
Sliding-Window Filtering:An Ef?cient Algorithm for
Incremental Mining
Chang-Hung Lee,Cheng-Ru Lin,and Ming-Syan Chen
Department of Electrical Engineering
National T aiwan University
T aipei,T aiwan,ROC
E-mail:mschen@https://www.doczj.com/doc/f28855980.html,.tw,{chlee,owenlin}@https://www.doczj.com/doc/f28855980.html,.tw
ABSTRACT
We explore in this paper an e?ective sliding-window?ltering (abbreviatedly as SWF)algorithm for incremental mining of association rules.In essence,by partitioning a transaction database into several partitions,algorithm SWF employs a ?ltering threshold in each partition to deal with the can-didate itemset generation.Under SWF,the cumulative in-formation of mining previous partitions is selectively carried over toward the generation of candidate itemsets for the sub-sequent partitions.Algorithm SWF not only signi?cantly reduces I/O and CPU cost by the concepts of cumulative?l-tering and scan reduction techniques but also e?ectively con-trols memory utilization by the technique of sliding-window partition.Algorithm SWF is particularly powerful for e?-cient incremental mining for an ongoing time-variant trans-action database.By utilizing proper scan reduction tech-niques,only one scan of the incremented dataset is needed by algorithm SWF.The I/O cost of SWF is,in orders of mag-nitude,smaller than those required by prior methods,thus resolving the performance bottleneck.Experimental studies are performed to evaluate performance of algorithm SWF.It is noted that the improvement achieved by algorithm SWF is even more prominent as the incremented portion of the dataset increases and also as the size of the database in-creases.
Keywords
Data mining,association rules,time-variant database,in-cremental mining
1.INTRODUCTION
The importance of data mining is growing at rapid pace recently.Analysis of past transaction data can provide very valuable information on customer buying behavior,and busi-ness decisions.In essence,it is necessary to collect and ana-lyze a su?cient amount of sales data before any meaningful Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for pro?t or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the?rst page.To copy otherwise,to republish,to post on servers or to redistribute to lists,requires prior speci?c permission and/or a fee.
Copyright2001ACM X-XXXXX-XX-X/XX/XX
...$5.00.
db i, j
P
i+1
P
j
P
j+
1
db i+1, j+1
P
i
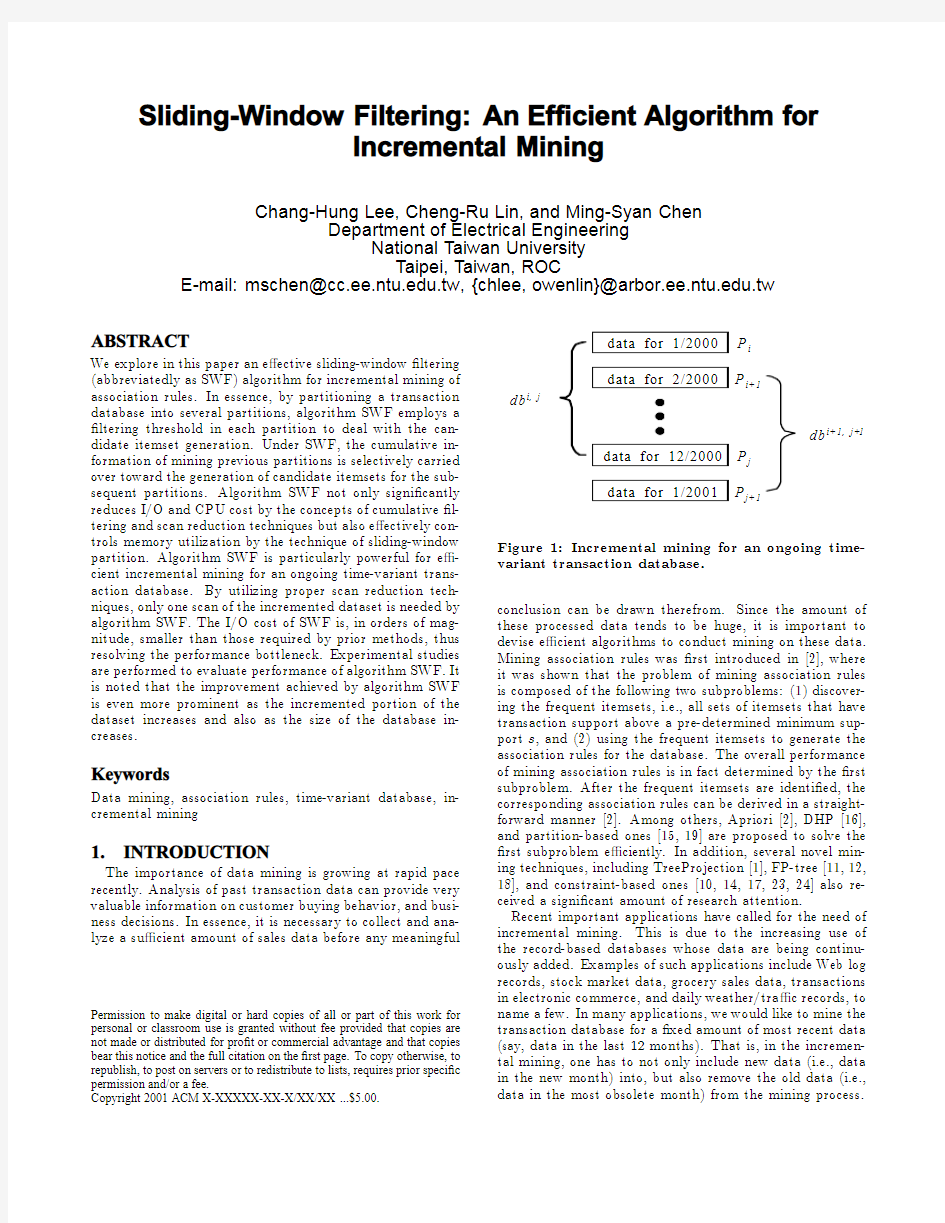
Figure1:Incremental mining for an ongoing time-variant transaction database.
conclusion can be drawn therefrom.Since the amount of these processed data tends to be huge,it is important to devise e?cient algorithms to conduct mining on these data. Mining association rules was?rst introduced in[2],where it was shown that the problem of mining association rules is composed of the following two subproblems:(1)discover-ing the frequent itemsets,i.e.,all sets of itemsets that have transaction support above a pre-determined minimum sup-port s,and(2)using the frequent itemsets to generate the association rules for the database.The overall performance of mining association rules is in fact determined by the?rst subproblem.After the frequent itemsets are identi?ed,the corresponding association rules can be derived in a straight-forward manner[2].Among others,Apriori[2],DHP[16], and partition-based ones[15,19]are proposed to solve the ?rst subproblem e?ciently.In addition,several novel min-ing techniques,including TreeProjection[1],FP-tree[11,12, 18],and constraint-based ones[10,14,17,23,24]also re-ceived a signi?cant amount of research attention.
Recent important applications have called for the need of incremental mining.This is due to the increasing use of the record-based databases whose data are being continu-ously added.Examples of such applications include Web log records,stock market data,grocery sales data,transactions in electronic commerce,and daily weather/tra?c records,to name a few.In many applications,we would like to mine the transaction database for a?xed amount of most recent data (say,data in the last12months).That is,in the incremen-tal mining,one has to not only include new data(i.e.,data in the new month)into,but also remove the old data(i.e., data in the most obsolete month)from the mining process.
Consider the example transaction database in Figure1. Note that db i,j is the part of the transaction database formed by a continuous region from partition P i to partition P j. Suppose we have conducted the mining for the transaction database db i,j.As time advances,we are given the new data of January of2001,and are interested in conducting an in-cremental mining against the new data.Instead of taking all the past data into consideration,our interest is limited to mining the data in the last12months.As a result, the mining of the transaction database db i+1,j+1is called for.Note that since the underlying transaction database has been changed as time advances,some algorithms,such as Apriori,may have to resort to the regeneration of can-didate itemsets for the determination of new frequent item-sets,which is,however,very costly even if the incremental data subset is small.On the other hand,while FP-tree-based methods[11,18]are shown to be e?cient for small databases,it is expected that their de?ciency of memory overhead due to the need of keeping a portion of database in memory,as indicated in[13],could become more severe in the presence of a large database upon which an incremental mining process is usually performed.
To the best of our knowledge,there is little progress made thus far to explicitly address the problem of incremental mining except noted below.In[8],the FUP algorithm up-dates the association rules in a database when new transac-tions are added to the database.Algorithm FUP is based on the framework of Apriori and is designed to discover the new frequent itemsets iteratively.The idea is to store the counts of all the frequent itemsets found in a previous min-ing https://www.doczj.com/doc/f28855980.html,ing these stored counts and examining the newly added transactions,the overall count of these can-didate itemsets are then obtained by scanning the original database.An extension to the work in[8]was reported in [9]where the authors propose an algorithm FUP2for up-dating the existing association rules when transactions are added to and deleted from the database.In essence,FUP2 is equivalent to FUP for the case of insertion,and is,how-ever,a complementary algorithm of FUP for the case of deletion.It is shown in[9]that FUP2outperforms Apri-ori algorithm which,without any provision for incremental mining,has to re-run the association rule mining algorithm on the whole updated database.Another FUP-based algo-rithm,call FUP2H,was also devised in[9]to utilize the hash technique for performance improvement.Furthermore,the concept of negative borders in[21]and that of UWEP,i.e., update with early pruning,in[4]are utilized to enhance the e?ciency of FUP-based algorithms.
However,as will be shown by our experimental results, the above mentioned FUP-based algorithms tend to su?er from two inherent problems,namely(1)the occurrence of a potentially huge set of candidate itemsets,and(2)the need of multiple scans of database.First,consider the problem of a potentially huge set of candidate itemsets.Note that the FUP-based algorithms deal with the combination of two sets of candidate itemsets which are independently gener-ated,i.e.,from the original data set and the incremental data subset.Since the set of candidate itemsets includes all the possible permutations of the elements,FUP-based algo-rithms may su?er from a very large set of candidate itemsets, especially from candidate2-itemsets.More importantly,in many applications,one may encounter new itemsets in the incremented dataset.While adding some new products in the transaction database,FUP-based algorithms will need to resort to multiple scans of database.Speci?cally,in the presence of a new frequent itemset L k generated in the data subset,k scans of the database are needed by FUP-based algorithms in the worst case.That is,the case of k=8 means that the database has to be scanned8times,which is very costly,especially in terms of I/O cost.The problem of a large set of candidate itemsets will hinder an e?ective use of the scan reduction technique[16]by an FUP-based algorithm.
