
形容词的基本概念及用法
一、形容词的定义:形容词是用来修饰名词或代词的,在句中可用作定语、表语和宾语补足
q五坐语等。
二、形容词的用法:
⑴ 用作前置定语,即放在名词前修饰该名词。例如:
China is a great country with a long history. 中国是一个历史悠久的国家。
⑵ 用作后置定语。形容词修饰不定代词或形容词短语修饰名词时,需要后置。例如:
He has something important to tell you. 他有重要的事告诉你。
She is a girl good at singing. 她是一位擅长唱歌的女孩。
⑶ 用作表语。例如:
It was rainy yesterday, but today it is sunny. 昨天下雨,今天天晴。
Your mother seems angry. 你母亲看上去生气了。
The milk in the glass has gone bad. 玻璃杯里的牛奶发臭了。
The leaves turn yellow in autumn. 树叶在秋天变黄。
注意:有一些形容词在句中只能用作表语,我们称之为“表语形容词”。初中英语中常见的表语形容
词有:afraid, alive, alone, asleep, glad, ill (生病的), ready, sorry, sure, unable, well (健康的)等。例如:
I ' m sorry not to have been ready for the party. 很抱歉,晚会我还没有准备好。
The children were asleep ju st now, but now they ' re 孩Wa们e刚才在睡觉,现在醒了。They were unable to help us. 他们没法帮助我们。
⑷ 用作宾语补足语。例如:
The news made her happy. 那个消息使她很开心。
Who left the door open? 是谁没把门关上?
三、名词化的形容词:
th+e 形容词”具有名词的功能,泛指一类人或抽象事物。用作主语时,谓语动词要用复数。
可以这样用的形容词有:blind, dead, old, poor, rich, young 等。例如:
The young are the hope of the country. 年轻人是国家的希望。
The rich are not always happy. 有钱人并不总是快乐。
四、形容词的比较等级:
1. 比较等级的构成:
形容词比较等级分为原级、比较级和最高级三种。比较级和最高级的构成有规则变化和不规则变化两种。规则变化由原级+ -er”勾成比较级、原级+ -est构成最高级,女如: small -smaller -smallest ;
形容词比较级的勾成规则 :
①. 单音节和部分双音节形容词或副词通常加后缀■er和-est构成比较级和最高级。如:
long T Ion ger 宀Ion gest clever-cleverer-cleverest few -fewer-fewest
small-smaller-smallest
②?原级以字母e结尾,则只加-r和-st;如:
large 宀larger 宀largest
nice-nicer-nicest
cute-cuter-cutest
③.原级以辅音字母+y”结尾,则应将y改为i,再加-er和-est构成比较级和最高级;如:
busy T busier 宀busiest easy-easier-easiest happy-happier-happiest
④. 原级为重读闭音节结尾,且末尾只有一个辅音字母,则双写这个辅音字母后再加词尾
-er 和-est构成比较级和最高级。如:
big t bigger t biggest fat-fatter-fattest thin -thinner-thinnest hot-hotter-hottest red-redder-reddest wet-wetter-wettest
⑤.多音节和部分双音节形容词在其前加more和most构成比较级和最高级。如:
useful t more useful t the most useful difficult t more difficult t the most difficult beautiful t more beautiful t the most beautiful . delicious t more delicious t the most delicious popular t more popular t -the most popular important t more important t the most important interesting t more interesting t the most interesting expensive t more expensive t the most expensive ▲部分双音节词也遵循此变化规律:careful t more careful t the most careful useful t more useful t the most useful
▲少数单音节词也是这样,如:
pleased t more pleased t the most pleased
tired t more tried t the most tired
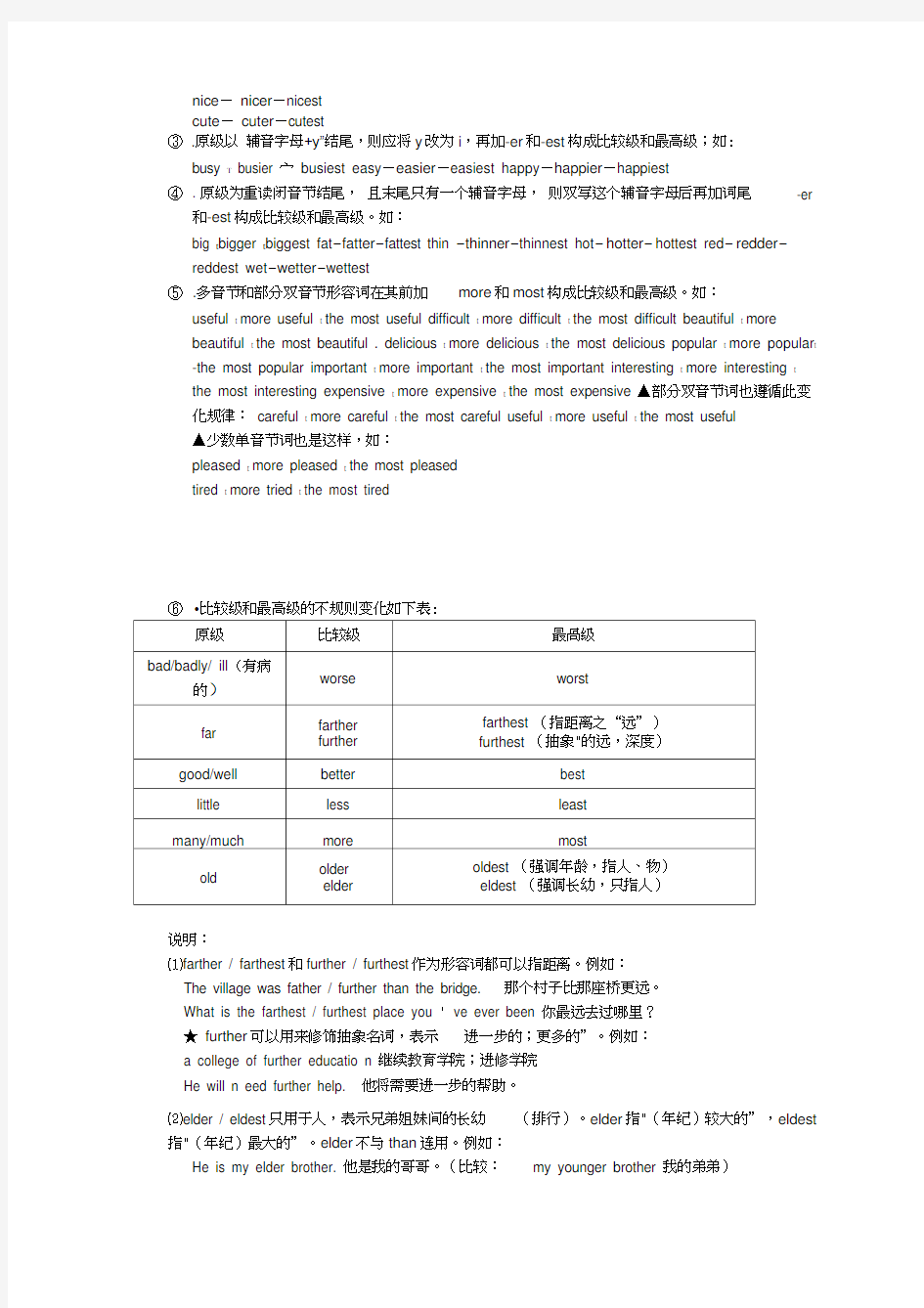
⑥?比较级和最高级的不规则变化如下表:
说明:
⑴farther / farthest和further / furthest作为形容词都可以指距离。例如:
The village was father / further than the bridge. 那个村子比那座桥更远。
What is the farthest / furthest place you ' ve ever been 你最远去过哪里?
