
小学英语基础知识汇总(总12
页)
-CAL-FENGHAI.-(YICAI)-Company One1
-CAL-本页仅作为文档封面,使用请直接删除
第一章名词
一、名词可分为:1.专有名词和普通名词 2.可数名词和不可数名词
1.专有名词和普通名词
1)专有名词:是指特定的人、地方、事物、机构的专有名称。开头的字母必须大写。如:Tom, Martin, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, China, Sunday, October, Chinese等。
2)普通名词:是指不属于特定的人名、地名、事物、概念的名词都是普通名词。
它分为四类:个体名词、集体名词、物质名词、抽象名词。
①个体名词:用来表示单个的人或事物。如:hospital, policeman, house, tree, cat, dog 等。
②集体名词:用来表示一群人或一些事物的总称。如:family, class, group, people, police, army等。
③物质名词:表示无法分为个体的物质。如:water, air, tea, sugar, butter, rice等。
④抽象名词:表示动作、状态、品质或其他抽象概念。如:happiness, health, life, manners, love等。
2.可数名词和不可数名词
1)可数名词:一般地说,个体名词和集体名词是可以计数的,所以称之为可数名词,有单数和复数形式。如:
a city---two cities a bird---three birds a book---ten books
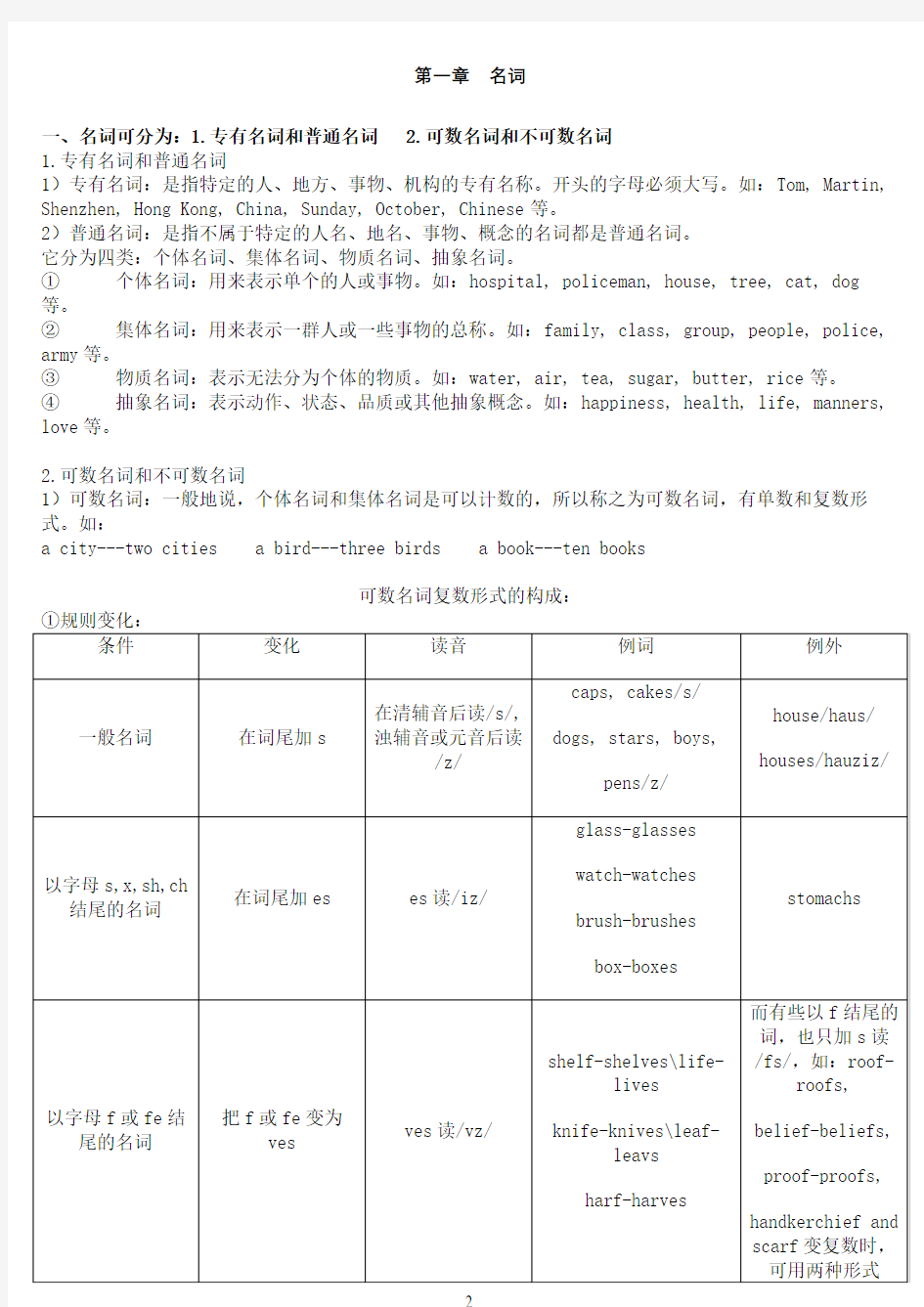
可数名词复数形式的构成:
②不规则变化:英语里有一部分名词的复试形式是不规则的。
a) 改变元音字母,发音也随之发生变化。如:man---men woman---women policewoman---policewomen postman---postmen policeman---policemen
foot---feet tooth---teeth goose---geese
注意:man和woman用作定语时,也有单复数变化。如:a man teacher---two men teachers a woman
nurse---three women nurses
b)有些名词单数和复数相同。如:a sheep---two sheep a fish---three fish a deer---two
deer an aircraft---four aircraft
c)有些名词通常以复数形式出现,如:scissors(剪刀) trousers(裤子) clothes(衣服) glasses(眼镜) shorts(短裤)
d)表示“某国人”的名词单数和复数形式因习惯不同而有不同的形式。这类词通常分为三类。
