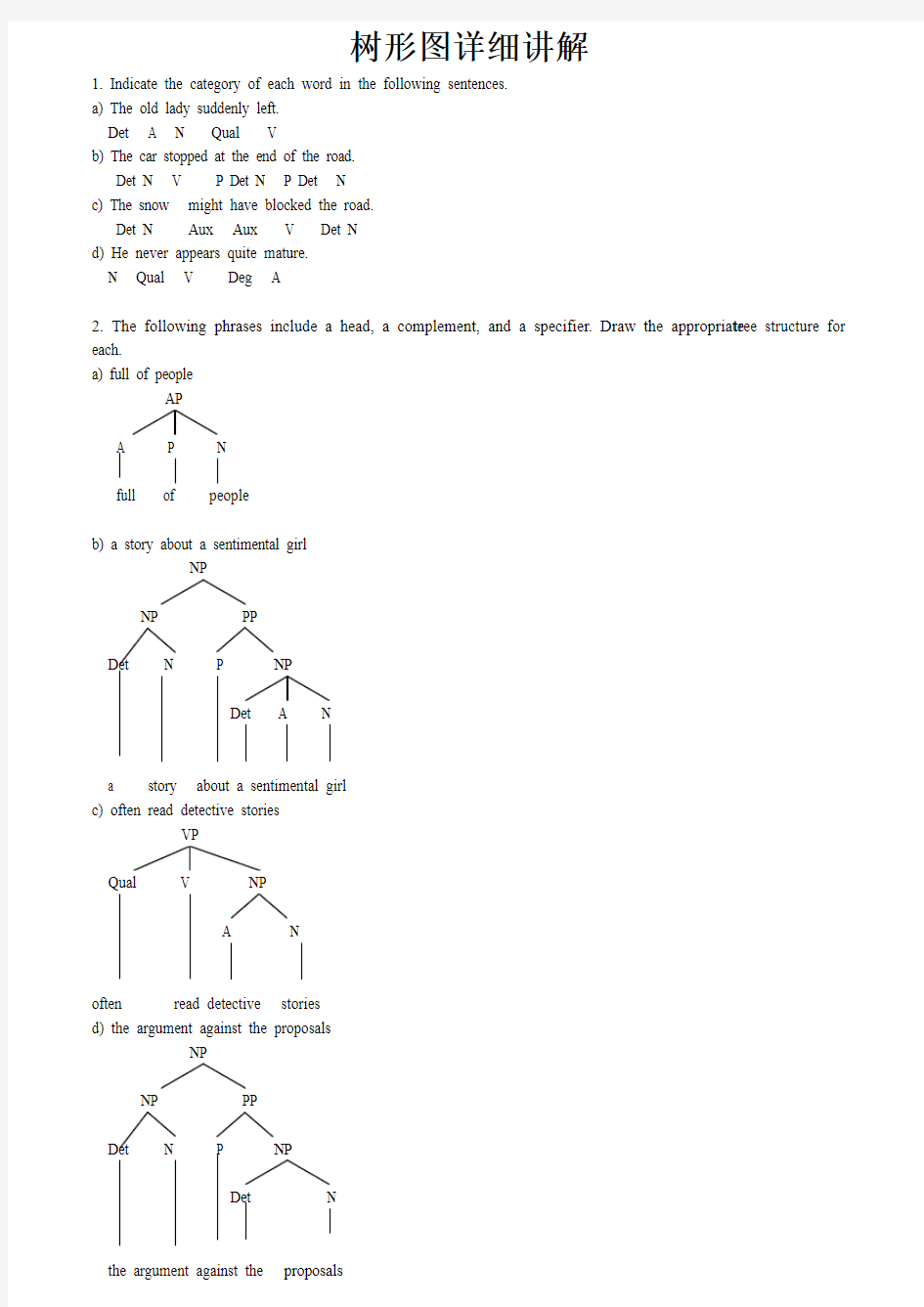

树形图详细讲解
1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.
a) The old lady suddenly left.
Det A N Qual V
b) The car stopped at the end of the road.
Det N V P Det N P Det N
c) The snow might have blocked the road.
Det N Aux Aux V Det N
d) He never appears quite mature.
N Qual V Deg A
2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.
a) full of people
AP
A P N
full of people
b) a story about a sentimental girl
NP
NP PP
Det N P NP
Det A N
a story about a sentimental girl
c) often read detective stories
VP
Qual V NP
A N
often read detective stories
d) the argument against the proposals
NP
NP PP
Det N P NP
e) move towards the window
VP
V PP
P Det N
move towards the window
3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.
a) The jet landed.
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
Det N Pst V
The jet landed
b) Mary became very ill.
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
N Pst V AP
Deg A
Mary became very ill
c) What will you talk about?
CP
NP C S
N Infl NP Infl VP
VP NP
V P N
S
NP VP
Det N Aux V NP
Det N
The apple might hit the man
OR
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
Det N V NP
Det N
The apple might hit the man
e) He often reads detective stories.
S
NP VP
N Qual V NP
A N
He often reads etective stories
OR
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
Pres
N Qual V NP
A N
He often reads etective stories
4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.
a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
Det A N Pst V NP
Det A N
A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane
b) A huge moon hung in the black sky.