★ further可以用来修饰抽象名词,表示进一步的;更多的”。例如:
a college of further educatio n 继续教育学院;进修学院
He will n eed further help. 他将需要进一步的帮助。
⑵elder / eldest只用于人,表示兄弟姐妹间的长幼(排行)。elder指"(年纪)较大的”,eldest 指"(年纪)最大的”。elder不与than连用。例如:
He is my elder brother. 他是我的哥哥。(比较:my younger brother 我的弟弟)
She is my eldest daughter.她是我的长女。(比较:my youngest daughter 我最小的女儿)
2. 比较等级的基本用法:
形容词和副词都有比较等级的用法,以下内容含有对副词比较等级的介绍。
⑴ 原级用于两者之间进行平级比较,其结构是“Ais as…as B.”,意思是“A和B 一样…”。
例如:Mary is as tall as her sister.玛丽和她姐姐个子一样高。
He can speaks En glish as well as an En glishma n.他英语说得跟英国人一样好。
She can read twice as fast as he does.她阅读速度比他快一倍。
该结构的否定式为“A is not as / so …as意思是“A不如B那样.......... ”。not as…多用于口语,not so…多用于书面语。例如:
This room is not as bright as that one.这间房间没有那间房间亮。
It is not so hot today as it was yesterday.今天不如昨天热。
He doesn ' t work as haas me.(= … as hard as I do.他工作不及我努力。
⑵ 比较级用于两者之间进行比较并且其中一者在程度上超过另一者,其结构是“A is-er than
B. ”,意思是“A比B更……”。例如:
The sun is bigger tha n the earth.太阳比地球大。
My room is smaller than yours.我的房间比你的小。
The houses here are higher tha n the ones over there.这边的楼房比那边的楼房高。
⑶ 最高级用于三者或三者以上之间进行比较并且其中一者程度最甚,其结构是“A is th&est
of /in ….意思是“A在其中最 "。形容词最高级前要用定冠词the。例如:The earth is bigger tha n the moon. The sun is bigger tha n the earth. So it is the biggest of the three. 地球比月亮大,太阳比地球大,所以太阳是三者中最大的。This building is the tallest in the city. 这座大楼全市最高。Tom works hardest in his class. 汤姆在班上学习最努力。
注意:最高级的比较范围如果是所在群体内的成员,就用of 引出;如果是群体所在地,就用in, among 等词引出。请比较:This is the best picture of the three. 这是三幅图画中最好的。This is the best picture in the hall. 这是大厅中最好的图画。
3?比较级前常见修饰语总结:比较级前可以有一个表示程度的状语,表示“……得多”或稍……”之类的意思。
①. 比较级前可用 a little, a bit, a little bit, 等修饰,表示“稍微”、“一点”。如:It 's a little colder today than it was yesterday. 今天比昨天稍冷一点。They ' re a little bit better now. 现在他们稍
好一点儿了。
②. 比较级前可用much, far, by far, a lot, a good deal, a great deal, rather 等修饰,表示“……得多”。如:She'sa good deal better today. 她今天好多了。There are far more people than we expected. 人比我们预计的多得多。
注意:quite也可修饰比较级,表示“??…得多”,但该比较级通常只限于better。如:He' s quite better now. 他现在好多了。
③.比较级前可用even, still 修饰,表示更...... ”。女口:It was even colder than yesterday. 今
天比昨天还要冷。The next day she got up still earlier. 第二天她起床更早些。
①.very , quite, so, too等一般不修饰比较级,而多用来修饰原级。
②.more可以构成比较级,一定不能修饰比较级。
4.比较等级的特殊用法:
⑴“the +比较级+ of the two (+复数名词)"表示二者之中更.......的”。例如:Of the two boys Mike is the taller one. 迈克是两个男孩中个子较高的一个。
注意:比较级前一般不加the,但表示两者中较突出者,且比较级后又有名词或出现了of the
two,这时比较级前一定要加the。例如:Which is the larger country, Canada or Australian? 加
拿大和澳大利亚,哪个国家更大? (区别:Which is larger, Canada or Australian? )Of the two jobs, he chose the harder.在两项工作中他选择了较艰苦的那一个。下列句型中也要加the:
The more we get together, the happier we ' ll be.
⑵ more and more 表示越来 ... 越.... ”。例如:He has become busier and busier now. 他现
在(变得)越来越忙了。Computers are becoming more and more important in our work. 电脑在我们的工作中变得越来越重要。
It is raining more and more heavily now. 现在雨下得越来越大了。
⑶ the more …the more 表示越.... 就越 .... "。例如:The busier he is, the happier he feels. 他
越忙越高兴。
The more I see it, the less I like it. 那样东西我越看越不喜欢。本结构常用省略句形式,例如:The more the better. 越多越好;多多益善。The sooner the better. 越早越好;(时间上)越快越好。
⑷"one of + the +形容词最高级+复数名词”表示“最... 之一”。最高级前还可以用物
主代词或名词所有格来修饰。Shanghai is one of the most beautiful cities in China. 上海是中国最美丽的城市之—。Our city is one of the safest cities in the world. 我们城市是世界上最安全的城市之—。One of the most important languages is English. 最重要的语言之一是英语。
5. 比较结构的同义转换:
⑴. 原级与比较级之间的转换:
①. 英语的几种倍数表达方法:
A. 表示几倍大小(长短;数量)”,由倍数+ the size (length, amount…)of…"结构组成。例如:The earth is forth-nine times the size of the moon. 地球是月亮的49 倍大。
B. 表示“……比……大几倍”,由“倍数+形容词(副词) 比较级”结构组成。例如:This box is three times bigger than that one. 这个盒子比那个盒子大三倍。
C. 表示“??…是倍”,由倍数+ as +形容词原级+ as +"结构组成。例如:Our factory is twice as big as theirs. 我们的工厂是他们的三倍。I have three times as many as you. 我有你三倍那么多。
注意: “一倍”用once,“两倍”用twice。“三倍”用three times 其他依次类推。
②.not so / as ... as 与比较级之间的转换。如:Miss Zhang isn't so old as Miss Wang. Miss Wang is older than Miss Zhang. / Miss Zhang is younger than Miss Wang.