·单数和复数相同:如:a Japanese---two Japanese a Chinese---two Chinese
·词尾加s:如:a German---two Germans an American---two
Americans
·变man为men:如:an Englishman---two Englishmen an Frenchwoman---two Frenchwomen
e)其他形式。如:a child---two children an ox---three oxen a mouse---four mice
2)不可数名词:物质名词和抽象名词一般是不可数的,所以称之为不可数名词。如:water, milk, oil,
soil, ink, bread, juice等。
它们通常只有单数形式。但是在具体的情况下也可以用作可数名词。如:food---foods(各种食
物) fruit---fruits(各种水果)
tea---teas(各种茶叶)gas---gases(各种气味)
如果需要表示名词的具体数量时,可用以下的短语写:
a glass of juice a piece of paper a slice of bread a bottle of oil
a box of …… a bowl of …… a dish of …… a pair of ……
a kind of …… a kilo of …… a kilogram of …… a basket of ……
a bag of …… a full of …… a basin of …… a cup of ……
a packet of …… a lot of ……
而有些物质名词和抽象名词的单复数含义不同,如:
people(人民/人们) peoples(民族)water(水) waters(海/潮水)
paper(纸) papers(报纸/试卷/文件)custom(习惯) customs(海关)
time(时间) times(次数/倍/时代)brain(头脑) brains(脑力/智力)
arm(胳膊) arms(武器)snow (雪snows(积雪)cloth(布) clothes(衣服)
第二章冠词
冠词分为:1.定冠词(the) 2.不定冠词(a, an)
一、定冠词(the)的用法:
1.特指某(些)人或某(些)事物;(冠词的基本用法)
2.用在由普通名词构成的专有名词前;
3.用在某些形容词前,表示某一类人;
4.用在姓氏复数形式前,表示“全家人”或“夫妇俩”。
5.用来表示前面已提到过的人和事;
6.指双方都知道的人和事;
7.世界上独一无二的事物;
8.用在江河、湖海等专有名词前;
9.用在序数词和最高级的前面;
10.用在乐器前面(球类前不加);
11.在单数的可数名词前;
I have a book. The book is interesting. I see a boy. The boy is Tony. I like playing the piano.