To remedy these problems,we shall devise in this paper an algorithm based on sliding-window?ltering(abbreviat-edly as SWF)for incremental mining of association rules.In essence,by partitioning a transaction database into several partitions,algorithm SWF employs a?ltering threshold in each partition to deal with the candidate itemset genera-tion.For ease of exposition,the processing of a partition is termed a phase of processing.Under SWF,the cumulative information in the prior phases is selectively carried over to-ward the generation of candidate itemsets in the subsequent phases.After the processing of a phase,algorithm SWF outputs a cumulative?lter,denoted by CF,which consists of a progressive candidate set of itemsets,their occurrence counts and the corresponding partial support required.As will be seen,the cumulative?lter produced in each process-ing phase constitutes the key component to realize the incre-mental mining.An illustrative example for the operations of SWF is presented in Section3.1and a detailed description of algorithm SWF is given in Section3.2.It will be seen that algorithm SW F proposed has several important ad-vantages.First,with employing the prior knowledge in the previous phase,SWF is able to reduce the amount of candi-date itemsets e?ciently which in turn reduces the CPU and memory overhead.The second advantage of SWF is that owing to the small number of candidate sets generated,the scan reduction technique[16]can be applied e?ciently.As a result,only one scan of the ongoing time-variant database is required.As will be validated by our experimental results, this very advantage of SWF enables SWF to signi?cantly outperform FUP-based algorithms.The third advantage of SWF is the capability of SWF to avoid the data skew in na-ture.As mentioned in[15],such instances as severe whether conditions may cause the sales of some items to increase rapidly within a short period of time.The performance of SWF will be less a?ected by the data skew since SWF em-ploys the cumulative information for pruning false candidate itemsets in the early stage.
Extensive experiments are performed to assess the per-formance of SWF.As shown in the experimental results, SWF produces a signi?cantly smaller amount of candidate 2-itemsets than prior algorithms.In fact,the number of the candidate itemsets C k s generated by SW F approaches to its theoretical minimum,i.e.,the number of frequent k-itemsets,as the value of the minimal support increases.It is shown by our experiments that SWF in general signi?cantly outperforms FUP-based algorithms.Explicitly,the execu-tion time of SWF is,in orders of magnitude,smaller than those required by prior algorithms.Sensitivity analysis on various parameters of the database is also conducted to pro-vide many insights into algorithm SWF.The advantage of SWF becomes even more prominent not only as the amount of incremented dataset increases but also as the size of the database increases.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.Prelimi-naries and related works are given in Section2.Algorithm
SW F is described in Section3.Performance studies on
various schemes are conducted in Section4.This paper
concludes with Section5.
2.PRELIMINARIES
Let I={i1,i2,...,i m}be a set of literals,called items.Let D be a set of transactions,where each transaction T is a set
of items such that T?I.Note that the quantities of items
bought in a transaction are not considered,meaning that
each item is a binary variable representing if an item was
bought.Each transaction is associated with an identi?er,
called TID.Let X be a set of items.A transaction T is said to contain X if and only if X?T.An association rule is an
implication of the form X=?Y,where X?I,Y?I and
X T Y=φ.The rule X=?Y holds in the transaction set D with confidence c if c%of transactions in D that contain
X also contain Y.The rule X=?Y has support s in the
transaction set D if s%of transactions in D contain X S Y. For a given pair of con?dence and support thresholds,the problem of mining association rules is to?nd out all the association rules that have con?dence and support greater than the corresponding thresholds.This problem can be reduced to the problem of?nding all frequent itemsets for the same support threshold[2].
Most of the previous studies,including those is[2,5,8,
16,20,22],belong to Apriori-like approaches.Basically,an
Apriori-like approach is based on an anti-monotone Apriori
heuristic[2],i.e.,if any itemset of length k is not frequent
in the database,its length(k+1)super-itemset will never be frequent.The essential idea is to iteratively generate the set of candidate itemsets of length(k+1)from the set of frequent itemsets of length k(for k≥1),and to check their corresponding occurrence frequencies in the database.As a result,if the largest frequent itemset is a j-itemset,then an Apriori-like algorithm may need to scan the database up to (j+1)times.
In Apriori-like algorithms,C3is generated from L2?L2.In
fact,a C2can be used to generate the candidate3-itemsets.
This technique is referred to as scan reduction in[6].Clearly,
a C03generated from C2?C2,instead of from L2?L2,will have a size greater than|C3|where C3is generated from L2?L2.However,if|C03|is not much larger than|C3|,and both C2and C3can be stored in main memory,we can ?nd L2and L3together when the next scan of the database is performed,thereby saving one round of database scan. It can be seen that using this concept,one can determine all L k s by as few as two scans of the database(i.e.,one initial scan to determine L1and a?nal scan to determine all other frequent itemsets),assuming that C0k for k≥3is generated from C0k?1and all C0k for k>2can be kept in the memory.In[7],the technique of scan-reduction was utilized and shown to result in prominent performance improvement.
3.SWF:INCREMENTAL MINING WITH
SLIDING-WINDOW FILTERING
In essence,by partitioning a transaction database into sev-eral partitions,algorithm SWF employs a?ltering threshold in each partition to deal with the candidate itemset gen-eration.As described earlier,under SWF,the cumulative information in the prior phases is selectively carried over to-
Figure2:An illustrative transaction database ward the generation of candidate itemsets in the subsequent phases.In the processing of a partition,a progressive candi-date set of itemsets is generated by SWF.Explicitly,a pro-gressive candidate set of itemsets is composed of the follow-ing two types of candidate itemsets,i.e.,(1)the candidate itemsets that were carried over from the previous progressive candidate set in the previous phase and remain as candidate itemsets after the current partition is taken into consider-ation(Such candidate itemsets are called typeαcandidate itemsets);and(2)the candidate itemsets that were not in the progressive candidate set in the previous phase but are newly selected after only taking the current data partition into account(Such candidate itemsets are called typeβcan-didate itemsets).As such,after the processing of a phase, algorithm SWF outputs a cumulative?lter,denoted by CF, which consists of a progressive candidate set of itemsets, their occurrence counts and the corresponding partial sup-port required.With these design considerations,algorithm SWF is shown to have very good performance for incremen-tal mining.In Section3.1,an illustrative example of SWF is presented.A detailed description of algorithm SWF is given in Section3.2.
3.1An example of incremental mining by SWF Algorithm SW F proposed can be best understood by the illustrative transaction database in Figure2and Figure3 where a scenario of generating frequent itemsets from a transaction database for the incremental mining is given. The minimum transaction support is assumed to be s= 40%.Without loss of generality,the incremental mining problem can be decomposed into two procedures:
1.Preprocessing procedure:This procedure deals with mining on the original transaction database.
2.Incremental procedure:The procedure deals with the update of the frequent itemsets for an ongoing time-variant transaction database.
The preprocessing procedure is only utilized for the ini-tial mining of association rules in the original database,e.g., db1,n.For the generation of mining association rules in db2,n+1,db3,n+2,db i,j,and so on,the incremental proce-dure is employed.Consider the database in Figure2.As-sume that the original transaction database db1,3is seg-mented into three partitions,i.e.,{P1,P2,P3},in the pre-
{A }, {B }, {C }, {D }, {E }, {F }, {B D }, {B E }, {D E }
C a n d id a te s in d b 1,3
:
{A }, {B }, {C }, {D }, {E }, {F }, {B D }, {B E }, {D E }, {D F }, {E F }, {B D E }, {D E F }
L a rg e Item s ets in d b 2,4
:
{A }, {B }, {C }, {D }, {E }, {F }, {A B }, {A C }, {B C }, {B D }, {B E }, {A B C }
L a rg e Item s ets in d b 1,3
:
{A }, {B }, {C }, {D }, {E }, {F }, {A B }, {A C }, {B C }, {B E }C a n d id a te s in d b 1,3:
Figure 3:Large itemsets generation for the incre-mental mining with SWF
processing procedure.Each partition is scanned sequentially for the generation of candidate 2-itemsets in the ?rst scan of the database db 1,3.After scanning the ?rst segment of 3transactions,i.e.,partition P 1,2-itemsets {AB,AC,AE,AF,BC,BE,CE}are generated as shown in Figure 3.In addition,each potential candidate itemset c ∈C 2has two attributes:(1)c.start which contains the identity of the starting partition when c was added to C 2,and (2)c.count which contains the number of occurrences of c since c was added to C 2.Since there are three transactions in P 1,the partial minimal support is d 3?0.4e =2.Such a partial minimal support is called the ?ltering threshold in this pa-per.Itemsets whose occurrence counts are below the ?lter-ing threshold are removed.Then,as shown in Figure 3,only {AB,AC,BC},marked by “°”,remain as candidate item-sets (of type βin this phase since they are newly generated)whose information is then carried over to the next phase of processing.
Similarly,after scanning partition P 2,the occurrence counts of potential candidate 2-itemsets are recorded (of type αand type β).From Figure 3,it is noted that since there are also 3transactions in P 2,the ?ltering threshold of those item-sets carried out from the previous phase (that become type αcandidate itemsets in this phase)is d (3+3)?0.4e =3and that of newly identi ?ed candidate itemsets (i.e.,type βcandidate itemsets)is d 3?0.4e =2.It can be seen from Figure 3that we have 5candidate itemsets in C 2after the processing of partition P 2,and 3of them are type αand 2of them are type β.
Finally,partition P 3is processed by algorithm SW F .The resulting candidate 2-itemsets are C 2={AB,AC,BC,BD,BE }as shown in Figure 3.Note that though appearing in the previous phase P 2,itemset {AD }is removed from C 2once P 3is taken into account since its occurrence count does
not meet the ?ltering threshold then,i.e.,2<3.However,we do have
one new itemset,i.e.,BE ,which joins the C 2as a type βcandidate itemset.Consequently,we have 5candidate 2-itemsets generated by SWF,and 4of them are of type αand one of them is of type β.Note that instead of 15candidate itemsets that would be generated if Apriori were used 1,only 5candidate 2-itemsets are generated by SW F .