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
Det A N Pst V PP
P NP
Det A N
A huge moon hung in the black sky
c) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
Det A N Pst V PP
P NP
Det N
An unusual event occurred before the meeting
d) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
Det A NP Pst V PP
A N P NP
Det A N
A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill
5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.
a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.
InflP(=S)
NP VP
N Aux V NP
Det A NP
N CON N
N Infl V NP
Det A NP
N CON N
Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants b) Helen put on her clothes and went out.
S
NP VP
N VP CON VP
VP NP V Adv
V P Det N
Helen put on her clothes and went out
OR
InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
N Pst VP CON VP
VP NP V Adv
V P Det N
Helen put on her clothes and went out
c) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.
S
NP VP
N VP CON VP
VP NP VP NP
V A P N V A P N
N Pres VP CON VP
VP NP VP NP
V A P N V A P N
Mary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics
d) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.
S
S CON S
NP VP NP VP
Det N V Adv Det A N V Adv
The detective went out and the mysterious man came in
e) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.
S
NP VP
N V C S
S CON S
NP VP NP VP
N Aux V Det N Aux V
Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt
6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.
a) You know that I hate war.
S
NP VP
CP
N V C S
NP VP
NP
N V N
OR CP
C InflP(=S)
NP Infl VP
CP
N Pres V C S
NP VP
N V NP
N
You know that I hate war
b) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.
S
NP VP
CP
N V C S
NP VP
CP
N V C S
NP VP
Det N VL A
He said that Tom asked whether the class was over
c) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.
S
NP VP
N VP NP
CP
Aux Neg V NP C S
Det N NP VP
N V NP
Det A N
d) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.
S
NP VP
CP
N VL A C S
NP VP
Det N V NP NP
N Det N
Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce
e) The children argued over whether bats had wings.
S
NP VP
CP
Det N VP C S
V P NP VP
N V NP
N
The children argued over whether bats had wings
7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.
a) The essay that he wrote was too long.
Deep structure
CP
C S
NP VP
Det N CP V AP
C S Deg P
NP Infl VP
N V NP
N
The essay he wrote that was too long
Surface Structure
CP
C S
NP VP
Det N CP V AP
C S Deg A
NP NP Infl VP
N N Pst V NP
N
The was too long
b) The dog that he keeps bites.
Deep structure
CP
C S
NP VP
Det N CP V
C Infl S
Pres NP VP
N V NP
N
The dog he keeps that bites
Surface Structure
CP
C S
NP VP
Det N CP V
C S
NP NP Infl VP
N N Pres V NP
N
The dog bites
c) Herbert found the man she loved.
Deep structure
CP
C S
NP VP
N Infl V NP
CP
Det N C S
NP Infl VP
NP
N V
N
Herbert found the man she loved who
Surface Structure
CP
C S
NP VP
N Infl V NP
CP
Det N S
C
NP Infl VP
NP NP
N V
N N Herbert found the
Deep structure
CP
C S
NP VP
Det N CP V PP
P NP
C Infl S
N
NP VP
PP
N Qual VP NP
V P N
The girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguistics
Surface Structure
CP
C S
NP VP
Det N CP V PP
P NP
C S
N
NP NP Infl VP
PP
N N Qual VP NP
V P N
The girl majors in linguistics
8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.
a) Would you come tomorrow?
Deep structure
CP
C S
VP
NP AdvP
N Infl V Adv
you would come tomorrow
Surface structure
CP
C S
VP
NP AdvP
Infl
N Infl V Adv
come tomorrow
b) Can you pass me the newspaper?
Deep structure
CP
C S
VP
NP NP NP
N Infl V N Det N
you can pass me the newspaper
Surface structure
CP
C S
VP
Infl NP NP NP
N Infl V N Det N
pass me the newspaper
c) Should the students report the incident?
Deep structure
CP
C S
VP
NP NP
Det N Infl V Det N
the students should report the incident
Surface structure
CP
C S
VP
Infl NP NP
Det N Infl V Det N
report the incident
d) What did you eat for lunch?
Deep structure
CP
C S
VP
NP PP
NP NP
N Infl V P
N N
you did eat what for lunch
Surface structure
CP
NP C S
VP
Infl NP PP
NP NP N N Infl V P
N N
for lunch
e) Who should this be reported to ?
Deep structure
CP
C S
VP
NP PP
VP NP
N Infl V V P
N
this should be reported to whom
Surface structure
CP
NP C S
VP
N Infl NP PP
VP NP
N Infl V V P
N
f) What was Helen bringing to the party?