12.用在某些固定的词组中。如:in the tree, on the tree, in the morning ,in the afternoon, in the evening, in the hat, look the same, go to the cinema, go to the zoo, go to the classroom
二、不定冠词(a和an)的用法:
不定冠词:不定冠词表示“一个或一”。不定冠词a用于辅音音素开头的单数可数名词前,an用于以元
音音素开头的单词可数名词前。泛指某一类人或事物。表示数量有“一”的意思,但语气没有one强烈。如:a book, a pen, a boy, a girl, a worker, an arm, an apple, an orange, an hour, an egg
以字母U开头的单词,U的发音为/ju:/时,前面要用冠词a,发元音为音音素的单词,前面要用冠词
an。
如:a useful book(一本有用的书),a university(一所大学),an umbrella, an hour, an ugly boy, an honest child, an interesting story
三、不用冠词的地方:
1. 抽象名词、物质名词和单个构成的专有名词(国名、任命等)前一般不用冠词。如:Chocolate is made of cocoa.
2. 表示月份、星期、季节的名词前通常不用冠词。如:Sunday is the first day of a week.
3. 可数名词的复数形式或不可数名词表示一般意义,而不特指具体的人或事物时,不与冠词连用。如:Women are usually more careful than men. Beef is more expensive than pork. Horses run much faster than sheep.
4. 名词前已有this, that, these those, my, your, whose, some, any, no, each, every等代词时,不用冠词。如:My school is far from here. Whose are these clothes? What will you do this week?
5. 表示球类、棋类、三餐、学科、语言的名词前不用冠词。如:Football is a very popular
sport in the world. I like playing chess. He is good at Chinese and English.
6. 在表示节日的名词前通常不用冠词。如:The Children’s Day in on June th e first.
Chinese New Year is coming soon.注:表示传统节日的名词前需要加冠词。如:The Spring Festival is the most important festival in China.
7. 某些短语中不用冠词。如:on foot, by plane, by train, at night, at noon.
8. 在有些名词前加定冠词和不定冠词的意思不同。如:in the class(在班上) in the bed(在
床里) in class(在课堂上) in bed(卧床) There is no school tomorrow.(明天我们不上学)
第三章代词
英语中的代词可分为:人称代词、物主代词、反身代词、指示代词、疑问代词等。
一、人称代词:
人称代词是指表示“你、我、他、她、它你们、我们、他们、它们”的代词。人称代词还有单数和复数之分,见下表:
人称代词的主格做主语,人称代词的宾格作宾语。如:He works in the factory.
I work on the farm. He likes her. We love them.
二、二、物主代词
物主代词是表示“你的,我的,他的,她的,它的,你们的,我们的,他们的,它们的”的代词。
物主代词分为:形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。见下表:
三、反身代词:
反身代词是指表示“我自己,你自己,他/她/它自己,我们自己,你们自己,他们/她们/它们自己”等的代词。见下表:
四、指示代词:
指示代词是指表示“这个this,那个that,这些these,那些those”的代词。见下表:
除此之外,在小学阶段出现的指示代词还有so, same, it,等。
的用法:
打电话时,常用that询问对方是谁,用this介绍自己是谁。It的用法比较多。
1)说话人不知道对方是谁可以说:Who’s that?It’s Li.
2)指时间:What’s the time? It is five.
3)指天气:What’s the weather like? It is cold.
4)指前面提到的事情:What’s is this? It is a book.
的用法:same的意思是“一样的,相同的”常与the连用。如:They are in the same class.
的用法:so也可以用作指示代词。如:—Can you mend the broken clock? —Sorry, I don’t think so.
五、疑问代词:
疑问代词和疑问副词它们都用来引导特殊疑问句。他们都叫做疑问词。疑问代词有who, whose, what, which等。How, when, where他们是疑问副词。
1.who是主格,和whom相对应,用于疑问句。如:Who’s the girl over there? Who are they
2.