After generating C 2from the ?rst scan of database db 1,3,we employ the scan reduction technique and use C 2to gen-erate C k (k =2,3,...,n ),where C n is the candidate last -itemsets.It can be veri ?ed that a C 2generated by SWF can be used to generate the candidate 3-itemsets and its sequen-tial C 0k ?1can be utilized to generate C 0k .Clearly,a C 0
3gen-erated from C 2?C 2,instead of from L 2?L 2,will have a size greater than |C 3|where C 3is generated from L 2?L 2.How-ever,since the |C 2|generated by SWF is very close to the
theoretical minimum,i.e.,|L 2|,the |C 0
3|is not much larger
than |C 3|.Similarly,the |C 0k |is close to |C k |.All C 0
k
can be stored in main memory,and we can ?nd L k (k =1,2,...,n )together when the second scan of the database db 1,3is per-formed.Thus,only two scans of the original database db 1,3are required in the preprocessing step.In addition,instead of recording all L k s in main memory,we only have to keep C 2in main memory for the subsequent incremental mining of an ongoing time variant transaction database.Table 1:Meanings of symbols used
The merit of SWF mainly lies in its incremental proce-dure.As depicted in Figure 3,the mining database will be moved from db 1,3to db 2,4.Thus,some transactions,i.e.,t 1,t 2,and t 3,are deleted from the mining database and other transactions,i.e.,t 10,t 11,and t 12,are added.For ease of ex-position,this incremental step can also be divided into three sub-steps:(1)generating C 2in D ?=db 1,3???,(2)gener-ating C 2in db 2,4=D ?+?+and (3)scanning the database db 2,4only once for the generation of all frequent itemsets L k .In the ?rst sub-step,db 1,3???=D ?,we check out the pruned partition P 1,and reduce the value of c.count and set c.start =2for those candidate itemsets c where c.start =1.It can be seen that itemsets {AB,AC,BC}were removed.Next,in the second sub-step,we scan the incremental trans-actions in P 4.The process in D ?+?+=db 2,4is similar to the operation of scanning partitions,e.g.,P 2,in the pre-processing step.Three new itemsets,i.e.,DE,DF,EF,join the C 2after the scan of P 4as type βcandidate itemsets.
Finally,in the third sub-step,we use C 2to generate C 0
k
as mentioned above.With scanning db 2,4
only once,SWF ob-1
The details of the execution procedure by Apriori are omit-ted here.Interested readers are referred to [3].
tains frequent itemsets {A,B,C,D,E,F,BD,BE,DE}in db 2,4.
3.2Algorithm of SWF
For ease exposition,the meanings of various symbols used are given in Table 1.The preprocessing procedure and the incremental procedure of algorithm SWF are described in Section 3.2.1and Section 3.2.2,respectively.
3.2.1Preprocessing procedure of SWF
The preprocessing procedure of Algorithm SWF is out-lined below.Initially,the database db 1,n is partitioned into n partitions by executing the preprocessing procedure (in Step 2),and CF,i.e.,cumulative ?lter,is empty (in Step
3).Let C i,j
2be the set of progressive candidate 2-itemsets generated by database db i,j .It is noted that instead of keep-ing L k s in the main memory,algorithm SWF only records C 1,n
2
which is generated by the preprocessing procedure to be used by the incremental procedure.
Preprocessing procedure of Algorithm SWF 1.n =Number of partitions;2.|db 1,n
|=P k =1,n |P k |;3.CF =?;
4.begin for k =1to n //1st scan of db 1,n
5.begin for each 2-itemset I ∈P k
6.if (I /∈CF )
7.I.count =N p k (I );
8.I.start =k ;
9.if (I.count ≥s ?|P k |)10.CF =CF ∪I ;11.if (I ∈CF )12.I.count =I.count +N p k (I );13.if (I.count 17.select C 1,n 2from I where I ∈CF ; 18.keep C 1,n 2in main memory;19.h =2;//C 1is given 20.begin while (C 1,n h =?)//Database scan reduction 21.C 1,n h +1=C 1,n h ?C 1,n h ;22.h =h +1;23.end 24.refresh I.count =0where I ∈C 1,n h ;25.begin for k =1to n //2nd scan of db 1,n 26.for each itemset I ∈C 1,n h 27.I.count =I.count +N p k (I );28.end 29.for each itemset I ∈C 1,n h 30.if (I.count ≥d s ?|db 1,n |e )31.L h =L h ∪I ;32.end 33.return L h ; From Step 4to Step 16,the algorithm processes one par-tition at a time for all partitions.When partition P i is pro-cessed,each potential candidate 2-itemset is read and saved to CF.The number of occurrences of an itemset I and its starting partition are recorded in I.count and I.start ,re-spectively.An itemset,whose I.count ≥d s ?P m =I.start,k |P m |e , will be kept in CF.Next,we select C 1,n 2from I where I ∈CF and keep C 1,n 2in main memory for the subsequent incremen-tal procedure.With employing the scan reduction technique from Step 19to Step 23,C 1,n h s (h ≥3)are generated in main memory.After refreshing I.count =0where I ∈C 1,n h ,we begin the last scan of database for the preprocessing proce-dure from Step 25to Step 28.Finally,those itemsets whose I.count ≥d s ?|db 1,n |e are the frequent itemsets. 3.2.2Incremental procedure of SWF As shown in Table 1,D ?indicates the unchanged portion of an ongoing transaction database.The deleted and added portions of an ongoing transaction database are denoted by 4?and 4+,respectively.It is worth mentioning that the sizes of 4+and 4?,i.e.,|4+|and |4?|respectively,are not required to be the same.The incremental procedure of SWF is devised to maintain frequent itemsets e ?ciently and e ?ectively.This procedure is outlined below. Incremental procedure of Algorithm SWF 1.Original database =db m,n ;2.New database =db i,j ;3.Database removed 4?=P k =m,i ?1P k ; 4.Database database 4+=P k =n +1,j P k ; 5.D ?=P k =i,n P k ; 6.db i,j =db m,n ?4?+4+; 7.loading C m,n 2 of db m,n into CF where I ∈C m,n 2;8.begin for k =m to i ?1//one scan of 4? 9.begin for each 2-itemset I ∈P k 10.if (I ∈CF and I.start ≤k )11.I.count =I.count ?N p k (I );12.I.start =k +1;13.if (I.count 17.begin for k =n +1to j //one scan of 4+18.begin for each 2-itemset I ∈P k 19.if (I /∈CF )20.I.count =N p k (I );21.I.start =k ;22.if (I.count ≥s ?|P k |)23.CF =CF ∪I ;24.if (I ∈CF )25.I.count =I.count +N p k (I );26.if (I.count 30.select C i,j 2from I where I ∈CF ; 31.keep C i,j 2in main memory 32.h =2//C 1is well known. 33.begin while (C i,j h =?)//Database scan reduction 34.C i,j h +1=C i,j h ?C i,j h ;35.h =h +1;36.end 37.refresh I.count =0where I ∈C i,j h ;38.begin for k =i to j //only one scan of db i,j 39.for each itemset I ∈C i,j h 40.I.count =I.count +N p k (I );41.end 42.for each itemset I ∈C i,j h 43.if (I.count ≥d s ?|db i,j |e )44.L h =L h ∪I ;45.end 46.return L h ; As mentioned before,this incremental step can also be divided into three sub-steps:(1)generating C 2in D ?