Deep structure
CP
C S
VP
NP PP
NP NP
N Infl V P
N Det N
Helen was bringing what to the party
Surface structure
CP
NP C S
VP
N Infl NP PP
NP NP
N Infl V P
N Det N
to the party
树形图详细讲解 1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences. a) The old lady suddenly left. Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road. Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road. Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A 2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. a) full of people AP A P N full of people b) a story about a sentimental girl NP NP PP Det N P NP Det A N a story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective stories VP Qual V NP A N often read detective stories
d) the argument against the proposals NP NP PP Det N P NP Det N the argument against the proposals e) move towards the window VP V PP P Det N move towards the window 3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences. a) The jet landed. InflP(=S) NP Infl VP Det N Pst V The jet landed b) Mary became very ill. InflP(=S) NP Infl VP N Pst V AP Deg A Mary became very ill
树形图详细讲解 网上的相对理想的树形图答案,注意正两 点: 1. 短语和中心词在一竖线上 2. 含有形容词修饰语的名词短语的画法 NP Det N A N a little boy 1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences. a) The old lady suddenly left. Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road. Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road. Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A 2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. a) full of people AP A P N
full of people b) a story about a sentimental girl NP NP PP Det N P NP Det A N a story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective stories VP Qual V NP A N often read detective stories
语言学概论习题 1.根据发音特点,音素可以分为__元音__和__辅音__两类,例如汉语音节中的声母,主要就是由__辅音__充当的。 2.每个元音的音质是由__舌位的高低__、__舌位的前后__、__嘴唇的圆展_三个方面的因素决定的。 7.汉语的调位可分__阴平__、__阳平__、__上声__和__去声__四类,其音质分别是__55__、__35__、__214__、__51__。 8.汉语的音节可分为__声母__、__韵母__、__声调__三部分,其中__韵母__又分__韵头__、__韵腹__、__韵尾__三部分。 9.常见的语流音变主要有__同化__、__异化__、__脱落__、__增音__四种,例如汉语的"豆腐",实际音质是[toufu],但人们说话时常说成[touf],这种现象是__脱落__。 1. __语法规则__是大家说话的时候必须遵守的习惯,不是语言学家规定的。 2.语法的__组合规则__和__聚合规则__构成一种语言的语法规则。 3.从形式上看,句子的最大特点是_____有一个完整的语调_______。 4.句子按其语气可以分为陈述、疑问、祈使、感叹等不同的类型,例如“他谁都认识”是__陈述__ 。 5.句子里根据表达的需要临时作出组合的词组叫__自由词组__ 。 6.固定词组中的成份一般不能__更换__、__增删__ ,次序不能__颠倒__ ,它在语法结构中的作用与词完全一样。 7.从意义和作用看,词可以分为__实词__和__虚词__两大类。 8.语法研究通常以词为界,词以上的规则叫__句法__ ,词以下的规则叫__词法__ 。 9.我们可以根据语素在词中的不同作用把它分成__词根__ 、__词缀__ 、__词尾__ 三类。 10.一个词,除去它的词尾,就是它的__词干__ 。 11.根据语素在词中的不同作用,我们可以把词根和词缀叫作__构词__ 语素,把词尾叫作__变词__语素。 12.汉语语素中,大部分是__词根__ 语素,词缀不多,没有词尾。这是汉语的特点。有的语法著作中常常把前缀、后缀叫作“词头”、“词尾”。 13.语素组合成词的规则叫 __构词法__,它和词的变化规则合在一起叫作__词法__ 。 14.由词根语素按一定的规则组合起来构成的词,称为__复合词__ 。由词根语
