在时而不用现在进行时。 9在由after,until,before,once,when,even if,in case,as long as,as soon as,the moment 以及if,unless等引导的时间状语从句或条件状语从句中,通常用一般现在时代替将来时。例如: 1)I will tell him the news as soon as I see him. 2)I will not go to countryside if it rains tomorrow. 10某些表示起始的动词,可用一般现在时表示按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,这类动词有:be,go,come,start,depart,arrive,begin,leave等。例如: 1)The plane leaves at three sharp. 2)The new teachers arrive tomorrow. 11在由why,what,where,whoever,who,that,as等引导的从句中,也常用一般现在时代替将来时。例如: 1)Free tickets will be given to whoever comes first. 2)You’ll probably be in the same train as I am tomorrow. 12一般现在时用于倒装句中可以表示正在发生的动作,动词以come, go为主。如:Here comes the bus. (车来了) / There goes the bell.(铃响了)。 13一般现在时常用于体育比赛的解说或寓言故事中。Now the midfield player catches the ball and he keeps it.
英语语法16种时态经典总结(收藏版) 一般完成进行完成进行 现在现在一般时 do 现在完成时 have done 现在进行时 is doing 现在完成进行时 have been doing 过去过去一般时 did 过去完成时 had done 过去进行时 was doing 过去完成进行时 had been doing 将来将来一般时 will do 将来完成时 will have do ne 将来进行时 will be doi ng 将来完成进行时 will have been d oing 过去将来过去将来一 般时 would do 过去将来完成 时 would have d one 过去将来进 行时 would be do ing 过去将来完成进行 时 would have been doing
16种时态形式(以do为例): 注:构成时态的助动词be (is, am, are), have (has, have), shall, will 等需根据主语的变化来选择。 在这16种时态中,其中有8种时态是最重要的,也是用得最多的,是初学者必须要掌握的,它们是一般现在时(也称一般现在时)、一般过去时(也称一般过去时)、一般将来时(也称一般将来时)、现在进行时、现在完成时、过去进行时、过去完成时、过去将来一般时(也称过去将来时),其余的时态相对用得较少。 1. 一般现在时 用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于