=db 1,3???,(2)generating C 2in db 2,4=D ?+?+and (3)scanning the database db 2,4only once for the genera-tion of all frequent itemsets L k .Initially,after some up-date activities,old transactions 4?are removed from the database db m,n and new transactions 4+are added (in Step 6).Note that 4??db m,n .Denote the updated database as db i,j .Note that db i,j =db m,n ?4?+4+.We de-note the unchanged transactions by D ?=db m,n ???= db i,j ??+.After loading C m,n 2of db m,n into CF where I ∈C m,n 2 ,we start the ?rst sub-step,i.e.,generating C 2in D ?=db m,n ???.This sub-step tries to reverse the cu-mulative processing which is described in the preprocessing procedure.From Step 8to Step 16,we prune the occur-rences of an itemset I ,which appeared before partition P i ,by deleting the value I.count where I ∈CF and I.start new potential C i,j 2in db i,j =D ?+4+and employs the scan reduction technique to generate C i,j h s from C i,j 2.Fi-nally,to generate new L k s in the updated database,we scan db i,j for only once in the incremental procedure to maintain frequent itemsets.Note that C i,j 2is kept in main memory for the next generation of incremental mining. Note that SWF is able to ?lter out false candidate itemsets in P i with a hash table.Same as in [16],using a hash table to prune candidate 2-itemsets,i.e.,C 2,in each accumulative ongoing partition set P i of transaction database,the CPU and memory overhead of SWF can be further reduced. Table 2:Meanings of various parameters 4.EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES To assess the performance of algorithm SWF,we per-formed several experiments on a computer with a CPU clock rate of 450MHz and 512MB of main memory.The trans-action data resides in the NTFS ?le system and is stored on a 30GB IDE 3.5”drive with a measured sequential through-put of 10MB/second.The simulation program was coded in C++.The methods used to generate synthetic data are described in Section 4.1.The performance comparison of SWF,FUP 2and Apriori is presented in Section 4.2.Section 4.3shows the I/O and CPU overhead among SWF,FUP 2H and Apriori.Results on scaleup experiments are presented in Section 4.4. 4.1Generation of synthetic workload For obtaining reliable experimental results,the method to generate synthetic transactions we employed in this study is similar to the ones used in prior works [4,8,16,21].Ex-plicitly,we generated several di ?erent transaction databases from a set of potentially frequent itemsets to evaluate the Figure 4:Relative performance performance of SWF.These transactions mimic the transac-tions in the retailing environment.Note that the e ?ciency of algorithm SWF has been evaluated by some real databases,such as Web log records and grocery sales data.However,we show the experimental results from synthetic transaction data so that the work relevant to data cleaning,which is in fact application-dependent and also orthogonal to the in-cremental technique proposed,is hence omitted for clarity.Further,more sensitivity analysis can then be conducted by using the synthetic transaction data.Each database con-sists of |D |transactions,and on the average,each trans-action has |T |items.Table 2summarizes the meanings of various parameters used in the experiments.The mean of the correlation level is set to 0.25for our experiments. Recall that the sizes of |?+|and |??|are not required to be the same for the execution of SWF.Without loss of generality,we set |d |=|?+|=|??|for simplicity.Thus,by denoting the original database as db 1,n and the new mining database as db i,j ,we have |db i,j |=|db 1,n ???+?+|=|D|,where ??=db 1,i ?1and ?+=db n +1,j .In the following,we use the notation T x ?Iy ?Dm ?dn to represent a database in which D =m thousands,d =n thousands,|T |=x ,and |I |=y .We compare relative performance of three methods,i.e.,Apriori,FUP-based algorithms and SWF. As mentioned before,without any provision for incre-mental mining,Apriori algorithm has to re-run the associa-tion rule mining algorithm on the whole updated database.As reported in [8,9],with reducing the candidate item-sets,FUP-based algorithms outperform Apriori.As will be shown by our experimental results,with the sliding win-dow technique that carries cumulative information selec-tively,the execution time of SWF is,in orders of magnitude,smaller than those required by prior algorithms.In order to Figure5:I/O cost performance Figure6:Reduction on candidate itemsets when the dataset T10-I4-D100-d10was used conduct our experiments on a database of size db i,j with an increment of?+and a removal of??,a database of db1,j is?rst generated and then db1,i?1,db1,n,db n+1,j,and db i,j are produced separately. 4.2Experiment one:Relative performance We?rst conducted several experiments to evaluate the relative performance of Apriori,FUP2and SWF.For inter-est of space,we only report the results on|L|=2000and N=10000in the following experiments.Figure4shows the relative execution times for the three algorithms as the minimum support threshold is decreased from1%support to 0.1%support.When the support threshold is high,there are only a limited number of frequent itemsets produced.How-ever,as the support threshold decreases,the performance di?erence becomes prominent in that SWF signi?cantly out-performs both FUP2and Apriori.As shown in Figure4, SWF leads to prominent performance improvement for var-ious sizes of|T|,|I|and|d|.Explicitly,SWF is in orders of magnitude faster than FUP2,and the margin grows as the minimum support threshold decreases.Note that from our experimental results,the di?erence between FUP2and Apriori is consistent with that observed in[9].In fact,SWF outperforms FUP2and Apriori in both CPU and I/O costs, which are evaluated next. 4.3Experiment two:Evaluation of I/O and CPU overhead To evaluate the corresponding of I/O cost,same as in [18],we assume that each sequential read of a byte of data consumes one unit of I/O cost and each random read of Figure7:Scaleup performance with the execution time ratio between SWF and FUP a byte of data consumes two units of I/O cost.Figure5 shows the number of database scans and the I/O costs of Apriori,FUP2H,i.e.,hash-type FUP in[9],and SWF over data sets T10?I4?D100?d10.As shown in Figure5, SWF outperforms Apriori and FUP2H where without loss of generality a hash table of250thousand