《语言学概论》练习测试题库 一、单项选择题 1、“人有人言,兽有兽语”中的“言”属于: A. 语言。 B. 言语。 C. 言语行为。 D. 言语作品。 2、人运用语言可以说出无限多的句子,这反映了语言的:(C) A. 民族性。 B. 符号性。 C. 生成性。 D. 系统性。 3、被社团作为母语使用和学习的语言是: A. 人工语言。 B. 自然语言。 C. 共同语。 D. 世界语。 4、从语言学分科来看,《语言学概论》课属于: A. 一般语言学。 B. 具体语言学。 C. 共时语言学。 D. 历时语言学。 5、“我爱家乡”中“爱”和“家乡”: A. 是聚合关系。 B. 是组合关系。 C. 既是聚合关系又是组合关系。 D. 既非聚合关系又非组合关系。 6、汉语南方方言比北方方言更接近于古汉语,这反映了语言发展的: A. 渐变性。 B. 相关性。 C. 规律性。 D. 不平衡性。 7、下列说法正确的是: A.义项是最小的语义单位。 B.义素是最小的语义单位。 C.词义的主要内容是语法意义。 D.词义不包括语法意义。 8、有人说语言是古代文化的“活化石”,这说明语言具有: A. 交际功能。 B. 思维功能。 C. 文化录传功能。 D. 认知功能。 9、“衣领”是“衣服”的: A. 上义词。 B. 下义词。 C. 总义词。 D. 分义词。 10、转换生成语言学的代表人物是: A. 乔姆斯基。 B. 菲尔默。 C. 皮亚杰。 D. 韩礼德。 11、下列说法正确的是 A.语言是无限的,言语是有限的。 B.语言是个人的,言语是社会的。 C.语言是一般的,言语是个别的。 D.语言是具体的,言语是抽象的。 12、人类最重要的交际工具是 A.文字。 B.语言。 C.书面语。 D.手势语。 13、下列说法正确的是 A.所有的符号都有任意性。 B.有些符号有任意性。 C.只有语言符号有任意性。 D.语言符号没有任意性。 14、词汇变化比语音语法快,这体现了语言发展的 A.渐变性。 B.稳固性。 C.相关性。 D.不平衡性。 15、“小王喜欢小李”中“喜欢”和“小李” A.是组合关系。 B.是聚合关系。 C.既是聚合关系又是组合关系。 D.既非聚合关系又非组合关系。 16、语言最重要的功能是 A.思维功能。 B.标志功能。 C.交际功能。 D.认知功能。 17、日语属于 A.屈折语。 B.粘着语。 C.词根语。 D.编插语。
树形图详细讲解 1. In dicate the category of each word in the follow ing senten ces. a) The old lady sudde nly left. Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road. Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road. Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He n ever appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A 2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. b) a story about a sen time ntal girl NP Det A N a story about a sen time ntal girl c) ofte n read detective stories Qual V NP ofte n read detective stories d) the argume nt aga inst the proposals NP NP a) full of people AP full of people NP PP VP Det N
八 Det N the argume nt aga inst the proposals
syntax 1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences. a) The old lady suddenly left. Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road. Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road. Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A 2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. a) full of people AP A P N full of people b) a story about a sentimental girl NP NP PP Det A N a story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective stories VP Qual V NP
A N often read detective stories d) the argument against the proposals NP NP PP Det N the argument against the proposals e) move towards the window VP V PP P Det N move towards the window 3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences. a) The jet landed. InflP(=S) NP Infl VP Det N Pst V The jet landed b) Mary became very ill. InflP(=S) NP Infl VP N Pst V AP
《语言学概论》作业参考答案 一、名词解释 1.音位:最小的可以区别意义的语音单位,通常由一簇互相不区别意义的音素构成。如|A|音位里就有前A、后A、央A等几个音素。 2.塞擦音:辅音的发音方式之一。其特点是发音时,两个发音部位紧靠在一起形成阻碍,在保持这个阻碍的同时,留出一个窄缝,让气流从窄缝中磨擦成声,最后除去这个阻碍。如:b‘p‘k‘就是。 3.递归性:语言的递归性是指,组合结构中的某个单位,可以不断地被一个同功能的短语替换,从而使基本结构里的某个扩展为非常复杂的结构,但其作用仍然等于原始项。也即语言的整体结构与基本框架不变。语法结构的这种性质,我们称之为语言结构的递归性。语言的递归性是语言结构一种非常重要的特性。如:人打倒了|敌人/凶恶的敌人/盘踞在中国大陆的敌人/曾经盘踞在中国大陆的不可以一世的敌人/曾经盘踞在中国大陆不可一世但最终被人民打倒的敌人 4.复综语:语言类型之一。这种语言的动词内有用不同的形态表示各种复杂的语法成分。多见于美洲印第安人的语言。举例。 5.自由变体:音位变体的一种类型。通常指对出现的组合条件没有硬性要求的音位变体。举例。 6.元音:音素的类型之一。即发音时气流在口腔中不受阻碍而形成的音。举例。 7.语法形式:表示语法意义方式与材料。举例。 8.词干:一个词的主要部分,词汇意义的承担者。举例。 9.音色:语音四要素之一,又叫音质,指声音的特色。由物体振动的不同形式所决定。举例。 10.塞音:辅音的发音方式之一。其特征发音时两个发音部位紧靠在一起,保持一段时间,然后突然除阻,爆破成声。也叫爆破音。举例。 11.共同语:随着社会政治经济集中,会以一种方言为基础形成共同语,以满足整个社会交际往来。共同语又叫天下通语、雅言。举例。 12.数:语法范畴之一。指是用一个词的不同形态表示出来的词语数的语法意义。在单数、复数、双数等。举例。 二、谈谈语言符号的特点 答案要点: 1.单位明晰性 2.任意性 3.结构二层性 4.开放性 5. 传授性 答:(1).语言是一种工具,即交际工具和思维工具;而思维是一种能力和过程,即人脑能动地反映客观现实的能力和过程。 (2).概念用词语表达,判断用句子表达,但概念按照逻辑规律构成的种种判断和词语按语法规则构成的啊、种种句子是有区别的。如:语言中的每个词不一定都表示一个概念,每个句子不一定都表示判断。 (3).思维过程是运用概念按照逻辑规律构成种种判断,语言运用过程则是运用词语,按照句法构成各种句子。 (4).语言是具有民族特点的,各民族都有自己的语言特点,世界上有许多种语言。但思维是各民族共同的,全人类具有共同的思维形式和思维规律。 三、试分析汉字跨越方言交际的特点与原因