⑵. 最高级与比较级之间的转换:
①.最高级与比较级+ than any other +名词单数之间的转换。女口:Wei Hua is the tallest boy in his class. T Wei Hua is taller tha n any otheroy in his class. / Wei Hua is taller tha n the other boys in his class.
②.最高级与比较级+than any of the other + 名词复数/ than the other two 之间的转换。如:
Robert is the best student in the school. t Robert is better than any of the other students in the school.
注意:比较级是同类别之间进行比较,不同类之间不可以比较:
The weather here is much colder than Beijing. (F)
The weather here is much colder than that in Beijing. (T)
The people in China are more friendly than those in America.
Tom has shorter hair than Jim. =Tom 's hair is shorter than Jim ' s.
6. 多个形容词作定语时的位置:
“冠代数形大,新色国材名” 。意思是“冠词、代词、数词放在前面,而形容词又根据大小、新旧、颜色、国籍、材料的顺序依次排列修饰名词”。例如: A small round table 一张小圆
桌 A tall white building 一幢高大的白色建筑物 A dirty old black shirt 一件又脏又旧的黑色衬衣 A famous American medical school 一个非常著名的美国医学院
【考题分析】
1.--- I n our English study ,reading is more important than speaking, I think.
------ I don 't agree. Speaking_i_s _______ reading.
A. as important as
B. so important as
C. the most important
D. the same as
分析:根据原题的上下文,要求表达“和……一样重要”的意思。as…as结构一般用于肯
定句,(not) so…a结构一般用于否定句。答案:A
2.--- Mum, could you buy me a dress like this?
------ Certainly, we can buy ______ one than this, but _______ this.
A. a better, better than
B. a worse, as good as
C. a cheaper, as good as
D. a more important, not as good as
分析:第一个空格后有than这个词,说明要用比较级。第二个空格后没有than,对照答案
选项,可以看出不用比较级。另外再从句意上去考虑,不可能买“更糟糕的( worse)”衣
服,而应是“更便宜的(cheaper)”衣服。答案:C
3.Remember this, children. ______ careful you are, __________ mistakes you will make.
A. The more, more
B. The fewer, the more
C. The more, the fewer
D. The less, the less
分析:本题考点较多:首先是the more…the more结构;根据题意,第一个空格应是副词,可考虑选填The more。其次,要注意和可数名词mistakes正确搭配的那个词,可在the more
和the less之间选择。第三,要注意句子前后的语义关系。答案:C
4.That is an __ book, but I don 'tthkenobwoywwhyas not ___ in it. (interest)
分析:英语动词的现在分词和过去分词可以用作形容词。一般来说,现在分词作形容词具有主动意义,可用于人或物;过去分词作形容词具有被动意义,通常用于人。请比较:amazing 令人惊愕的—amazed 感到惊奇的exciting 令人激动的—excited 激动的
interesting 令人感兴趣的—interested 感兴趣的pleasi ng (=pleasa nt)令人愉快的一pleased 高兴的surprising 使人惊奇的—surprised 吃惊的worrying 使人焦虑的一worried 焦虑的
本题中,book应当是“令人感兴趣的”,而the boy则应对其“感兴趣”。答案:interesting interested
【同步练习】
一、选择填空:
1. The story sounds ___ .
A. to be true
B. as true
C. being true
D. true
2. These oranges taste ____ .
A. good
B. well
C. to be good
D. to be well
3. 一Mum, I think I ' m ______ to go to school.
一Not really, my dear. You 'd better stay at home for another day or two.
A. so well
B. so good
C. well enough
D. good enough
4. He told us _____ story that we all forgot about the time.
A. such an interesting
B. such interesting a
C. so an interesting
D. a so interesting
5.It is impossible for so ____ workers to do so ______ work in one day.
A. few, much
B. few, many
C. little, much
D. little, many
6. 一Lucy, do you have a ruler?
一Yes, I do. But it ' s ___________ .
A. very small one
B. an only small ruler
C. quite small ruler
D. only a small one
7. ___ food you have cooked!
A. How a nice
B. What a nice
C. How nice
D. What nice
8. They all looked ____ at the master and felt quite _____ .
A. sad, sad
B. sadly, sad
C. sad, sadly
D. sadly, sadly
9. He' d like to sleep with the window ____ at night.
A. open wide
B. open widely C wide open D. opened wide
10. The little boy looks ___ .
A. lovely
B. carefully
C. heavily
D. sadly
11. The United States, Britain, New Zealand and so on are ____ countries.
A. speaking-English
B. English-speaking
C. spoken-English
D. English-spoken
12. The trip was ___ and everyone was _____ with it.
A. pleasant, pleased
B. pleased, pleasant
C. pleased, pleased
D. pleasant, pleasant
13. What ___ news! A. an exciting B. exciting C. an excited D. excited
14. This is a ____ story about a ______ woman teacher.
A. true, real
B. real, true
C. truly, really
D. really, true
15. Can you retell the text in _____ English? It is not _____ for you.
A. easy, hardly
B. easily, hard
C. hard, easily
D. easy, hard
16. His child broke the new glass, but he doesn ' t get ______ .
A. angrily
B. angry
C. well
D. good
17. _____________ He was the next morning.
A. found die
B. found dying
C. found dead
D. found death
18. Jim was just falling ___ when I came into his room quietly.
A. asleep
B. sleep
C. slept
D. slept
19. Computers can help people do ___ work in ______ time.
A. many, few
B. much, little
C. more, more
D. more, less
20. What a _____ cough! You seem _____ ill.
A. terrible, terribly
B. terribly, terrible
C. terrible, terrible
D. terribly, terribly
21. This kind of cake looks _____ and smells _____.
A. good, good
B. good, well
C. well, well
D. well, good
22. Did you notice the ___ boy at the back of the classroom?
A. asleep
B. sleepy
C. sleep
D. sleeps
23. There ' s _____ with your mother. Don ' t worry.
A. something serious
B. anything serious
C. nothing serious
D. serious nothing
24. The teacher found him ___ boy.
A. clever
B. was a clever
C. a clever
D. is a clever
25. Lots of visitors come to Nanjing because she is ____ city.
A. so a beautiful
B. very beautiful
C. such beautiful a
D. quite a beautiful
26. We find it __ to do some reading every day.
A. easily B be enjoyable C. helpful D. interested
27. Lucy said she hadn ' t heard _____ music before.
A. such a beautiful piece of
B. a beautiful
C. so beautiful
D. such a wonderful
28. The boy wasn ' t _______ at English, butwnohe does ____ in it.
A. good, good
B. well, better
C. better, well
D. good, better
29. ____ children there are in a family, _____ their life will be.