entries is employed for those methods.Note that the large amount of database scans is the performance bottleneck when the database size does not?t into main memory.In view of that,SWF is advantageous since only one scan of the updated database is required,which is independent of the variance in minimum supports. As explained before,SWF substantially reduces the num- ber of candidate itemsets generated.The e?ect is particu-larly important for the candidate2-itemsets.The experi-mental results in Figure6show the candidate itemsets gen-erated by Apriori,FUP2H,and SWF across the whole pro-cessing on the datasets T10?I4?D100?d10with minimum support threshold s=0.1%.As shown in Figure6,SWF leads to a99%candidate reduction rate in C2when being compared to Apriori,and leads to a93%candidate reduc-tion rate in C2when being compared to FUP2H.Similar phenomena were observed when other datasets were used. This feature of SWF enables it to e?ciently reduce the CPU and memory overhead.Note that the number of candidate 2-itemsets produced by SWF approaches to its theoretical minimum,i.e.,the number of frequent2-itemsets.Recall that the C3in either Apriori or FUP2H has to be obtained by L2due to the large size of their C2.As shown in Fig-ure6,the value of|C k|(k≥3)is only slightly larger than that of Apriori or FUP2H,even though SWF only employs C2to generate C k s,thus fully exploiting the bene?t of scan reduction. 4.4Experiment three:Scaleup on the incre- mental portion To further understand the impact of|d|to the relative per- formance of algorithms SWF and FUP-based algorithms,we conduct the scaleup experiments for both SWF and FUP2 with two minimum support thresholds0.2%and0.4%.The results are shown in Figure7where the value in y-axis corre-sponds to the ratio of the execution time of SWF to that of FUP2.Figure7shows the execution-time-ratio for di?erent values of|d|.It can be seen that since the size of|d|has less in?uence on the performance of SWF,the execution-time- ratio becomes smaller with the growth of the incremental transaction number|d|.This also implies that the advan-tage of SWF over FUP2becomes even more prominent as the amount of incremental portion increases. 5.CONCLUSION We explored in this paper an e?cient sliding-window?l-tering algorithm for incremental mining of association rules. Algorithm SWF not only signi?cantly reduces I/O and CPU cost by the concepts of cumulative?ltering and scan reduc-tion techniques but also e?ectively controls memory utiliza-tion by the technique of sliding-window partition.Extensive simulations have been performed to evaluate performance of algorithm SWF.With proper sampling and partitioning methods,the technique devised in this paper can be applied to progressive mining. Acknowledgment The authors are supported in part by the Ministry of Educa-tion Project No.89-E-FA06-2-4-7and the National Science Council,Project No.NSC89-2219-E-002-028and NSC89-2218-E-002-028,Taiwan,Republic of China. 6.REFERENCES [1]R.Agarwal,C.Aggarwal,and V.V.V.Prasad.A Tree Projection Algorithm for Generation of Frequent Itemsets.Jornal of Parallel and Distributed Computing(Special Issue on High Performance Data Mining),2000. [2]R.Agrawal,T.Imielinski,and A.Swami.Mining Association Rules between Sets of Items in Large Databases.Proc.of ACM SIGMOD,pages207—216, May1993. [3]R.Agrawal and R.Srikant.Fast Algorithms for Mining Association Rules in Large Databases.Proc.of the20th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases,pages478—499,September1994. [4]N.F.Ayan,A.U.Tansel,and E.Arkun.An E?cient Algorithm to Update Large Itemsets with Early Pruning.Proc.of1999Int.Conf.on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining,1999. [5]S.Brin,R.Motwani,J.D.Ullman,and S.Tsur. Dynamic Itemset Counting and Implication Rules for Market Basket Data.ACM SIGMOD Record, 26(2):255—264,May1997. [6]M.-S.Chen,J.Han,and P.S.Yu.Data Mining:An Overview from Database Perspective.IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 8(6):866—883,December1996. [7]M.-S.Chen,J.-S.Park,and P.S.Yu.E?cient Data Mining for Path Traversal Patterns.IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 10(2):209—221,April1998. [8]D.Cheung,J.Han,V.Ng,and C.Y.Wong. Maintenance of Discovered Association Rules in Large Databases:An Incremental Updating Technique. Proc.of1996Int’l Conf.on Data Engineering,pages 106—114,February1996. [9]D.Cheung,S.D.Lee,and B.Kao.A General Incremental Technique for Updating Discovered Association Rules.Proc.International Conference On Database Systems For Advanced Applications,April 1997. [10]J.Han,https://www.doczj.com/doc/f28855980.html,kshmanan,and R.T.Ng. Constraint-Based,Multidimensional Data Mining. COMPUTER(special issues on Data Mining),pages 46—50,1999. [11]J.Han and J.Pei.Mining Frequent Patterns by Pattern-Growth:Methodology and Implications.ACM SIGKDD Explorations(Special Issue on Scaleble Data Mining Algorithms),December2000. [12]J.Han,J.Pei,B.Mortazavi-Asl,Q.Chen,U.Dayal, and M.-C.Hsu.FreeSpan:Frequent pattern-projected sequential pattern mining.Proc.of2000Int.Conf.on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining,pages 355—359,August2000. [13]J.Hipp,U.Güntzer,and G.Nakhaeizadeh. Algorithms for association rule mining—a general survey and comparison.SIGKDD Explorations, 2(1):58—64,July2000. [14]https://www.doczj.com/doc/f28855980.html,kshmanan,R.Ng,J.Han,and A.Pang. Optimization of Constrained Frequent Set Queries with2-Variable Constraints.Proc.of1999 ACM-SIGMOD Conf.on Management of Data,pages 157—168,June1999. [15]J.-L.Lin and M.H.Dunham.Mining Association Rules:Anti-Skew Algorithms.Proc.of1998Int’l Conf.on Data Engineering,pages486—493,1998. [16]J.-S.Park,M.