树形图详细讲解 1、 Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences、 a) The old lady suddenly left、 Det A N Qual V b) The car stopped at the end of the road、 Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road、 Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature、 N Qual V Deg A 2、 The following phrases include a head, a plement, and a specifier、 Draw the appropriate tree structure for each、 a) full of people AP A P N full of people b) a story about a sentimental girl NP NP PP Det N P NP Det A N a story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective stories VP Qual V NP A N often read detective stories d) the argument against the proposals NP NP PP Det N P NP Det N the argument against the proposals e) move towards the window VP
导言 一、单项选择题 1. 普通语言学从理论上研究() A 个别民族语言的特殊规律 B 人类各种语言一般的共同规律 C 几种民族语言的一般与个别的规律 D 汉语普通话的发展规律 2. 语言学可以分为两大类别,即() A 理论语言学、应用语言学 B 汉语语言学、英语语言学 C 英语语言学、俄语语言学 D 个别语言学、一般语言学 3. 语言学概论属于() A 个别语言学的范围 B 一般语言学的范围 C 应用语言学的范围 D 汉语言学的范围 4. 结构主义语言学独特的研究方法是() A 历史比较法 B 归纳法 C 分布分析法和直接成分分析法 D 句子成分分析法 二、填空题 1. 古中国、古印度、古希腊具有悠久的历史文化传统,是语言学的三大发源地。 2. 文字、训诂、音韵是我国传统的语文学。 3. 研究语言的结构,主要是研究语音、语法、语汇三个部分。 4. 历史比较语言学的建立,标志着语言学开始走上独立发展的道路。 5. 布龙菲尔德的代表著作《语言论》,是美国结构主义语言学的奠基性著作,对美国结构主义语言学的形成、发展有重要的作用和深远的影响。 6. 索绪尔被称为现代语言学之父,其代表作《普通语言学教程》在语言学史上具有十分重要的地位。 7. 结构主义语言学派可以分为布拉格学派、哥本哈根学派、美国结构语言学派三派。 三、判断题 1. 历史比较语言学不仅标志着语言学科的独立而且为普通语言学的建立打下了坚实的基础。() 2. 我国的语文学通称“小学”。() 3. 普通语言学是以汉语普通话为研究对象的语言学分支学科。() 4. 每个人至少掌握一种语言,所以都能准确地回答“什么是语言”这个问题。() 四、名词解释
8.(c)the argument against the proposals PP NP P NP Det N Det N against the (d)already above the windows PP AdvP P NP Adv Det N already above the window
NP Infl VP Det AP N pst V PP A P NP Det AP N A huge moon hung in the black sky (C) The man examined his car carefully yeseterday S NP Infl VP Det N pst V NP AdvP Det N AdvP Adv Adv A man examined his car carefully yesterday 10.(b)Helen put on her clothes and went out S
N pst V PP Con V PP P NP P Det N Helen put on her clothes and went out c)Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics. S NP Infl VP N Pre V AP Con AP A PP A PP P NP P NP N Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics 11.(b) Gerry belives the fact that Anna fluncked the English exam. S NP Infl VP