A. The less, the better
B. The fewer, the better
C. Fewer, richer
D. More, poorer
30. Now China had joined WTO, so I think English is ___ useful than before.
A. more
B. most
C. much
D. many
二、下列各句中均有一处错误,请找出并改正:
1. He saved a six-years-old boy from the river yesterday. __________________
2. Could I ask for leave? I want to visit an ill aunt in a hospital. ______________
3. This question is very important than that one. _________________________
4. He is my older brother. ___________________________________________
5. _______________________________________________________________ The here fresh water is very good. _______________________________________________________
6. The boys in Class One are good at playing football than those in Class Two.
7. ________________________________________________________ He is luckily enough to get the ticket for the football match. ___________________________________
8. We' ll never forget the pleased trip to Beijing. __________________
9. The little boy looks sadly. __________________________________
10. Please tell the children to be careful in crossing a full of traffic street.
三、同义句转换(含副词练习)
1. Liu Ying does well in physics.
Liu Ying _________ _________ _________ physics.
2. John ran faster than Jeff in the 100-meter race.
Jeff ran _________ _________ _________ John in the 100-meter race.
3. Alice was born in 1990 and so was Linda.
Alice is _________ _______ ________ Linda. They were both born in 1990.
4. Maria sings best of the girls in her class.
Maria sings _______ ________ _______ _______ ______ in her class.
5. The door is too narrow for the fatty to go through.
The door _________ ________ ________ for the fatty to go through.
6. The Changjiang River is the longest in China.
_________ river in China is _________ _________ the Changjiang River.
7. I think football is more exciting than basketball.
I think basketball is _________ ________ _________ football.
I ________ think basketball is __________ _________ ________ football.
8. If you work harder, you ' ll get higher scores.
_________ ________ you work ,_________ _________ scores you 'll get.
形容词用法归纳March 27, 2008 一. 形容词的定义和用法: 形容词用来修饰名词或代词, 表示人或事物的性质, 状态,和特征。形容词在句中作定语, 表语, 宾语,补语。 She is a good student, and she works hard. 她是一个好学生,她学习努力。 This bike is expensive. 这辆自行车很贵。 I am sorry, I'm busy now. 对不起,我现在很忙。 Have you got everything ready for the meeting? 你为这次会议做好准备吗? 二. 形容词在句中的位置: 形容词作定语一般放在被修饰的名词之前。如果有两个或两个以上的形容词修饰一个名词时, 则由它们和被修饰的名词之间的密切程度而定, 越密切的形容词越靠近名词。如果几个形容词的密切程度差不多则按音节少的形容词放在前面, 音节多的形容词放在后面。 注意: 1. 英语单词中,something, anything, nothing 等不定代词被形容词修饰时,形容词 放在名词后面。 I have something important to tell you. 我有重要的事要告诉你。 Is there anything interesting in the film. 电影里有什么有趣的内容吗? There is nothing dangerous here. 这儿一点都不危险。 2. 由两个或两个以上的词组成的形容词词组修饰名词时须放在名词之后。
This is the book easy to read. 这是一本容易读的书。 3. 用 and 或 or 连接起来的两个形容词作定语时一般把它们放在被修饰的名词后面。起进一步解释的作用。 Everybody, man and woman, old and young, should attend the meeting. 每一个人,男女老少,都应该参加会议。 You can take any box away, big or small. 这些箱子,不管大小,你都可以拿走。 三. 形容词的原级、比较级和最高级: 绝大多数形容词有三种形式,原级,比较级和最高级, 以表示形容词说明的性质在程度上的不同。 1. 形容词的原级: 形容词的原级形式就是词典中出现的形容词的原形。例如: poor, tall ,great, glad ,bad 等。 2. 原级常用结构:主语+谓语(系动词)+as+形容词原形+as+从句。表示两者对比相同。 This box is as big as mine. 这个盒子和我的一样大。 This coat is as cheap as that one. 这件衣服同那件衣服一样便宜。 I study English as hard as my brother. 我同我兄弟一样学习努力。 3. 形容词的比较级和最高级形式变化: 形容词的比较级和最高级形式是在形容词的原级形式的基础上变化的。分为规则变化和不规则变化。规则变化如下: 1) 单音节形容词的比较级和最高级形式是在词尾加 -er 和 -est 构成。 great (原级) greater(比较级) greatest(最高级)
古汉语意动用法 学案博苑 2011-12-16 1005 古汉语意动用法 在文言文中还有一种特殊的动宾关系,那就是意动关系,在文言词法中叫意动用法。 意动用法是古汉语的词类活用一种,一个词加上一个宾语,在意义上是“认为(宾语)是……”“把(宾语)当作……”“以为(宾语)是……”的意思,这里的“认为,以为”就是意动,是根据意思加上去的。意动中的"“意”,就是“主观认为”,就是“主观上把某个事物当作”的意思。 如“王欲将孙膑”中的“将”就是“把(孙膑)作为将军”之意。 又如:“先天下之忧”中的“先”即是“把(天下之忧)当作最重要的”。 又如,“以其小,劣之”中的“劣”即为“(因为它小,所以)认为(它)很劣”。 意动用法只限于形容词和名词的活用,动词本身没有意动用法。 使动用法是主语使宾语在客观上产生某种动作行为,而意动用法是主语主观上认为(或以为)宾语具有谓语所表示的内容,是存于意念的想法或看法,客观上不一定如此。一般可译为“认为......”“以......为......”等。
例如“孔子登东山而小鲁,登泰山而小天下”句子中的两个“小”都是形容词而且都带了宾语,意思是“认为…小”了,全句的意思是:"孔子登上东山以后,鲁国就在自己的脚下,就像鲁国变小了一样,登上泰山以后,天下就在自己的脚下,天下如同变一样。“鲁”“天下”都是客观存在,是主观上认为事物发生了变化。公式:常用的是“以……为……”,或者用:认为(觉得)十宾语十意动词,也可以翻译成把(对)十其语十当作(感到)十意动词。 因为意动用法是一种主观上的意念,所以,在文言文中表心理活动的动词常会出现意动用法。常见的词有:"怪""羞""耻"等,如"孟尝君怪之",这个"怪"就是"对……感到奇怪"的意思,简单说就是"以之为怪"。 再看一个例子,韩愈的狮说》里有这样一句话"于其身也,则耻师焉"这里的"耻"是"认为(觉得)……羞耻"的意思。最后举一个名词的例子韩愈的《师谢里有"生乎吾后,其闻道也亦先乎吾,吾从而师之"的句子,这里的"师"是名词作意动用,意为"把……作老师"。 1.名词的意动用法 名词用作意动,是把它后面的宾语所代表的人或事物看做这个名词所代表的人或事物。 例1:邑人奇之,稍稍宾客其父。(《伤仲永》) 宾客:本为名词,这里活用为意动词。“宾客其父”是动宾结构,意为“以其父为宾客”。 例2:父利其然也。(《伤仲永》) 利:是名词活用作意动词。“利其然”即“以其然为利”(把这种情况视为有利可图)。 2.形容词的意动用法 形容词用作意动,是主观上认为后面的宾语所代表的人或事物具有这个形容词所代表的性质或状态。 例1:渔人甚异之。(《桃花源记》) 异:原为形容词,这里用作意动词。“异之”,即“以之为异”(认为这件事奇怪) 例2:邑人奇之,稍稍宾客其父。(《伤仲永》)
形容词的用法 形容词用来修饰名词或者代词,表示人物或者事物的性质,状态和特征。 一、形容词的位置和用法。 1.多数形容词既能做定语又能做表语。作定语时放在名词的前面。做表语时放在连系动词的be,taste,smell,look,sound,fell,become,get,turn,等的后面。 如; 。(名词前作定语) 。(连系动词后面表语) 2.有些形容词只能做表语不能作定语。 如;ill,well,sorry,glad,worth等以及以“a”开头的形容词;asleep,alone,afraid,alive,awake,alike等。 如;Theboyisasleep.(不能说成anasleepboy) 3形容词修饰something,anything,someone,anybody等不定代词时,放在不定代词的后面。 如; 1.多个形容词同时修饰一个名词时,顺序是限定词(冠词,指示代词,形容词 性物主代词,名词所有格,数词)+描述次+大小,长短,高低等形状+年龄,新旧+颜色+国籍,地区+材料+名词。ThetownhasabeautifultalloldwhiteChinesestonebuilding. 二、形容词的级。 (一)原级比较 句型1;主语+谓语(系动词)+as+形容词(原级)+as。。。(如。。。。那样)HeistallasI(aam). Thisisasgoodasthat(isgood) 句型2;主语+谓语(系动词)+notas/so+形容词(原级)+as。。。(不如。。。。那样) Heisnotas/sohiswife(isold). TheweatherinBeijingisnotas/sohotasthatinGuangzhou。 (二)比较级;两者之间进行比较。 句型1.主语+谓语(系动词)+形容词比较级+than+对比成分(。。。比。。。更。。。)Heistallerthanshe。 Thispictureismorebeautifulthanthatone. 句型2主语+谓语(系动词)+形容词比较级+ofthetwo.(…两者中比较…的) -----Whichisolder,MaryorJenny? -----Jennyistheolderofthetwo.