-S.Chen,and https://www.doczj.com/doc/f28855980.html,ing a Hash-Based Method with Transaction Trimming for Mining Association Rules.IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,9(5):813—825, October1997. [17]J.Pei and J.Han.Can We Push More Constraints into Frequent Pattern Mining?Proc.of2000Int. Conf.on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, August2000. [18]J.Pei,J.Han,and https://www.doczj.com/doc/f28855980.html,kshmanan.Mining Frequent Itemsets with Convertible Constraints.Proc. of2001Int.Conf.on Data Engineering,2001. [19]A.Savasere,E.Omiecinski,and S.Navathe.An E?cient Algorithm for Mining Association Rules in Large Databases.Proc.of the21th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases,pages432—444, September1995. [20]R.Srikant and R.Agrawal.Mining Generalized Association Rules.Proc.of the21th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases,pages407—419, September1995. [21]S.Thomas,S.Bodagala,K.Alsabti,and S.Ranka.An E?cient Algorithm for the Incremental Updation of Association Rules in Large Databases.Proc.of1997 Int.Conf.on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 1997. [22]H.Toivonen.Sampling Large Databases for Association Rules.Proc.of the22th VLDB Conference,pages134—145,September1996. [23]A.K.H.Tung,J.Han,https://www.doczj.com/doc/f28855980.html,kshmanan,and R.T.Ng.Constraint-Based Clustering in Large Databases.Proc.of2001Int.Conf.on Database Theory,January2001. [24]K.Wang,Y.He,and J.Han.Mining Frequent Itemsets Using Support Constraints.Proc.of2000 Int.Conf.on Very Large Data Bases,September2000. 福州格致中学2014-2015学年第一学段 高一英语《必修一》模块考试 第二部分:英语知识运用 单项填空 从每题所给的A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出可以填入空白处的最佳答案,并在答题卡上将该选项涂黑。 21.In _______ distance is a tall tree which is said to have ______ history of over 500 years. A. the; a B. /; / C. a; a D. the; / 22.--- Look! The telephone is broken. Someone damaged it _______ purpose. --- That may be right. But perhaps it was broken ________ accident. A. on; on B. on; by C. by; by D. by; on 23.It might be very difficult to find _______ of the information. A. cause B. resource C. source D. course 24. Shall we go there by bus or by taxi? The ______ seems to be quicker. A. late B. latter C. later D. lately 25. After living in the United States for fifty years, he returned to the small town where he ______. A. brought up B. grew up C. gave up D. turned up 26. The engine of the ship was out of order and the bad weather ________ the helplessness of the crew(船员) at sea. A. added to B. added up to C. added up D. was added to 27. --- Daddy, I don’t want to go to Jimmy’s birthday. --- You had better go. ______ you make a promise, you have to keep it. A. Even B. Once C. Unless D. In case 28. --- Won’t you stay for lunch? --- No, thanks, I _______ my uncle at the airport at 10:30. A. met B. have met C. meet D. am meeting 29. ________ out for food, Some work in the nest as guards or workers. A. All the bees not go B. Both the bees don’t go C. Not all the bees go D. All the bees go 30. The old town has narrow streets and small houses _______ are built close to each other. A. they B. where C. what D. that 31. --- Don’t you know our town at all? --- No, It is the first time I _______ here. A. was B. am coming C. came D. have come 32. Can you make sure _____ the gold ring? A. where Alice had put B. where had Alice put C. where Alice has put D. where has Alice put 33. He decided to help the poor girl _______ were killed in the earthquake. A. which parents B. parents of them C. whose parents D. whom parents 34. The settlement is home to nearly to 1,000 people, many of _______ left their village homes for a better life in the city. A. whom B. which C. them D. who 35. ---We could invite John and Barbara to the Friday night party. --- Yes, _______ ? I’ll give them a call right now. A. why not B. what for C. why D. what 第二节完形填空(共20 小题;每小题一分,满分20分) 阅读下面短文,从短文后各题所给的四个选项(A,B,C,D)中选出可以填入相应空白处的最佳选项,并在答题卡上将该选项涂黑。 This little story I’m going to tell you happened when I was about 11 years old and I’II never forget it. I was at my friend Jenny’s __36__ after school one day, and we were doing (or not doing) homework.. __37__ I was there, Jenny’s mom came over to visit. I don’t remember her name__38__ what her face looked like. I just remember her hands, her voice and the__39__ she taught me. I can still see her hand __40__ for mine in our introduction. __41__ were so 尊重的素材(为人处世) 思路 人与人之间只有互相尊重才能友好相处 要让别人尊重自己,首先自己得尊重自己 尊重能减少人与人之间的摩擦 尊重需要理解和宽容 尊重也应坚持原则 尊重能促进社会成员之间的沟通 尊重别人的劳动成果 尊重能巩固友谊 尊重会使合作更愉快 和谐的社会需要彼此间的尊重 名言 施与人,但不要使对方有受施的感觉。帮助人,但给予对方最高的尊重。这是助人的艺术,也是仁爱的情操。—刘墉 卑己而尊人是不好的,尊己而卑人也是不好的。———徐特立 知道他自己尊严的人,他就完全不能尊重别人的尊严。———席勒 真正伟大的人是不压制人也不受人压制的。———纪伯伦 草木是靠着上天的雨露滋长的,但是它们也敢仰望穹苍。———莎士比亚 尊重别人,才能让人尊敬。———笛卡尔 谁自尊,谁就会得到尊重。———巴尔扎克 人应尊敬他自己,并应自视能配得上最高尚的东西。———黑格尔 对人不尊敬,首先就是对自己的不尊敬。———惠特曼 每当人们不尊重我们时,我们总被深深激怒。然而在内心深处,没有一个人十分尊重自己。———马克·吐温 忍辱偷生的人,绝不会受人尊重。———高乃依 敬人者,人恒敬之。———《孟子》 人必自敬,然后人敬之;人必自侮,然后人侮之。———扬雄 不知自爱反是自害。———郑善夫 仁者必敬人。———《荀子》 君子贵人而贱己,先人而后己。———《礼记》 尊严是人类灵魂中不可糟蹋的东西。———古斯曼 对一个人的尊重要达到他所希望的程度,那是困难的。———沃夫格纳 经典素材 1元和200元 (尊重劳动成果) 香港大富豪李嘉诚在下车时不慎将一元钱掉入车下,随即屈身去拾,旁边一服务生看到了,上前帮他拾起了一元钱。李嘉诚收起一元钱后,给了服务生200元酬金。 这里面其实包含了钱以外的价值观念。李嘉诚虽然巨富,但生活俭朴,从不挥霍浪费。他深知亿万资产,都是一元一元挣来的。钱币在他眼中已抽象为一种劳动,而劳动已成为他最重要的生存方式,他的所有财富,都是靠每天20小时以上的劳动堆积起来的。200元酬金,实际上是对劳动的尊重和报答,是不能用金钱衡量的。 富兰克林借书解怨 (尊重别人赢得朋友) 春风拂面 每每想起老师,仿佛总有一股春风从面前拂过。它那样温暖,那样和煦,像润物无声的细雨,慢慢地催开了我心底那美丽的花儿。 老师,您是否还记得那次午休?同学们都伏在课桌上睡觉,后来外面下起了雨,阵阵凉凉的风吹进教室,吹乱了您的头发,也吹乱了同学的衣裳。您正想起身做点什么,突然您好像想起了什么,又坐了下来——噢!只见您脱下了您的高跟鞋,轻轻地走到窗户边,悄悄地把每一扇窗户都关上了。啊!老师,您是怕吵醒了那些可爱的熟睡的孩子呀!老师,您知道吗?那一刻,我觉得自己就像是一个孩子,生活在母亲的怀抱。那一刻,我觉得您就像一 股春风,悄悄从我们身边吹过。 老师,您可曾想起那个炎热的下午?我们在楼梯口相遇,我道了一句“老师好”,您甜甜一笑,走过来,轻轻地拉了拉我的衣领:“热不热?”突然,您发现我的脖子上那些红肿的小疱,您关切地问:“呀!这是怎么回事,蚊子咬的吗?”我点了点头。没想到第二天早上,您就给我带来了驱蚊花露水。那一刻,我又惊讶又感动。望着同学们羡慕的眼光,我的心底仿佛拂过一缕春风,温暖而幸福。 老师,您是否记得那次晨读?同学们都在教室里认真地读书,忽然,我感觉有个身影从我身旁走过。一抬头,我才发现桌子上多了一瓶牛奶,上面还有几个有趣的字“喝了长高噢”。再朝那个身影望去——乌黑笔直的秀发飘在肩后,我知道,是老师您。 老师!您知道吗?在住校的那段时间,我时常会记起您,我时常会抱着那花露水瓶子睡觉,我时常会穿着您送我的带着香味的衣裳…… 一阵春风轻轻拂过,我仿佛又看到了您那熟悉的身影。 春风拂面 岁月是爱人的,每年,即使春已逝去,也会在某一个时候给人以春风拂面的感动。 我平时喜欢写作文,语文老师就鼓励我向报刊投稿。“我?能行吗?”看着老师坚定的眼睛,我下定了决心。但是一次又一次的石沉大海,我又开始灰心了。 “来,文章见报了……”声音温和,是语文老师。似乎早有预感,庆幸却又疑惑。我已忘了自己还死僵僵地坐在座位上。老师满脸笑容地离开了。“真没礼貌!”身旁的男生嘀咕道。这才醒悟:我,就是一个忽视了最简单的礼貌的人。 仿佛为我的坏心情应景一般,风儿大了,调皮地飞驰而过,掠走了我的微笑。上课后,老师就就一些难题向我们指点迷津。教材第110页……”黑板上显现出一行醒目的大字。还没等老师说完,我就心急火燎地开始复制克隆,笔走龙蛇。不料被老师撞见,批评了一句:“做题时要看清题目,再去对照答案……当时,真是无地自容,还是科代表呢!名不副实。这才明白:我,就是一个冒冒失失的人。 下课的时候,狂风骤起,刹那间将我无奈的寂寞卷入云层。学习上的退步,甚至让我怀疑自己就是一个超低智商的人。于是,一次次地摔跤、失落、放弃、流泪。感觉生活就是一座幽深的城堡,欲离去却始终找不着方向。可是,在晚饭时,当妈妈把熟悉的饭盒递到我手中,接着是匆忙的问候,我忘记了吃饭,那一刻,忽然感觉到如春风拂面,幸福无比。 我总是这样,预先准备了对待苦难的从容,却没学会从苦难中体验快活,总是注重自己的感受,却忽视了身边一直伴随提醒我的亲人朋友。同学的良言规劝是幸福,老师的悉心开导是幸福,亲人馈赠的欣悦是幸福……这样的幸福太多太多。 一路上,被人提醒,如沐春风。 [点评]这篇文章在选材时注重了“小处着眼”,写生活中时时处处有人提醒:忽视礼节,冒冒失失,忘记吃饭,这些琐碎的生活片段,写出了对生活深层次的感悟,紧扣“提醒”,揭示主题:原来,生活中有了提醒,是一种莫大的幸福。 春风拂面 春风,在我心目中是最纯洁、最高尚的。它从容淡定、缥缈虚无,同时又是世间自由不羁的精神所在,亦如那些从历史里缓缓走来的身影…· 那不羁的风,我想,是李白吧!他有"飞流直下三千尺,疑是银河落九天"的气魄,他有"仰天大笑出门去,我辈岂是蓬蒿人"的潇洒,他有"安能摧眉折腰事权贵,使我不得开心颜" 小学语文《想象作文》教案设计之一 小学语文《想象作文》教案设计之一 一、教学目的 1.启发学生自由地想象,培养学生的创新思维能力。 2.指导学生有序地、重点突出地、主次分明地说和写。 3.培养学生热爱学校、热爱生活、热爱科学的思想感情。 二、教学重点 启迪学生展开大胆、丰富、新奇的想象,并指导学生有序地、主次分明地说和写。 三、课前准备 1.课前学生绘制自己心目中《未来的......》构想图。 2.制作多媒体课件。 