3.whose兼有名词和形容词的性质。如:Whose is this pen? Whose pen is this
4.
5.What内容丰富,即可单独使用,也可和一些名词组成词组使用。如:What are you doing? They
are writing poems. What colour is your new dress? What’s your name
6.
7.which用来指人或物。如:Which one do you like best? Which of you will go with me
8.你们那一位愿意和我去?六、
六、不定代词:
不定代词:不指明代替任何特定名词的代词。它具有计量作用,表示不同的数量概念。如:
some any no every others all both somebody
anyone nobody another each one someone anybody no
one everybody much few little something anything nothing everything many a few a little a lot
some和any表示“一些”。Some通常用于肯定句,any用于否定句和疑问句。如:There are some cups on the table. Have you any stamps?遇到“Would you like…
”句型,要用some,如:Would you like some tea?
a few少许,少数;few少数,几乎没有用于否定;都用于修饰可数名词。
a little少许,少数;little少数,几乎没有用于否定;都用于修饰不可数名词。
much和many的意思是“许多,大量”,much修饰或指代不可数名词,many修饰或指代可数名词。much还可以用在比较级前面。如:She has much water. How many pens do you have?
everyone意思是“每个人”。用作主语时,谓语动词要用单数形式。如:Everyone is here today.
one指代可数名词,既可以指人,也可以指物;它有复数形式ones和所有格one’s。
other意思是“别的”、“其他的”。既可以指人,也可以指物,但不确指;用the other表示“两者中的另一个”。Another表示“另外的”。如:Some students like playing basketball, but other students like playing football. Bruce has two son. One is a teacher, the other is an engineer. I don’t like this pen, Please give me another one.
第四章形容词和副词
一、形容词的基本用法:用来修饰名词,说明事物或人的特征或性质的词。形容词一般放在名词、代词
的前面。如:She is a cute girl.
1.形容词修饰something, anything, nothing, everything等词时,须放在其后。如:something important.
2.表示长、宽、高、深及年龄的形容词,应放在相应的名词之后。
只能作后置定语,修饰疑问代词what, who, whom, whose和不定代词something, anything, nothing, somebody, anybody, nobody等。
4..貌似副词的形容词有lovely, friendly, lively等。
跟名词:enough time(名词在enough后)enough跟形容词:tall enough(形容词在enough前)
二、副词的基本用法:副词主要修饰动词、形容词、副词或其他结构。一般表示方式、时间、率、方位、程度等。表示方式的如:happily, fast, angrily ;表示时间的如:tonight, now;表示频率的如:often, sometimes, every day;表示方位的如:home, there, here;表示程度的如:very, quite等
三、形容词、副词的比较级的构成及句型:
1. 形容词、副词的比较级和最高级变化规律。
1)一般加-er,-est。如:tall---taller---tallest
2)以e结尾的加-r,-st。.如:late---later---latest
3)以辅音字母加y结尾的,把y变I加-er,-est。如:early---earlier---earliest
4)重读闭音节,双写末尾的辅音字母,加-er,-est。如:big---bigger---biggest
2.双音节和多音节形容词、副词比较级和最高级的构成。
部分双音节和多音节形容词分别在原级前加more和most构成比较级和最高级。如:important---more important---most important
3.形容词、副词的比较级和最高级的常用法。
比较级主要用于两者的比较。即:“形容词、副词比较级+than”这一结构表示:“比……更……”;any other+名词单数
1 )较级常用句型结构。如:
①I’m taller than you.②Shanghai is larger than any other city in China.
③Most of people in Shenzhen are getting richer and richer
形容词、副词的最高级的常用法:
形容词、副词的最高级主要用于三者或三者以上的人和事进行比较。其结构是:the+形容词、副词的最高级(+名词)+表示范围的短语,即:表示“最……的”意思
2 )最高级常用句型结构。如:
①The boy runs fastest in his class. ②China is one of the most beautiful countries in the world.
③Which is the cheapest, a computer, a TV set or a DVD player?