形容词比较级和最高级用法 英语中大多数形容词有三个等级:原级,比较级和最高级。 (在同类事物中比较) 一、比较级的构成 1.规则变化: 1)原级比较级最高级 great greater greatest small smaller smallest clean cleaner cleanest 单音节词比较级在尾加最高级在词尾加。 2)原级比较级最高级 fine finer finest wide wider wider 单音节如以e结尾,比较级在尾加最高级在词尾加。 3)原级比较级最高级 big bigger biggest hot hotter hottest red redder reddest 闭音节单音节词如末尾只有一个辅音字母,须先这个辅音字母,比较级在尾加 最高级在词尾加。 4)原级比较级最高级 happy happier happiest early earlier earliest 以辅音字母+y结尾, 把y , 比较级在尾加最高级在词尾加。5)原级比较级最高级 clever cleverer cleverest narrow narrower narrowest able abler ablest 少数以-y,-er,ow,-ble结尾的音节词,比较级末尾加,最高级加。6)原级比较级最高级 careful more careful most careful difficult more difficult most difficult delicious more delicious most delicious 其它音节和音节词,比较级在单词前面加,最高级在单词前面加。2.不规则变化 原级比较级最高级 good/well better best bad/ill worse worst many/much more most little less least far farther/further farthest/furthest 注:less important least important 形容词前如加less 和least 则表示" "和" "。 二、比较级用法 (一)同级比较 I am as tall as you. He runs as fast as you.. 1.表达A和B一样,用的结构。 A + be 动词+ + 形容词的+ … + B A + 实义动词+ + 副词的+ …+ B This film is as as that one.(interest) Your pen writes as as mine.(smooth) Your answer is the same as his. He wants to buy the same shirt as I have. 2.以上两个句子用到,表示。 A +动词+the same+名词+as...+B或者 A +动词+the same as...+ B Your answer is his. Don’t make mistakes you did last night. (二)两者比较 1. I am taller than you. He runs faster than I. A+be动词+形容词+ +B… A+实义动词+副词+ +B… This pencil is__ _ than that one.(long)
形容词比较等级的用 法及练习
形容词比较等级的用法 基本形式: 原级as + 原级 + as 表示“…… 和…… 相同” 比较级比较级 + than 表示“比……较为……” 最高级the + 最高级 + of/in 表示“在……中最为……” 形容词原级的句型 1. 肯定句:A + 动词 + as + 形容词原级 + as + B e.g.: He is as busy as before 2. 否定句:A…+ not + so + 形容词原级 + as + B e.g.: He is not so busy as before 3. 疑问句:be动词 + A + as +形容词原级 + as + B? e.g.: Is he as busy as before? 4. 表倍数:…times + as + 形容词原级 + as e.g.: The ruler is three times as long as that one. 5. 表半数:half as + 形容词原级 + as e.g.: My hand writing is not half as good as yours. 6. 表“尽可能”: as + 形容词原级 + as possible e.g.: He is coming here as fast as possible. 形容词比较级的句型 1. A + 动词 + 形容词比较级 + than + B表“A比B更……一些” e.g.: His brother is younger than I. 2. …times + 形容词比较级+ than…表“比……大/长/多……几倍” e.g.: Your room is three times larger than mine. 3. 表示数、量的词 + 形容词比较级表“大几岁,高几厘米”等
形容词比较级的用法 形容词比较级通常可分为原级、比较级、最高级三种基本形式,具体而言,它们分别以下列形式出现在句中: 它们分别以下列形式出现在句中: (1)as+原级+as (2)比较级+than (3)the+最高级+of (in)... 需注意的原级的用法: (1)否定结构有A..。not as+形容词原级+as B及A...not so +形容词原级+as B两种结构。 (2)表示倍数有...times as+形容词原级+as的句型。如: This garden is ten times as large as that one. This room is twice as large as that one. (3)half as+形容词原级+as表示“……的一半”。 如:This book is half as thick as that one. 需注意的比较级的用法: (1)than后面接代词时,一般要用主格,但在口语中工也可换成me。 (2)比较级前还可以用much,even,still,a little来修饰。 (3)表示倍数时,试比较 Our room is twice as large as theirs.我们的房间是他们的两倍那样大。 Our room is twice larger than theirs.我们的房间比他们的大两倍。 (4) I’ m two years older than you.我比你大两岁。 (5)“比较级+and+比较级”表示“越来越……”。 如: He becomes fatter and fatter. (6)"The+比较级…,the+比较级”表示“越……,越……”。如:The busier he is,the happier he feels.他越忙就越高兴。 需注意的最高级的用法: (1)常见结构有:“of+复数意义的词”表示“在……之中的”,“在……中”;“in+范围、场所”表示“在……之中”。如:
如何区分使动用法和意动用法 一、使动用法 使动用法是一种特殊的动宾关系,是指谓语动词所表示的动作不是由主语所代表的人物发出,而是在主语的影响下使宾语发出的,谓语动词具有“使宾语干什么(怎么样)”的意思。使动用法主要有四种:名词的使动用法;动词的使动用法;形容词的使动用法;数词的使动用法。 (一)名词的使动用法: 表示使宾语成为这个名词所代表的人或事物,或使宾语产生这个名词用作动词后所表示的动作。例如: ①域民不以封疆之界。(使……定居) ②桓公解管仲之束缚而相之。(让……做丞相) (二)动词的使动用法: 动词的使动用法主要发生在不能带宾语的动词上。例如: ①焉用亡郑以陪邻?(使……灭亡) ②广故数言欲亡,忿恚尉。(使……发怒) “亡”“忿恚”都不能带宾语,但因分别跟了“郑”“尉”,需用使动用法解释。 某些可带宾语的动词也有使动用法。例如: 谨食之,时而献焉。(“食”,吃,这里是捕蛇者“使蛇吃”即让蛇吃东西,可译为喂养。“食”用作使动意义后读sì。) (三)形容词的使动用法: 形容词的使动用法同动词的使动用法略有区别,它的特点是使宾语所表示的人或事物具有这个形容词所表示的性质或状态。例如: ①今媪尊长安君之位。(使……尊贵) ②诸侯恐惧,会盟而谋弱秦。(使……势力削弱) (四)数词的使动用法