四、教学时间 二课时(第二课时为写作及讲评) 五、教学过程 第一课时 (一)导入 1.谈话:(出示课件1后)小的时候,我就曾经幻想过,如果我能够像小鸟一样,有那样一对翅膀,那该多好啊!现在你们又有怎样的想象呢?(板书:想象) 2.结合学生回答表扬“你的想象真大胆!”.“你的想象真丰富!”.“你的想象真新奇!”(教师板书:大胆.丰富.新奇) 3.小结:希望同学们能把大胆.丰富.新奇的想象,在自己的作文中体现出来。(4分钟) (二)本次作文指导经过。 1.让我们乘上宇宙飞船,穿越时空隧道,去未来看一看吧!(出示课件2)(1分钟) 2.我们还在去未来的路上,但是伟大的科学家爱因斯坦曾经说过:“想象是一切创造之源。”(出示课件3)这节课让我们用想象创设一下未来吧!同学们,今天这节课,我们就来写一写未来的......(板书:未来的......)(出示课件4)(1分钟) 1.读一下课题,你觉得可以写什么?进行讨论。(3分钟) 提示:人物、事物、军事、科技、农业、环境、体育等等。 估计可能有的题目:《未来的我》、《未来的生日》、《未来的母校》、《未来的教师》、《未来的祖国》,以及《未来的地球》、《未来的汽车》、《未来的学校》。 明确:在现实生活的基础上,随着科技发展,将来可能实现的设想或可能拥有的事物才可写。 2.我们选好了要写的题目,那么怎么来写,具体写些什么呢? 3.学习小组进行讨论,要求: 25. 第一部分听力(共两节。满分30分) 第一节(共5小题;每小题l.5分,满分7.5分) 听下面5段对话。每段对话后有一个小题,从题中所给的A、B、C三个选项中选出最佳选项,并标在试卷的相应位置。听完每段对话后,你都有l0秒钟的时间来回答有关小题和阅读下一小题。每段对话仅读一遍。 1.What is the probable relationship between the speakers? A. Father and daughter. B. Doctor and patient. C. Teacher and student. 2.Why can’t the machine work according to the woman? A.The power may have been cut off. B.There is something wrong with it. C.Both of the speakers can’t operate it. 3.What does the woman mean? A She is tired of keeping pets. B She wants to have a dog. C She won’t have a dog as a friend. 4.What can we learn from the conversation? A.The man will invite Mary to dinner. B The man will buy his daughter a gift. C.Mary has a lovely girl. 5.Which of the following does the woman like best? A. Fishing.13.Swimming.C.Climbing. 第二节(共15小题;每小题l.5分,满分22.5分) 听下面5段对话或独白。每段对话或独自后有几个小题,从题中所给的A、B、C 三个选项中选出最佳选项,并标在试卷的相应位置。听每段对话或独白前,你将有时间阅读各个小题,每小题5秒钟;听完后,各小题将给出5秒钟的作答时间。每段对话或独自读两遍。 听第6段材料。回答第6,7题。 6.What season is it now? A Spring. B Summer. C Autumn. 7.What will the speakers do? A. Drive to San Diego. B.Have take—away food in the park. C. See an outdoor movie. 听第7段材料。回答第8,9题。 8.What color is the tie the man is looking for? A. Green. B. Blue. C. Brown. 三年级下册语文第五单元作文《奇妙的想象》写作指导 一、审题 写一个想象故事。展示自己的奇妙想象,创造出属于自己的想象世界。 二、选材 写想象的故事。,而不是现实生活中的事,如矮人国的故事、大熊开面馆的故事、小狗变巨人、我有魔法了……只要是你能想到的故事都可以。 三、构思 我们以《最好玩的国王》为例进行构思,简要列出习作提纲。 开头:交代国王的爱好:微服私访。(略) 中间:微服私访时发现了一本畅销书,他大受启发,自己也写了一本书,后来这本书也非常畅销。(详) 结尾:交代畅销的原因:这本书太无聊,人们买来治疗失眠。(略) 四、表达 ①为习作起一个有趣的名字,如《播种女巫》:②大胆想象,让想象的内容神奇、有趣;③记得上自己平时积累的一些好词佳句哟! 写作素材 一、题目 《瞌睡虫多多》《小豆苗历险记》《白雪公主后传》《月亮又瘦了》 二、好词 无影无踪大摇大摆活灵活现转瞬即逝 神秘莫测窃窃私语一模一样大吃一惊 远走高飞 三、好句 开头 1.晚上,一道金光闪过,我突然发现睡在身边的妹妹变成了一个巨大的金蛋。我急坏了,怎么才能把妹妹救出来呢?把蛋砸破,可能会伤到里面的妹妹。把蛋刹开妹妹会不会变成蛋清流出来呢?我想了又想,最后决定把妹妹从蛋里孵 出来。 2.在离天河不远的地方,有三颗小星星。说来也巧,这三颗小星星是同年、同月、同日、同时生的,可它们彼此都不一样:一颗是蓝的,一颗是红的,第三颗最小,似乎没有什么颜色,只有一点儿微弱得可怜的光。 结尾 1.从此,绿森林里多了一个永久性的居民,绿森林的动物们多了一个永远的朋 友,绿森林的故事里多了一份传奇。 2.大力士风孩子回来了,呼呼吹了几口气,白烟被吹跑了,烟筒和房子被吹倒了那几个黑衣人被吹到了森林外。大树们开心地笑了。 福州格致中学2015级高一学段第一学期质量评定 高一年级第五次月考英语试卷 时间:100分钟分值120分 ★祝考试顺利★(完型填空启用备用卷题号不同答题卡区域注意区别) 第Ⅰ卷选择题(共两部分,满分70分) 第一部分阅读理解(共两节,满分40分) 第一节、完形填空(共20小题;每小题1.5分,满分30分) 阅读下面短文,从短文后所给各题的四个选项(A、B、C和D)中,选出可以填入空白处的最佳选项。 Most of us are highly aware of various channels through which we can obtain information on food safety. A majority of us have shown much __36___ in experts and authorities and taken a(n) __37___ part in science activities organized by such experts. __38_, we do not always form an accurate picture When there is __39_news about one brand, our trust in all brands or similar products tends to be __40___ . We would doubt not only the brand in __41___ but also similar brands when a safety issue (问题)_42___ in the news. At the same time,our purchase __43___ change as food safety incidents occur. We are becoming _44___ confident in domestic(国内的)food companies ,for they have done too little in publishing and sharing food safety __45__ so far. As a result ,we would turn to __46__ brands more often. Food safety incidents in China have attracted a lot of attention. As a matter of fact ,we only have a very _47__ knowledge base on the issue. In developed countries,there have been relatively _48__ measures and response system toward safety issues. Therefore, the __49___ in those countries are less likely to become over-panicked and form serious _50 about all brands. Food companies should pay more attention to our insights, listen to our voices, _51___ the opinions of experts and authorities ,have effective strategies for response _52____ various media channels, and __53___ information in time and face the public honestly. In addition ,both the government and an independent third - party should have a role to play in providing information about food companies__54___ in raw material selection, production and distribution (流通) However, this might require several years and we still need to learn more about food __55___ 36. A. respect B.enthusiasm C. distrust D. confidence 37. A. slight B. broad C. active D. natural 38. A. However B. Consequently C. Meanwhile D. Furthermore 39. A. negative B. exciting C. detailed D. special 40. A. protected B. affected C. increased D. preserved 关于春风的作文(6篇) 【第1篇】关于春风的作文:春风赞 所谓的春风,如此温柔。瞧!春风轻吻着柳枝,柳枝有节奏地摇摆着,摆动着它那细腻的腰姿,微微地吹皱了水面,偷偷地传送着花香。如此温柔、如此温柔,就像万物的母亲,无微不至地亲切体贴着万物,让万物生机勃勃地活动着。微风吹拂着千万条嫩黄色的柳枝,为它们换上了新衣裳;迎春话、牡丹花……春风吹拂着那娇媚的花儿,人们不由得分外爱惜! 一切万物只因它! 它就像一位慈祥而细心的“母亲”,她辛勤地培育着“儿女”,用她那甜美的乳汁来赋予营养给儿女,为的是什么呢?她为的是给儿女更好的东西、更好的生活和更好的体魄。儿女长大了,母亲给了他们最好的教育和贴心的爱护。如今儿女已经可以挣脱开母亲的怀抱,展翅飞翔,翱翔在天空中,那这些功劳归功于谁呢?一切都是母亲在儿女的背后默默支持的结果。 春风仿佛是一种生命的动力,它可以唤醒万物,也可以成为人的力量。春风扑面而来,使我想起了“一年之季在于春”春给人带来了新的一年,新的希望,新的人生目标……一阵春风吹来,我的头脑顿时清醒了,明白了人不仅要学,还要懂得运用。用春风来唤醒自己心中的渴望,让它告诉自己应该努力发奋,为自己的渴望而发奋实现 这美好的愿望。所以我们要珍惜这种源之动力之风。 春风如此温柔、如此细腻,怎能不让人心动去珍惜呢?让我们一起珍惜这股动力之风吧! 【第2篇】关于春风的作文:春风拂面 春天来了,太阳公公擦擦自己的眼,戴上眼镜,俯瞰世界,感叹:“这会是美好的一天。”风姑娘轻悄悄地来到了人间,用手轻抚柳树姑娘的头发,柳树姑娘醒来了,才发现这时的头发被某人梳理了一下,风姑娘摸着小草的头,轻声说:“该起床了!”这时,小草睡眼惺忪的睁开了眼睛,伸了伸懒腰。不一会儿,世间万物都从睡梦中醒来了。 她在床上熟睡,“起来,快起来!”闹钟好不耐烦的叫着,她醒了来“哎!好梦就这样被破坏了!”迅速的穿好衣服,急匆匆地走到了学校。她从书包里拿出书,大声朗读书中的内容,读着读着,就觉得有点困,本想伏在桌上休息的,她看到成绩比较好的来到了教室,她于是从书包里来翻到有问题的一页,走到他们面前寻求解题思路,问题进一步得到解决。此时春风拂面,振作了他疲惫的精神。 他和同学坐在一起,它却只能沉默过眼地陪伴这同学,他深感歉疚,同学忍不住要和他讲话,她在旁边认真地听,认真的回答他们提出问题,把心中的烦恼全部说出来了。心中舒服了好一阵子。这时春风拂面,排除了她心中的烦恼,则多了一份快乐。 从窗外望——处处都充满绿色,五彩缤纷的花点缀着绿,小鸟 小学语文想象类作文的构思技巧整理 给文字插上想象的翅膀,想象类作文的构思技巧整理! 学生在作文时,往往觉得没有合适的素材可写,或是不知从何想象。其实呢,不是生活中没有作文素材,而是学生缺少善于捕捉作文素材的能力。连素材都有限,自然就很难展开想象了。因此,培养学生的观察生活的能力,养成留心观察周围事物的习惯显得十分重要。 01 怎样指导孩子观察呢? 1.观察周围尽可能看到的所有事物,捕捉典型材料。 孩子的视线往往局限于一个小圈子,觉得一些司空见惯的小事没什么可写的。其实,平常的小事也可写出新意来。要选择最佳的观察对象,安排合理的观察顺序,认真观察。2.动用多种感官,丰富写作素材。 心理学认为,观察是思维的知觉,没有思维的观察是肤浅的,不是真正的观察。观察不仅仅是看,要动用耳、口、鼻、手、脑等感官去多方面地感知或判断,获得真实、全面、深刻的印象,为作文提供丰厚的材料。3.填写观察记录,养成观察习惯。 观察不应只是一次作文之前的例行公事。还应填写观察记录(观察顺序、观察方法)。 02 如何构思 以《卖火柴的小女孩》为例题,小女孩五次擦燃火柴所看到的奇异景象是作者的想象。这些想象奇特而大胆,而读者仍然觉得合情合理。 为什么呢?因为作者亲眼目睹了穷苦孩子的悲惨遭遇,深深地理解他们的内心需求。在文章中,想象与现实有着相似的地方,那就是穷孩子对幸福生活的渴望。 作者想象小女孩在神志不清时见到了温暖的火炉,喷香的烤鹅,美丽的圣诞树,慈祥的奶奶并和奶奶一起飞走,就显得自然而合理了。 