第五章数词
数词可分为1.基数词2.序数词
数词是用来表示事物的数目或顺序的词,表示“多少”的词叫做基数词;表示“第几”的词叫做序数词。
一、基数词
1. one,two,three,four,five,six,seven,eight,nine,ten;11-12用心记,13-19-teen结尾,20-90-ty结尾。
2. 表示“几十几”(21-99)的基数词是由十位数和个位数之间加连“-”构成。如:26:twenty-six.
3. 表示“几百几”(101-999),先说“几百”后加“and”再加“末两位数”或“末位数”。其中的“百”用单数形式。如:102:one hundred and two 284:two hundred and eighty-
four 1284:one thousand two hundred and eighty-four.(“千”和“百”之间不加“and”)
4. 房间号码和电话号码要一个数字一个数字的读。
二、序数词
1.序数词的构成
1)一般在相应的基数词后加词尾-th,注意下列的特殊变化:one-first ,two-secend,
three-third, five-fifth, eight-eighth, nine, ninth, twelve-twelfth
2 )以-ty结尾的基数词变序数词时,讲y改为I,再加eth。如:twenty-twentieth, thirty-thirtieth
3 )表示“几十几”或“几百几”的基数词变序数词时,只要将个位数变为序数词即可,十位数或百位数不变。如:twenty one-twenty first
4 )序数词的缩略式,由阿拉伯数字加上序数词最后两个字母构成。如:first-1st,second-2nd,third-
3rd,fourth-4th,twelfth-20th,twenty first-21st
2.序数词的用法:
1)序数词前要加定冠词the,在句中作定语,放在被修饰的名词前。
2)给东西编号时,序号在名词前用序数词,序号在名词后用基数词。
三、年份、日期、时刻的读法
1.年份:四位数通常分两组来读。如:1998读nineteen ninety-eight.但是2000-2009年不断开读。如:2008读two thousand and eight.
2.日期、世纪用序数词表示。如:May 时刻有两种读法:
一是直接读数字,先说钟点数,后说分钟数。这种读法英语叫做顺读法。
二是先说分钟数,后说钟点数。用介词past表示几点过几分(不超过半小时)或用to表示几点差几分(超过半小时还差多少分钟到下一个钟点)。这种读法英语叫做倒读法。
①整点:如:4:00 four o’clock②半点:如:4:30 half past four/four thirty
③不到半点如:2:05 five past two ④超过半点:如:3:45 a quarter to four
第六章介词
一、表示时间的介词:
1. at常用于表示钟点、夜里、中午的词之前及某些词组中。如:at si x o’clock在六点钟;at half past five在五点半;at night在夜晚;at noon在中午;at sunset在傍晚;at night在夜晚;at the end of在…末;at the beginning of在…开始时;at the age of在…岁时;at the weekend在周末;at Christmas在圣诞。
2. on用表示确定的时间,如:某日的上午、下午,晚上或一般节日等之前。如:on December 1st,1994在1994年12月1日;on Monday morning在星期一上午;on Christmas Day在圣诞节;on Teachers’ Day在教师节;on weekdays在平日。
3. in用于年、月、季节,上午、下午、晚上、白天等名词前。如:in the
morning/afternoon/evening在上午/下午/晚上;in October在十月;in spring/summer/autumn/winter 在春季/夏季/秋季/冬季。
4. in表示“在……时间内”或“时间后”。如:I’ll be back in an hour.我将在一小时后回来。
二、表处所方位的介词:
1. at/in/on表示“在……” :in表示“在……内”,用于内部;on意为“在……上面”,用于表面接触。表示在某地时;at后接小地方,in后接大地方。
2. between/among表示“在……之间” :between表示在两者之间;among表示在三者或三者以上之间。
3. in/to/on表示“位于”:in表示在某范围之内;to表示在某范围之外;on表示“毗邻、接壤”。
4. above/over/on表示“在……上面” :above的意思是“在……之上”,“高于……”,表示相对高度,不一定是在正上方,它的反义词是below。over的意思是“在……之上”,表示垂直的上方,其反义词是under。on的意思是“在……上面”,表示与表面接触。
5. by/beside/near表示“在……附近” :by表示“就在旁边”,较near更近;beside有“近旁”,“紧靠”之意,相当于next to;near表示“在……附近”,距离不远。
6. across/through表示“穿过”,“通过” :across和through都表示“穿过”,“通过”的意思,across表示从物体表面“穿过”,“通过”;而through则表示从内部“穿过”,“通过”。
7. in/into表示“进入……内”:in表示“在……之内”,表示位置或所处,侧重状态;into 意为“进入……”,表示运动或变化,侧重动作。