数词活用为动词后也有使动用法。例如: 籍令秦始皇长世,……虽四三皇,六五帝,曾不足比隆也。(假若秦始皇长寿的话,……那么即使是使秦始皇与三皇并列成为四皇,与五帝并列成为六帝,也不能比拟秦始皇的隆盛) 数词的使动用法,在于使事物发生数量的(如例句的“四”可解释为“使……成为四个”,“六”可解释为“使……成为六个”)或以数量为比喻的变化。 二、意动用法 意动用法也是一种特殊的动宾关系。是指谓语动词具有“认为(或以为)宾语怎么样”或者“把宾语当作什么”的意思,总之,动作是主语意念上发出的。意动用法有两种:形容词的意动用法;名词的意动用法。 (一)形容词的意动用法 由形容词活用而来的动词,表示主观上认为(觉得)宾语具有这个形容词所表示的性质或状态;例如: ①滕公奇其言,壮其貌,释而不斩。(认为其言奇,认为其貌壮,可译为:认为其言出众不凡,其貌壮美) ②孔子登山而小鲁,登泰山而小天下。(认为……小,可译为:孔子登上东山就觉得鲁国小了,登上泰山就觉得天下小了) (二)名词的意动用法 名词用作意动,是把它后面的宾语看作这个名词所代表的人或事物。例如: ①今我在也,而人皆藉(欺侮)吾弟,令我百岁后,皆鱼肉之。(把……当作鱼肉任意宰割) ②孟尝君客我。(把……当作客人) 区分“使动”“意动”实践操练 下列各句中均有活用的词,或“意动”,或“使动”,请你分别指出。 1. 广故数言欲亡,忿恚尉。(《陈涉世家》)
1. 形容词在句中主要可用作: 1)定语: What a fine day! 多好的天气! He is a self-made man. 他是个自学成材的人。 2)表语: The scene was horrifying. 这景象很恐怖。 I am getting bored and homesick. 我感到有些厌烦想家。 His comments were well-meant. 他说这些都是出于好心。 3)宾语的补语(构成合成宾语): I find this hot weather very trying. 我感到这种炎热天气很难受。 Do you think it necessary? 你认为这有必要吗? 4)状语: She was back, eager to see her friends. 她回来了,极想见她的朋友们。 She gave him the overcoat, anxious to be of service. 她把大衣拿给他,极愿为他服务。 He arrived home, hungry and tired. 他又饿又累的回到家里。 2. 形容词在句中的位置 有的形容词放在被修饰的名词之前,称为前置形容词;少数形容词放在被修饰的名词之后,称为后置形容词。 1)当名词被多个前置形容词修饰时,形容词之间有一个先后顺序问题。一般规则为:
(限定词)→一般描绘性形容词→表示大小、长短、高低的形容词→表示年龄、新旧的形容词→表示国籍、地区、出处的形容词→表示物质、材料的形容词→(名词)。用一句话来说就是“美小圆旧黄,法国木书屋”。如: There is a famous fine old stone bridge near the village. 村子附近有一座著名的漂亮的古代石桥。 I bought a cheap blue plastic pencil box yesterday. 昨天我买了一个便宜的蓝色塑料铅笔盒 They have got such a round brown wooden table. 他们有一张褐色的木制圆桌。 2)当形容词词组相当于一个定语从句时,或形容词用来修饰somebody, something, a nything, nothing 等的时候,便会出现后置形容词。如: The boy (who is) interested in music is my brother. 对音乐赶兴趣的那个男孩是我弟弟。 Guilin is a city (which is) famous for its scenery. 桂林是一个以风景闻名的城市。 Do you have anything interesting to tell us? 你有什么趣闻告诉我们吗? There is nothing wrong with the machine. 这台机器没有毛病。
形容词、副词"级别"口诀 I.变比较级形式前有甲、后有乙中间来个比较级。比较级前用个be,比较级后用个"比"(than)。 原级变成比较级,er结尾要牢记;一般情况直接加,单辅重闭双写加;辅音加y变i加,以e结尾去e加;少数部分双音节,规则如同单音词。其余双音多音节,词前加more就可以;不规则词没几个,它们需要特殊记。 II.变最高级形式 最高级,也容易, 原级后面加est, 规则类同比较级, 提醒一点便可以; 其余双音、多音节, 前加most牢牢记。 还有一点要留意, 最高级前要用the; 若是副词最高级, 用不用the皆可以。 III.变不规则形式 合二为一有三对, "病坏""两多"与"两好",① 一分为二有两个, 一个"远"来一个"老"。② 还有一个双含义, 只记"少"来别记"小"。③
注: ①ill/ bad→worse→worst; many/ much→more→most; good/well→better→best ②far→farther/further→farthest/furthest; old/older/elder→oldest/ eldest ③little→less→least 形容词比较等级 形容词最高级前不加the的情况 在句中使用形容词最高级时,一般要加定冠词the.但以下几种情况,最高级之前不加定冠词。 一、如果形容词最高级用来加强语气,表示"非常、极其"的意思时,前面一般不用定冠词,但有时可以加不定冠词。例如: He is a most careful student in our class. 他是我们班上一个非常细心的学生。 She is in closest touch with us .她和我们保持非常密切的联系。 二、作表语的形容词最高级,只用来同本身比较,实际上并无比较范围,此时前面不用定冠词。例如: I'm busiest on Monday. 我在星期一最忙。 It's best to do so. 这样做最好。 The lake is deepest at this place .湖的这个地方最深。 三、如果形容词最高级用在由that, thought, as引导的让步状语从句中,前面不用定冠词。 Youngest though he is, he is the wisest. 虽然他最年轻,但他最聪明。 Cleverest thought he is, he doesn't study hard.虽然他最聪明,但他不认真学习。 四、在at (the) least至少,at (the ) latest最近,at(the) farthest最远,at(the) worst最坏等短语中,作名词用的形容词最高级前的the常可省去。例如: They will come back on June 1 at (the ) latest. 他们最迟将在六月一日回来。
英语形容词比较级的用法与构成规则 (一)一般句式的构成:A + is / are+ 形容词比较级+ than + B A 是主格 B 是宾格 如:She is taller than me. 主格+ be + 形容词比较级+ than + 宾格 (二)英语形容词比较级的构成 英语形容词比较等级有三个:原级,比较级和最高级。 形容词比较等级形式变化有规则的和不规则的两种。 规则变化: 1)单音节词末尾加-er(比较级),-est(最高级) 【例】原级比较级最高级 great greater greatest clean cleaner cleanest 2)单音节如以e结尾,只加-r(比较级),-st(最高级) 【例】fine finer finest nice nicer nicest wide wider widest 3)闭音节单音节词如末尾只有一个辅音字母,须先双写这个辅音字母,再加-er(比较级),-est(最高级) 【例】big bigger biggest hot hotter hottest red redder reddest 4)少数以-y,-er,ow,-ble结尾的双音节词,末尾加-er(比较级),-est(最高级)。以-y结尾的词,如-y前是辅音字母,则变y为-i,再加-er和-est。以-e结尾的词只加-r 和-st。 【例】clever cleverer cleverest narrow narrower narrowest able abler ablest easy easier easiest