无论写哪类想象作文,我们都必须做到以现实生活为基础,想象要合理、丰富,表达要真实、具体。 03 以现实生活为基础 现实生活是我们想象的源泉,离开了现实生活,想象就如同空中楼阁,成为无本之木、无源之水,变成空想或幻想。 所以,写想象作文必须勤于观察,丰富自己的生活,积极思考,驰骋想象,创新思维,这样才能引发你进行写作的灵感,进而写出优秀的想象作文。 04 怎样做到想象合理、丰富呢 1.再现 侧重于写景状物或叙事的想象作文,可以搜寻脑海中对相关事物的印象,加以再现。2.移植 有时候,想象可以进行嫁接、移植,把优美的景色移为一处,或把有趣的现象归为一物,或把美好的品质浓缩在一人之身。即,学生可以按自己的意愿中的特定形象,结合生活实际,进行移植想象。只有善于把想象与现实生活中的事实联系起来,巧妙地设计人物之间的关系,才能使文章生动有趣。3.幻想 春风送暖,如丝般的触感滑过脸际,送来温暖的气息。像圣洁的天使飘落的羽毛,又似冬日的火光映照着脸颊,勾起心底潜藏着的那暖暖的记忆。 “怦”,好险,好险。将将赶上这班车,不然,可又得等上半小时呢! “呼”,长舒一口气,抓好扶手。提着袋子,心头嘟囔:大夏天的还得去给表弟送书,什么世道,补课竟然都不带书,学的好才怪!心里愤愤的咒骂着。 “喂,我说这个女生,不想买票哟!”售票员不耐的声音总算唤回了我的神思。吐吐舌头,开始找钱包、掏钱、买票。等等!我钱包呢?糟了,莫不是跑得急忘在家里了?! 天哪,别开玩笑了。不过很可惜,上帝爷爷今天似乎睡觉去了,我全身上下摸不出一毛钱。 售票员看着我着急的样子冷笑着:“你这样的学生我见多了,什么‘钱包没带’‘钱掉了’的,我听得多了。小小年纪什么不学,学人家坐霸王车,害不害羞哟。撒起慌来脸都不红,羞不羞!” 我长这么大,什么时候被这样当众骂过。委屈的泪水一下子涌上了眼眶:“阿姨,对不起,我下车总行了吧。” “哟,装撒。现在的小孩哟,太会演了,怕是都已经到了要去的地方了吧。” 我咬着唇,拼命忍住眼里酸涩的泪水,自知理亏,也没办法反驳。 “阿姨,她是个女生,不过忘了带钱嘛,谁不没有点难处。你话也不能这样说啊。不就一块五嘛,我帮她买了。” 闻言侧头,身边是个和我差不多大的男孩儿。看着我,他轻轻眨了眨眼。清澈的目光既像关心,又像安慰,却更像春风拂过面庞,在炎炎夏日里带来阵阵温暖的清凉。眼里充盈的泪水,在此时,落了。 “谢谢,你叫什么名字。”我低低道着谢。 “呀,我叫什么呢?嗯,说‘雷锋’太老土了。有了!”他故意顿了顿,眼里满是狡黠,“我叫‘春风’。呵呵……” 春日,细雨蒙蒙。我望着窗外如丝般的雨,发着呆。忽的,我的童年记忆像一缕春风拂面而来,将我带回童年时代…… 小学语文教学论文:想象作文教学浅谈 作文是语文教学的重点,也是难点,而想像作文更是难中之难,小学生大都有“恐作症”,老师也常常为此头疼不已。那么怎样才能让学生在想象作文中有内容可写,有话可说呢?我认为可以从以下几方面训练。 一、观察现实生活,激发相关想象。 想像离不开现实,离开现实的想象是空洞的,无论哪一类想象作文都脱离不了现实生活。例如童话式想象作文,它是根据小学生喜爱动物的特点,用动物代替人类的形象来表达他们对世界的认识,在想像力作用下的动物附上了人的动作、语言、神态和思维。这类作文实际上是对现实的再现。 如想像作文“未来的×××”,这一类写未来生活的想象作文对学生而言有难度。未来是什么样的,学生除了接触到一些科幻片、科幻小说以外,其他的十分抽象,不知如何写。教师可引导学生仔细观察现实生活,展开想像的翅膀。例如现在的房屋,一旦完工,它便固定下来。如果让学生大但想象,让未来的建筑由一个个组装件构成,根据不同的需要进行不同的组合,这样既适合不同人的需求,又便于搬迁、移动,还可以维修,那该多好。又如当看到学校操场只有一处,空间过于狭小时,可以引导学生想象地下或空中操场,用电梯或升降机来回启用……这些现实中人们追求的更加便捷、完美的东西,都可以大胆想象它的样子、形状、功能。如果激发了学生想象的火花,那么展现在学生面前的空间不知有多大! 二、结合课文内容,进行再造想象。 课文是学生学习文化知识的重要材料,也是学生写作的典型范例。教师可充分利用课文资源,结合课文内容,让学生练习改写、续写、扩写等想象性作文,是一种行之有效的再造想象途径,能有效提高学生的想像能力。 例如《凡卡》一文,当凡卡满怀希望地把信寄出去后,爷爷能收到吗?爷爷在乡下会怎样想念凡卡呢?小凡卡后来的命运又会如何呢?让学生大胆去想象,续写出符合事情发展的故事,这样既加深了对课文内容的理解,又激活了学生想象的火花。 另外,还可以根据文中的插图进行补充或扩写。如《我的战友邱少云》一文在的插图,邱少云被烈火烧身时的巨大痛苦,是通过作者的心理活动侧面描写的,那么邱少云的心理感受会怎样呢?可引导学生观察他的神态、动作进行想象。 三、填补一些空白,设置整体形象。 在教学中选取一些相关的事物或词语,让学生进行整合,填补其中的空白,也是提高学生想象能力的重要手段。例如:画下几种不同的小动物,让学生按照自己的思维说出它们之间的关系,并想象出这些小动物之间会发生什么样的故事,然后进行口述表演,这样激起学生的童趣,他们的想象力就会更活跃。或者随便写下几个词语,让学生编上一段故事,用上这几个词语。这类填空白的训练,可以让学生的想象能力得到逐步提高。坚持长期训练,会收到意想不到的效果。 总之,学生作文能力的提高与教师的训练密不可分。我们应该在平时的作文教学中善动脑子,力求科学、有效,为学生作文插上想像的翅膀,让他们飞得更高、更远。 谈如何尊重人尊重他人,我们赢得友谊;尊重他人,我们收获真诚;尊重他人,我们自己也 获得尊重;相互尊重,我们的社会才会更加和谐. ——题记 尊重是对他人的肯定,是对对方的友好与宽容。它是友谊的润滑剂,它是和谐的调节器, 它是我们须臾不可脱离的清新空气。“主席敬酒,岂敢岂敢?”“尊老敬贤,应该应该!”共和 国领袖对自己老师虚怀若谷,这是尊重;面对许光平女士,共和国总理大方的叫了一 声“婶婶”,这种和蔼可亲也是尊重。 尊重不仅会让人心情愉悦呼吸平顺,还可以改变陌生或尖锐的关系,廉颇和蔺相如便是 如此。将相和故事千古流芳:廉颇对蔺相如不满,处处使难,但蔺相如心怀大局,对廉颇相 当的尊重,最后也赢得了廉颇的真诚心,两人结为好友,共辅赵王,令强秦拿赵国一点办法 也没有。蔺相如与廉颇的互相尊重,令得将相和的故事千百年令无数后人膜拜。 现在,给大家举几个例子。在美国,一个颇有名望的富商在散步 时,遇到一个瘦弱的摆地摊卖旧书的年轻人,他缩着身子在寒风中啃着发霉的面包。富 商怜悯地将8美元塞到年轻人手中,头也不回地走了。没走多远,富商忽又返回,从地摊上 捡了两本旧书,并说:“对不起,我忘了取书。其实,您和我一样也是商人!”两年后,富商 应邀参加一个慈善募捐会时,一位年轻书商紧握着他的手,感激地说:“我一直以为我这一生 只有摆摊乞讨的命运,直到你亲口对我说,我和你一样都是商人,这才使我树立了自尊和自 信,从而创造了今天的业绩??”不难想像,没有那一 句尊重鼓励的话,这位富商当初即使给年轻人再多钱,年轻人也断不会出现人生的巨变, 这就是尊重的力量啊 可见尊重的量是多吗大。大家是不是觉得一个故事不精彩,不够明确尊重的力量,那再 来看下一个故事吧! 一家国际知名的大企业,在中国进行招聘,招聘的职位是该公司在中国的首席代表。经 过了异常激烈的竞争后,有五名年轻人,从几千名应聘者中脱颖而出。最后的胜出者,将是 这五个人中的一位。最后的考试是一场面试,考官们都 作文话题素材之为人处世篇:尊重 思路 人与人之间只有互相尊重才能友好相处 要让别人尊重自己,首先自己得尊重自己 尊重能减少人与人之间的摩擦 尊重需要理解和宽容 尊重也应坚持原则 尊重能促进社会成员之间的沟通 尊重别人的劳动成果 尊重能巩固友谊 尊重会使合作更愉快 和谐的社会需要彼此间的尊重 名言 施与人,但不要使对方有受施的感觉。帮助人,但给予对方最高的尊重。这是助人的艺 术,也是仁爱的情操。———刘墉 卑己而尊人是不好的,尊己而卑人也是不好的。———徐特立 知道他自己尊严的人,他就完全不能尊重别人的尊严。———席勒 真正伟大的人是不压制人也不受人压制的。———纪伯伦 草木是靠着上天的雨露滋长的,但是它们也敢仰望穹苍。———莎士比亚 【篇一】一缕春风拂面来初三作文800字 无论冬天怎样漫长,春天就如同樱花般总会熬过严冬,以最美的姿态绽放于枝头,与你相见。——题记 20XX年的冬天似乎格外漫长,一场突如其来的新冠肺炎疫情袭卷神州大地。原本热热闹闹的新年,突然变得冷冷清清,和煦的春风也被阻隔在口罩之外。 出于安全考虑,人与人之间时刻注意保持安全距离,每个人的微笑也被隐藏在口罩之中。有一天上完网课,有些疲惫的我抬头看向窗外,突然发现门前的那棵树居然长出了嫩芽。之前因为功课太繁忙,每天早出晚归,披星戴月,所以从未注意到窗前的那棵树。今年春天延迟开学,我在家里上网课,所以有幸能见证它的生长。 那些刚刚长出的幼小嫩叶簇拥在一起,就像一朵小小的绿色荷花。那绿就像被雨水冲洗过一般,即使身在火热的夏天,也能让你的心底泛起一阵清凉。生命有时很脆弱,也许一场大雨就能把这些嫩叶摧残,可生命又如此顽强,即使被暴雨摧残,它们依旧能够长出新芽,继续生长。我们人类又何尝不是这样呢? 也许无情的病毒会夺走我们的生命,但是我们有能力、有信心从死神手里抢回。在这场人与病毒的战争中,我们看不到硝烟四起,但每天都有生死离别,阴阳两隔。疫情发生以来,每个人都在全力为抗疫作贡献。你看,爱与希望总比死亡与病毒蔓延得更快,这就是生命的张力与尊严。回顾历史,人类经受过很多苦难,在苦难面前,生命是何等渺小,但我们从不放弃活下去的希望。即使在苦难中,我们也艰难地摸索前行,去等待属于我们的春天,去感受那春风拂面的温柔。 这个春天,即使我们遭受过挫折,但生命却不会因为这些挫折而停滞,相反,它会拼命生长,在苦难中开花、结果。我想每一个熬过冬天的种子都有一个春天的梦想。让我们再等等,等到这个春天真正的到来,等到所有的花儿都开放,等到看樱花的人比樱花还要多,等到和煦的春风又再次抚摸脸颊。我们一定会摘下口罩,微笑问好。 【篇二】一缕春风拂面来初三作文800字 春风拂面,在其他任何季节,也会有一番如沐春风的舒畅与感动。 冬,一个寒冷的冬日,呼呼的寒风猛烈地刮着,呵气成冰的天气让我倍感不适,我因病体育课时在班中休息,听着外面强烈的风声,望着自己已冻得通红甚至有些僵硬的手,不禁一阵猛搓。这是,老师轻轻推开了门走了进来,端来一杯热水,关切的问道:“感觉好些了吗?喝点水,暖暖身子,如果不舒服直接去办公室打电话啊,不用找我。”我点点头,喝着水,感到无比的暖意,在这寒冬,我有一份感动,如同春风拂面。 不仅是在冬日,在夏日,也会有春风拂面的感觉。 小学分类作文全攻略之怎样写好想象类作文未来因为不可预知而显得神秘莫测,令人神往;想象,因为未能定格而让人激情膨胀。当我们置身于高科技时代,我们其实就是在不断地享受着人类的创造之果给我们的生活带来的舒适、方便与快捷。人类社会,在想象中不断完善,在创造中走向壮大。 <一>想象 1.定义:想象是人在头脑里对已储存的表象进行加工改造形成新形象的心理过程。想象作文与平时作文中的“想象”有所不同。如写桃花,可根据桃花的形想象它像一颗颗五角星,根据它盛开的样子想象它像小姑娘绽开的笑脸,这样就可以把桃花这个事物写具体生动。以上例子只能说是平时作文中一个想象的小节,并不代表它就是想象作文,想象作文不是细节和局部情节的想象,而是整篇作文的想象。 2.想象的分类 (1)再造想象含义:根据别人的描述或图样,在头脑中形成新形象的过程。意义:使人能超越个人狭隘的经验范围和时空限制,获得更多的知识;使我们更好理解抽象的知识,使之变得具体、生动、易于掌握。 形成正确再造想象的基本条件:一是能正确理解词与符号、图样标志的意义;二是有丰富的表象储备。 (2)创造想象含义:不根据现成的描述,而在大脑中独立地产生新形象的过程。创造想象的特殊形式——幻想:与个人生活愿望相联系并指向未来的想象。两个特点:体现了个人的憧憬或寄托,不与当前的行动直接联系而指向于未来。具有积极意义:积极的幻想是创造力实现的必要条件,是科学预见的一部分;是激励人们创造的重要精神力量;是个人和社会存在与发展的精神支柱。 <二>想象类作文的分类: 【1】童话 童话写作时,首先要有一定的故事情节,在设计情节时不要太复杂,可采用拟人的手法,把物当做人来写,让物具有人的思想感情。其次要充分发挥想象,把生活中本质的事物,通过想象编成趣味性的故事,展现在读者面前。再次要注意想象与现实生活的联系。现实生活时想象的基础,通过艺术加工后,表达一种 试卷第1页,总5页 福州格致中学2017-2018学年第一学段 高一物理检测 命题题:林枝钦 审核:王宇 日期:2017.11.7 (完卷时间:70分钟 全卷满分:100分) 一.选择题(每题4分,共40分,其中1-6题为单项选择,7-10题为多项选择;多项选择选全对得4分,选不全得2分,错选不得分) 1.下列各组物理量中全部是矢量的是( ) A .位移、时间、速度、加速度 B .速度、平均速度、位移、加速度 C .质量、路程、速度、平均速度 D .位移、路程、时间、加速度 2.下面几组力中,可能成为平衡力的有( ) A .3N 、4N 、8N B .2N 、5N 、9N C .4N 、6N 、8N 、12N D .7N 、6N 、12N 、26N 3.一物体由某一高度做自由落体运动,第1s 内下降的高度是总高度的1/16,g=10m/s 2,则( ) A .物体下落的高度为5m B .物体下落的高度为25m C .物体下落的高度为45m D .物体下落的高度为80m 4.一个光滑的圆球搁在光滑斜面和光滑的竖直挡板之间,如图.当竖直挡板由竖直逆时针转到由图示虚线位置至水平位置过程中,则圆球受到的弹力( ) A .斜面对圆球的弹力先变小后变大 B .斜面对圆球的弹力逐渐变大 C .挡板对圆球的弹力先变小后变大 D .挡板对圆球的弹力逐渐变小 5.如图所示,两个质量均为m 的物体分别挂在支架上的B 点(如图甲所示)和跨过滑轮的轻绳BC 上(如图乙所示),图甲中轻杆AB 可绕A 点转动,图乙中水平轻杆一端A 插在墙壁内,已知θ=30°,则图甲中轻杆AB 受到绳子的作用力F 1和图乙中滑轮受到绳子的作用力F 2分别为( ) A .F 1=mg 、F 2= mg B .F 1= mg 、F 2=mg C .F 1= mg 、F 2=mg D .F 1= mg 、F 2=mg福建省福州格致中学2014-2015学年高一上学期期中考试英语试题 Word版无答案
尊重的素材
春风拂面范文
小学语文《想象作文》教案设计之一
福建省福州格致中学高考英语备考听力训练二十五试题 含答案
三年级下册语文第五单元作文《奇妙的想象》
福建省福州格致中学(鼓山校区)高一英语上学期第五次月考(期末)试题
关于春风的作文(6篇)
小学语文想象类作文的构思技巧整理
一缕春风拂面来600字作文三篇(最新)
小学语文教学论文 想象作文教学浅谈
尊重议论文
最新一缕春风拂面来初三作文800字
【部编人教版】最新版语文六年级上册-小学分类作文全攻略之怎样写好想象类作文
2017-2018福州格致中学高一上期中试卷