《语言学概论》习题答案(自考,新版教材) 选择题 第一章总论 1 言语是 ×. 言论与语言×. 音义结合的符号系统√. 说话和所说的话 2 语言是一种 ×. 形式和内容相统一的视觉符号 √. 音义结合的听觉符号系统 ×. 用来交际的触觉符号系统 3 抽象思维的一般特性是 ×. 概括性、民族性×. 概念、判断、推理 ×. 固定、再现、改造√. 概括性、社会性 4 语言是思维的工具指的是 ×. 一切思维必须由语言完成 √. 主要指抽象思维和直观动作思维、形象思维的高级阶段离不开语言×. 指直观动作思维和表象思维离不开语言 5 思维的三种类型是 √. 直观动作思维、表象思维、抽象思维 ×. 概念、判断、推理 ×. 固定、再现、改造 6 语言符号的任意性是 ×. 语言符号的创造和使用总是任意的 ×. 我们可以任意理解语言的符号 √. 语言符号音义之间没有本质的联系 7 语言符号的线条性 ×. 语言符号的排列没有阶级性,象一根线条排列在一起 ×. 语言符号一个跟一个依次出现,随时间推移不分层次逐渐延伸√. 语言符号在时间的线条上逐个出现,同时不排除层次性 8 "他肯定不会来了!" 这句话强调了说者的 ×. 说话行为√. 施事行为 ×. 取效行为×. 言语行为 9汉语声调从中古到现代的"平分阴阳,入派三声"的规律是 √. 个别语言的发展规律×. 一般语言的发展规律 ×. 汉民族各种方言的发展规律 □一个民族内部共同使用的语言称为 √. 民族共同语×. 民族交际语 ×. 国际交际语 10 克里奥尔语是语言的 √. 混合×. 融合 ×. 分化×. 整化 11 语言融合的"底层"现象是 ×. 语言装置的最下面一层,即语音部分
Keys to Linguistics of Xiamen University Charpter 3 3.1.1 1. A word is characterized with the following four features: (1) A word is a sound or combination of sounds which we make voluntarily with our vocal organs. (2) A word is symbolic, i.e. it stands for something else, such as objects, happenings or ideas. (3) A word is part of the large communication system we call language. (4) Words help human beings to interact culturally with one another. 2. The relation between the sound or sound combination of a word and its meaning is almost always arbitrary. There is no logical relationship between the sound or the combination of sounds which stands for an entity (including a thing, a happening or an idea) and the entity itself. On the one hand, the same sound may stand for different entities in different languages. On the other hand, the same meaning can be represented by different sound of combination of sounds. 3. Apart from the conceptual meaning (also called "denotative", "logical" or "cognitive" meaning), a word normally has various associated meanings, including the connotative meaning, social meaning, affective meaning, reflected meaning, and collocative meaning. We can turn to the dictionary for its conceptual meaning. As for its various associated meanings, however, we have to relate the word with its context, including the linguistic context as well as the context of situation and the context of culture. 3.1.2 1. In (prep.) practice (n.), writers (n.) on (prep.) style (n.) have (primary v.) differed (full v.) a (det.) great (adj.) deal (n.) in (prep.) their (pron.) understanding (n.) of (prep.) the (det.) subject (n.), and (conj.) one (num.) source (n.) of (prep.) disagreement (n.) has (primary v.) been (full v.) the (det.) question (n.) "To (prep.) what (pron.) or whom (pron.) do (primary v.) we (pron.) attribute (full v.) style (n.)? In (prep.) the (det.) broadest (adj.) sense (n.), STYLE (n.) can (modal v.) be (primary v.) applied (full v.) to (prep.) both (adv.) spoken (adj.) and (conj.) written (adj.), both (adv.) literary (adj.) and (conj.) non-literary (adj.) varieties (n.) of (prep.) language (n.); but (conj.) by (prep.) tradition (n.), it (pron.) is (full v.) particularly (adv.) associated (full v.) with (prep.) written (adj.) literary (adj.) texts (n.), and (conj.) this (pron.) is (full v.) the (det.) sense (n.) of (prep.) the (det.) term (n.) which (pron.) will (modal v.) concern (full v.) us (pron.). 