5)其它双音节和多音节词皆在前面加单词more和most。 【例】careful more careful most careful difficult more difficult most difficult delicious more delicious most delicious 不规则变化: 原级比较级最高级 good/well better best bad worse worst many/much more most little less least far farther/further farthest/furthest 注:有些形容词一般没有比较等级。如:right, wrong, woolen等。 形容词的比较等级的用法:比较级用于二者的比较 【例】Li Ping is older than Wang Hai. 李平比王海年纪大。 There are more students in Class One than in Class Two.一班比二班学生多。 ★基数词变序数词口诀 英语中基数词变为序数词时,一般在基数词后加词尾-th,但有几个词变化特殊,只要记住下面这个口诀,这些问题即可迎刃而解。 一、二、三,单独记;八去t,九除e,ve要用f替,整十基数变序数,先把ty变成tie;要是遇到两位数,十位基数个位序,th最后加上去。 解析口诀:one→first,two→second,three→third这三个词变化特殊,要单独记;eight→eighth,nine→ninth,八去t,九去e后再加-th;five→fifth,twelve→twelfth,五、十二把ve换成f再加-th;twenty→twentieth,thirty→thirtieth... 整十先把词尾y改为ie再加-th。两位数时则十位数用基数词,个位数用序数词,如:twenty-first。
.形容词和副词比较等级的用法 I)同级比较: 1甲与乙相比程度相同:用as+原级形容词/副词+as 2甲与乙相比,甲不及乙:用notas/so+形容词/副词as。如:Dickisastallashisbrother. TomspeaksChineseasfrequentlyasJack. Thepictureis(not)asbeautifulasthatone. II)比较级: 1.表示A超过B。此时用形容词和副词的比较等级more(adj/adv+er)+than Ourclassroomisbrighterthanyours. HedidmorecarefullyintheexamthanI. Idon’tthinkmathismoreimportantthanphysics. .2表示A不及B用句型:less+形容词/副词的原级+than=notas/so+形容词/副词as=notmore---than---如:这幅画比不上那幅画漂亮 2.比较级的修饰语。这些修饰语通常为副词或短语,置于比较级前面,说明比较级的程度。这些词有:alittle,little,abit,bit,alot,agreatdeal,much,far,rather,slightly,byfar, even,still,nearly,almost,any,just,(…)times等。Themoonismuchsmallerthantheearth. Theresultoftheexperimentturnedouttobeevenbetterthanexpected. Speakabitmoreslowly,please. 3.形容词和副词比较级的特殊用法
形容词比较级和最高级的用法 形容词原级的用法 1.说明人或事物自身的特征、性质或状态时,用形容词原级。 Eg.The flowers in the garden are beautiful. 2.有表示绝对概念的副词very,so,too,enough,quite等修饰时,用形容词原级。 3.表示A与B在某方面程度相同或不同时用形容词原级。 肯定句中的结构:A +as+形容词原级+as+B 否定句中的结构:A+as/so+形容词原级+as+B 表示“A是B的……倍”时,用“A+倍数+as+形容词原级+as+B”结构(一倍once,两倍twice,三倍及以上:数字+times) half as +形容词原级+as表示“……是……的一半” 形容词比较级的用: 1.比较级:常用于“比较级+than”结构。如:Cats aremore lovely than other animals 2.形容词的比较级可用much,a little,a lot,even。a bit,still,far,rather,any等修饰,使原来的比较级在语意上更加明确。如:Chickens are much smaller than cows. 3.表示两者之间进行选择“哪一个更……”时,用句型“which/who is +形容词比较级,A or B?”表示。 4.表示“几倍于……”时,用“倍数+比较级+than”表示。如:I’m three years younger than you 比较结构中还须注意以下问题: 1.比较级与最高级的结构还可以转换,意思不变。如:The Changjiang River is longer than any other river in China=The Changjiang River is the longest river in China. 2.当某一事物与其他事物做比较时,被比较事物中不能包括本身。如:He is taller than any other student in his class. 3.如果比较对象相同,可用that/those代替第二个比较对象。如:The weather in Shanghai is better than that in Wuhan. 4.两个比较级用and 连在一起可表达全面增加或减少,意为“越来越……”。
文言文中意动用法、使动用法和为动用法 一、意动用法: 所谓意动用法,是指谓语动词具有“以之为何”的意思,即认为宾语怎样或把宾语当作怎样。一般可译为“认为……”“以……为……”等。 意动用法只限于形容词和名词的活用,动词本身没有意动用法。 1、名词的意动用法:名词用作意动,是把它后面的宾语所代表的人或事物看做 这个名词所代表的人或事物。 例1:邑人奇之,稍稍宾客其父。(《伤仲永》) 宾客:本为名词,这里活用为意动词。“宾客其父”是动宾结构,意为“以其父为宾客”。 例2:父利其然也。(《伤仲永》) 利:是名词活用作意动词。“利其然”即“以其然为利”(把这种情况视为有利可图)。 2、形容词的意动用法:形容词用作意动,是主观上认为后面的宾语所代表的人 或事物具有这个形容词所代表的性质或状态。 例1:渔人甚异之。(《桃花源记》) 异:原为形容词,这里用作意动词。“异之”,即“以之为异”(认为这件事奇怪) 例2:邑人奇之,稍稍宾客其父。(《伤仲永》) 奇:原为形容词,这里用作意动词。“奇之”,即“以之为奇”(认为他才能非凡) 二、使动用法: 所谓使动用法,是指谓语动词具有“使之怎么样”的意思,即此时谓语动词表示的动作不是主语发出的,而是由宾语发出的。实际上,它是以动宾的结构方式表达了兼语式的内容。 使动用法中的谓语动词,有的是由名词、形容词活用来的。由于原来的词类不同,活用作使动之后,它们所表示的语法意义也不完全相同。 1、动词使动用法:动词和它的宾语不是一般的支配与被支配的关系,而是使宾 语所代表的人或事产生这个动词所表示的动作行为。 例1:行仁义而怀西戎,遂王天下。(《五蠹》) 怀:使……归顺。 例2:直可惊天地,泣鬼神。(《〈黄花冈七十二烈士事略〉序》)惊:使……震惊。泣:使……悲泣。 例3:操军方连船舰,首尾相接,可烧而走也。(《赤壁之战》) 走:使操军逃跑。 2、名词使动用法:名词用作使动词,是指这个名词带了宾语,并且使宾语所代 表的人或事物变成这个名词所代表的人或事物。翻译时要采 用兼语式的形式。 例1:文王以百里之壤而臣诸侯。(《毛遂自荐》) 臣:使……称臣。 例2:先破秦入咸阳者王之。(《鸿门宴》)
考点一形容词和副词的基本用法 一、形容词的用法及位置 说明人或事物的特征、性质或状态,常用来修饰名词和不定代词的词叫形容词。 1.作定语放在名词前,复合不定代词之后。如: The nice girl is my sister. I have something important to tell you. 2.做表语放在系动词之后。 She is so beautiful. He looks very happy. 3.作宾补,放在宾语之后,常与make,leave,keep等动词连用。如: You must keep the classroom cleaned. We should make our city more beautiful. 二、常见名词变形容词方法 三、副词的功能 1.作状语 He works hard. He parked car very easily. 2.作表语 做表语的副词多数是表示位置或状态的,入in, out, on, down, up, off, away, upstairs. He is in.
What’s on this evening? 3.作宾语补足语 Let them in. 四、副词的分类 1. 时间副词 时间副词要有now, then, today, tomorrow, yesterday, before, soon, lately, already, just等。时间副词是确定句子时态的重要标志,所以一定要牢固掌握不同时态的时间标志。 2. 地点副词 地点副词有outside, inside, upstairs, here, there, home, near, away, in , back, off, up, anywhere等。地点副词和动词连用时,不加介词。 3. 方式副词 方式副词有quickly,happily,loudly,suddenly,badly,easily,fast等。方式副词大多由“形容词+ly”构成。 4. 程度副词 程度副词有very,quite,rather,too,much,so等。有些程度副词可以修饰形容词、副词的原级,有些能修饰形容词、副词的比较级。 5. 疑问副词 疑问副词有when,where,why,how,how long,how soon,how often等。疑问副词常用来构成特殊疑问句。 6. 关系副词 关系副词有when,where,why。关系副词常用来引导定语从句。 7. 频度副词 频度副词有often,usually,never等。 考点二形容词(副词)的比较等级 一、形容词(副词)原级的用法 1、一些副词如very,so,too,enough,quite等修饰形容词或副词的原级。如; The boy is too young. 2、表示A与B在某方面程度相同或者不同时用形容词(副词)的原级。 (1)肯定句中的结构:“A…+as+形容词(副词)的原级+ as + B” English is as interesting as Chinese. Li Lei runs as fast as Li Hua. (2)否定句中的结构:“A…+ not + as/so + 形容词(副词)原级+ as + B” This book isn’t so new as that one. I can’t type as/so fast as my brother. (3)否定句的结构中,部分双音节和多音节形容词(副词)除使用“not…as/so+ 形容词(副词)原级+ as”的结构外,还可以使用“less+形容词(副词)原级+than”的结构 He thinks Chinese is less interesting than English.
形容词比较级的用法讲解与练习 高密市立新中学李伟 一、原因分析: 1、英语中形容词的比较等级这一用法与汉语语言习惯有着很大不同,因而学生在理解和使用上会存在一些障碍。 2、英语形容词比较级有着很多灵活多变的使用方法,学生初次接触这一语法,需要老师进行必要的指导。 二、采取措施: 1、从形容词原级的用法开始引入比较级的用法。 2、使用多媒体等教学手段,给学生创造交际环境。 3、采用小组、同桌、师生之间的多种交流、讨论的形式,进行对话练习,学习、理解并正确使用该语法。 三、教学设计: (一)、教学目标: 1、掌握一些常用形容词的比较级的形式。good---better; bad/ill----- worse; fat---fatter; heavy-----heavier; boring---- more boring… 2、掌握形容词比较级的构成规则,正确运用形容词的比较级。 A good friend likes to the same things as me. The harder you work at your study, the better grades you will have. This book is far more interesting than that one. He has learned as many English words as his brother. Of the two girls, Linda is the taller. We’ll make our country more and more beautiful.
形容词的等级 一、形容词的概念 形容词:(adj.) 是修饰名词(人或事物),表示名词的性质,特征或属性一种词类。 它在句中作定语、表语和宾语补足语。 二、形容词的用法 ①形容词作定语一般放在被修饰的名词之前。 如:a /an _____book, two _ ___trees等。 ②形容词放在系动词be 、look/ sound/ feel/smell(感官系动词), get/turn/become/ grow(变化类系动词0、seem、等之后。 如: 1.I am short. 2.She looks fine. 3.The leaves turn green. ③形容词作宾语补足语 1:I find the story interesting. 2: You must keep the classroom clean. 三:形容词的等级 How many grades(等级)do the adjectives have? 形容词有三个等级:原级、比较级、最高级 1.原级:即形容词的原形: small, good, pretty, big, many, hard, 2.比较级:两个人或物之间的比较。表示“较……”或“更……一些”。 如:smaller, better, taller, older, more, harder, more interesting , 3.最高级:三个或三个以上的人或物之间的比较。 如:smallest, tallest, newest, best,the most interesting, the most difficult 形容词的比较级和最高级的变化规则:
一、对主、从句的理解? The more I read the book,the more I liked it.? 这本书我越看越喜欢。? The more difficult the questions are, the less likely he is able to answer them.? 问题越难,他回答出来的可能性就越小。? The earlier you start,the sooner you’ll be back.? 你出发得越早,回来得就越早。? The more you practise, the better you can understand.? 你练习得越多,理解得就越透。? ? He is the busier, the happier he feels.? 他越忙越高兴。? You climb the higher, the farther you will see.?
你爬得越高,就看得越远。? ? The noisier they were, the happier was their mother.? 孩子越吵闹,他们的母亲就越高兴。? The harder you work, the more progress you will get.? 你越努力,进步就越快。? ? 三、省略? ? 1.在通常情况下,如果主、从句中的谓语动词是联系动词be,而且主语非代词时,此时be常常省略。例如:? The better the food (is), the more popular a restaurant gets.? 食物越可口,饭店的生意就越红火。? The higher the tree (is), the stronger the wind (is).? 树大招风。? The more exercise you take, the stronger you are.?