2. No. These two categories of words have different distribution in speech and writing. Lexical words denote objects, happenings, ideas and their attributes, features, and/or manners, thus relating the words with entities existing outside the text. Grammatical words, instead, denote certain grammatical meanings, thus relating one element within the text with another. In speech there are more grammatical words, while in writing there are more lexical words. Moreover, the more formal the style is, the more lexical words there are. 3. Open-class words refer to those classes of words to which we can add new words. In English, nouns, notional verbs, adjectives and adverbs belong to this category. Such words normally convey certain semantic contents and thus are also called "content words". Closed-class words refer to those classes to which new words can hardly be added. In English, closed-class words include pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, relatives, prepositions, auxiliary verbs, modal verbs and the linking verb
习题(一) 一、填空题 1、语言是人类社会的(交际)工具,而且也是(思维)的工具,这是语言的两大功能。 2、任何符号,都是由(意义)和(标记)两个方面构成的。 3、语言符号的形式是(音),语言符号的内容是(义)。 4、语言的底层是一套(音位),上层是符号和符号的序列,可以分为若干级,第一级是(语素),第二级是(词),第三级是(句子)。 5、语言体系中的一切成分都以关系为基础,语言系统中的所有符号既可以同别的符号组合,又可以被别的符号替换,这两种关系就是(组合关系)和(聚合关系)。 二、思考题 1、语言与言语的区别和联系是什么? 一方面,言语和语言有着本质的区别,另一方面,两者又有着密切的联系。 语言和言语的关系,犹如工具和工具运用的关系。 区别:语言是有限的,言语是无限的。语言是社会的,言语是个人的。 联系:言语是对语言的运用,语言存在于言语之中。 2、为什么说语言也是一种符号? 符号:符号是一个社会全体成员共同约定用来表示某种意义的记号或标记。 语言符号:语音和语义相结合的统一体。 其中,音是语言符号的物质表现形式,义是语言符号的内容。 所以说,语言也是一种符号 3、语言符号和一般符号有什么不同? 语言符号具有自身的特点: 任意性:就音义的结合来说。表现在三个方面,不同的语言可以用相同的声音表示不同的意义;不同的语言可以用不同的声音表示相同的意义;相同的语言可以用不同的声音表示相同的意义。 线条性 4、语言符号的任意性具体体现在哪些方面?既然语言符号有任意性的特点,为什么对于使用语言的人又具有强制性? 符号的任意性只是就创制符号时的情景说的,符号一旦进入交际,也就是某一语音形式与某一意义结合起来,表示某一特定的现实现象以后,它对使用的人来说就有强制性。 5、谈谈你对语言符号组合的线条性和层次性的认识。 线条性:是语言符号与符号之间的相互关系表现出来的特点,说话的时候,语言符号只能一个跟一个依次出现,在时间的线条上延伸,不能在空间上展开。
术语解释 1.语言学:语言学就是专门以语言为研究对象的一门独立的科学。语言学的任务就是研究语言的性质、功能、结构 及其运用等问题,揭示语言存在和发展的规律,使人们理解并掌握语言的理性知识。 2.语文学:语文学是从文献角度研究语言文字学科的总称。它以文献评审为主,目的在于解释、注疏和考订。 3.语言:语言是一种特殊的社会现象,它作为人类最重要的交际工具为全社会服务,它同人的思维有密切的联系, 是人区别于其他动物的本质特征之一,语言是音义结合的符号系统。 4.言语:言语是人们为了某种目的,在特定条件下发生的说话行为和说出来的话。这里的“说话行为”是指说话的 动作和过程;“说出来的话”是指一连串有意义的声音。 5.索绪尔:现代语言学的历史,是从瑞士语言学家费尔迪南·德·索绪尔开始的。索绪尔的代表作是《普通语言学 教程》。索绪尔被誉为“现代语言学之父”,《普通语言学教程》是现代语言学的奠基之作。索绪尔的语言学思想和19世纪以前的语文学最根本的区别在于:把语言看成是由各个符号之间的关系组成的有价值的结构系统。 6.布龙菲尔德:是美国描写语言学派的核心人物。他们注重语言行为的描写,而不注重语言能力的解释;着眼于语 言间的差异,而不重视语言的普遍性。其著作有《语言论》 7.乔姆斯基:1957年美国语言学家诺姆·乔姆斯基《句法结构》的出版,标志着“转换生成语法”的诞生。这一理 论是建立在理性主义的哲学基础之上的,它完全不同于建立在经验主义基础之上的美国结构主义,因此,它的出现是对当时居于主流地位的美国结构主义语言学的一大挑战,被人称作“乔姆斯基革命”。 8.菲尔墨:是格语法的代表,其代表作是1968年发表的《格辩》。他认为标准理论无法说明类似下列两个句子中名 词短语与动词短语之间的关系究竟有何区别:Thechildopensthedoor./Thekeyopensthedoor.这种名词短语与动词短语之间的功能关系只有用更深一层的语义区别才能解释清楚。 9.普通语言学:也叫“一般语言学”,它的研究对象从理论上讲应该是全世界所有的语言。普通语言学探究人类语言 的共同规律以及各种语言在结构上的共同点和一般原理。“语言学概论”课是普通语言学的入门课程。普通语言学还可以根据研究的不同侧面再分为语音学、语义学、词汇学、语法学、语用学、风格学、修辞学等各门学科。 10.符号:符号就是指代他种事物的标记。具体地说,在认识活动中人们常常用甲事物来代表乙事物,这代表乙事物 的甲事物就成了乙事物的符号。比如十字路口的信号灯就是一种符号系统。 11.语言的层级性:语言结构要素的各个组成单位,在语言这个结构系统中,并不是处在同一个平面上,而是组成一 个有层级的立体结构体系。具体地说,它可以分为单面体单位和双面体单位。而双面体单位又可分成静态层和动态层。 12.语言的结构要素:语言的结构要素可以分为不同的层面和级面。单面体单位是构成语言这个层级系统的根基,它 是由语音大小单位和语义大小单位组成的。双面体单位分两个层次,其一是语言结构系统的静态层,它是由语言结构系统中的没有进入交际的静态单位构成的,即语素、词、短语。其二是语言结构系统的动态层,它是由语言结构系统中的已经进入交际的动态单位构成的,即句子和语篇。 13.聚合关系:聚合关系是指在一定条件下,在语言链条的某一环节上,能够互相替换的具有某种相同作用的各个符 号之间形成的纵向关系。 14.表象思维:或称“形象思维”。“表象”是指事物被感觉时在脑中留下的形象,它可以凭记忆而重现。表象思维就 是思维时在头脑中唤起表象并在想象中对表象进行加工改造的思维活动。 15.抽象思维:也叫“逻辑思维”或“语言思维”。是指以语言为工具,运用逻辑形式来进行的思维活动。 16.语用学:语用学作为语言学的一门新兴的独立学科,它研究在特定情景中的特定话语,特别是研究在不同的语言 交际环境下如何理解和运用语言的过程。 17.音质:音质指声音的个性或特色,也叫音色。研究各种语言音质的情况和它在语言中的作用是语音研究的重要任 务。音质是声音的四个要素中最重要的一个,它决定于发音体振动的形式。
《语言学概论》习题答案 选择题 第一章总论 □ 言语是 ×. 言论与语言×. 音义结合的符号系统 √. 说话和所说的话 □ 语言是一种 ×. 形式和内容相统一的视觉符号 √. 音义结合的听觉符号系统 ×. 用来交际的触觉符号系统 □ 抽象思维的一般特性是 ×. 概括性、民族性×. 概念、判断、推理 ×. 固定、再现、改造√. 概括性、社会性 □ 语言是思维的工具指的是 ×. 一切思维必须由语言完成 √. 主要指抽象思维和直观动作思维、形象思维的高级阶段离不开语言×. 指直观动作思维和表象思维离不开语言 □思维的三种类型是 √. 直观动作思维、表象思维、抽象思维 ×. 概念、判断、推理 ×. 固定、再现、改造 □ 语言符号的任意性是 ×. 语言符号的创造和使用总是任意的 2 ×. 我们可以任意理解语言的符号 √. 语言符号音义之间没有本质的联系 □ 语言符号的线条性 ×. 语言符号的排列没有阶级性,象一根线条排列在一起 ×. 语言符号一个跟一个依次出现,随时间推移不分层次逐渐延伸√. 语言符号在时间的线条上逐个出现,同时不排除层次性 □ "他肯定不会来了!" 这句话强调了说者的 ×. 说话行为√. 施事行为 ×. 取效行为×. 言语行为 □ 汉语声调从中古到现代的"平分阴阳,入派三声"的规律是 √. 个别语言的发展规律×. 一般语言的发展规律 ×. 汉民族各种方言的发展规律 □ 一个民族内部共同使用的语言称为 √. 民族共同语×. 民族交际语
×. 国际交际语 □ 克里奥尔语是语言的 √. 混合×. 融合 ×. 分化×. 整化 □ 语言融合的"底层"现象是 ×. 语言装置的最下面一层,即语音部分 √. 被融合的语言的某些遗留下来的因素 ×. 被压迫的阶层 第二章语音 □ 声调决定于 √. 音高×. 音强 ×. 音长×. 音质 □ [p、t?、b、k]在发音方法上的共同特点是 ×. 清音×. 不送气 √. 塞音×. 擦音 □ 舌尖后浊擦音是 ×. [x] ×. [b] √. [?] ×. [z] □ [tA](大)是 √. 开音节×. 闭音节 ×. 元音首音节√. 辅音首音节 □ [???](血)中的[?]是 ×. 起音√. 领音 ×. 收音 □ [kai51](盖)中的[i]是 ×. 起音×. 领音 √. 收音×. 辅音 □ 普通话[?in55k?u214](辛苦)快读是[?i? 55k?u214]这种现象是×. 顺同化√. 逆同化 ×. 顺异化×. 逆异化 ×. 弱化×. 脱落 □ 普通话[f?n214pi214]快读是[f?m35pi214]这种现象是 ×. 顺同化√. 逆同化 ×. 顺异化√. 逆异化 课后答案网 阳光大学生网https://www.doczj.com/doc/be12755087.html, 4 ×. 弱化×. 脱落 □ 普通话[tou51fu214](豆腐)快读是[tou51f]这种现象是 ×. 同化×. 异化 ×. 弱化√. 脱落 ×. 增音
语言学概论试题及答案 A 一、填空题、(每空 1 分,共 15分) 1、( )的建立,使语言学摆脱了过去的附庸地位,成为一门独立发展的科学。 2 、语言符号的形式是( ),语言符号的内容是( ) 3 、一个音节可以没有起音和( ),但决不可缺少( )。 4 、方言词是诣( )。 5、附加在词根上,一般表示附加性词汇意义的语素叫( )。 6、交际的基本单位是( )。 7、语法手段可以分力两大类型:( )和( )。 8 、语言发展有两个特点:( )和( )。 9、根据语言的亲属关系对语言的分类叫做( ),也叫做( )。 10、文字起源于(记事的图画)。 二、单选题 (在本题的每一小题的备选答案中,只有一个答案是正确的,请把你认确答案的 题号,填入题干的括号内。多选不给分。每题 1分,共 15 分) 1、社会语言学属于( ) ① 理论语言学 ②广义应用语言学 ③ 普通语言学 ④狭义应用语言学 2 、元音[ ]的名称是( ) ① 舌尖后高圆唇元音 ②舌尖前高圆唇元音 ③舌尖后高不圆唇元音 ④舌尖前高不圆唇元音 3、下列汉字的读音中,包含有三合元音的是( ) ① 邮 ②欧 ③玩 ④农 4、汉语普通话音节结构( ) 5、下列词中,属于单纯词的是( ) ①玻璃 ②黑扳 ③语言 ④红旗 6、下列词中,属于复台词的是( ) ①傻子 ②席子 ③天子 ④椅子 7、下列词组中,属于多义的是( ) ①两只学生送的花瓶 ②两位学生送的花瓶 ①最长由三个音素组成 ③最长由五个音素组成 ② 最长由四个音素组成 ④ 最短由两个音素组成
8、下列词中粗体的成分,属于同音关系的是() ①杜鲁门——杜绝②负荆一负担 ③忽然--突然④花朵——浪花 9、英语的‘ foot ”(脚,单数)变为“ feet”(脚,复数)运用的语法手段是() ①附加②异根③内部屈折④重叠 10、汉语普通话中的:“卡通片”中的“卡”是一个() ①语素②音节③前缀④词 11、汉语中的:“了、着、过”在古代具有实实在在的词汇意义,到现代变成只表语义的助词,这属于() ①异化②类化③新语法范畴的形成④实词虚化 12、下列语言中属于粘着语的是() ①苗语②越南语③俄语④日语 13、在一种语言内部划脑言时,最主要的依据是() ①语法②语义③语音④词汇 14、下列词的词义,属于词义缩小的是() ①“皮”原指兽皮②“涕”原指眼泪 ③“瓦”原指一切烧好的上器④“江”原捐“长江” 15、人类几种古老文字的原始字形,都是() ①象形的②会意的③表音的④形声的 三、多选题(在本题的每一小题的备选答案中,正确答案有三个或三个以上多请把为正确答案的题号,填 入题干的括号内。少选、多选不给分。每题 2分,共 20 分) 1、根据舌位的高低,元音可分为() ①高元音②央元音③半高元音④半低元音⑤低元音 2、下列汉字的读音中多包含有辅音[飞]的有() ①男②拉③拿④拦⑤驴 3、下列词中带有前缀的是() ①老鼠②画家③阿姨④超越⑤超现实主义 4、下列词组叫,带双宾语的是() ①托你一件事②托你办件事 ③请你办这件事④借你五元钱 ⑤给你一本书