8. on/onto表示“在/到……之上” :on意为“在……上”,表示位置,侧重状态;onto意为“到……上”表示位置的改变。
9. 另外这些介词也常用:behind在……后面;in front of在……前面;under在……下面;below在……下方;next to在……隔壁
常用于表处所方位的介词词组:
in the house/in the bowl/in the book/in Shenzhen/in the east of/in the front of/behind the boy/go into the soil/on the ground/on the table/on the bus/on the top of the hill/on the left/on the right/at the bus stop/at the mall/beside the door/above the window/below the light/between the camera shop and the pet shop/under the chair/near the window/next to the hospital/around the world/across the world/across the street/through Lion Land/over
there/over the building
三、常用介词的其他用法:
1. about意为“关于”,表示内容。
2. on作“关于”讲,表示论题。如:a book on radio一本关于无线电的书
3. like作“像……”解,表示相似。
4. into作“成为……”解,表示转变。
5. in表示“穿着”,“戴着”或“用某种语言、材料”等。
6. as作“作为”解,表示身份。
7. with有“和……一起”,“具有”,“用某种工具”等意思。
8. without表示“没有”,“无”。
9. except作“除了……之外,都……”解,表示“排除”等。
10. by表示“通过交通工具、手段、通讯等方式”等。如:by bus乘公共汽车;by train乘火车;by air/plane乘飞机;by ship/sea乘船。(on foot步行除外)
11. for表示目的、原因。
12. on, over, through, by作“通过”解,表示“途径”。如:through newspapers/televisions通过报纸/电视;on/over the radio通过收音机;on TV通过电视;by telegraph通过电报
13. about(大约),over(=more than)(多于,超过),below(=less than)(少于、不足)等介词表示“数量”。
常用介词的其他用法表:
about the story/What’s the weather like/in red dress/with the boys/by bus/by train/by
plane/by ship/for supper/the legs of the desk/look at/look for/look after/look like/get
on/get off/be good at/be interested in/be late for/at breakfast/at first/at home/at night/at school/at a party/come to/go to/pick up/play with/a lot of/a cup of/on foot
四、含介词的常见固定搭配:
1. 动词+介词:look at, look for, look after, look up, look like等;get on, get
off ,get on well with, get to等。
2. 动词+副词+介词:catch up with, do well in等。
3. be+形容词+介词:be afraid of, be angry with, be famous for, be good at, be interested in等。
4. 介词+名词:at breakfast, at home, at night, at once, at school, on foot等。
常见的介词以及固定搭配:
look at/get on/pick up/at night/on the left/at home/look for/get off/turn on/on the right/at the crossing/next to…/look after/get to/be good at/at first/in the street/famous for/look like/look over/turn off/ by plane play with/at noon/do well in
第七章动词和时态
一、动词:是表示动作和状态的词。可分为:行为动词,如:come, go等;联系动词,如:
be(am ,is ,are, was, were);助动词do(does, did);情态动词can(could),many, must等。
英语动词有四种形式,分别为:动词原形、第三人称单数、现在分词、动词过去式。(这里动词过去分词不讲)下面以四个单词为例,看看它们的基本形式。
1.动词的原型:只是在一般现在时用它(除she, he, it外)。
2.动词第三人称单数:当主语是(she, he, it)时,动词要发生变化。
1)一般在动词后加s;如:sing---sings, listen---listens
2)辅音字母+y结尾的动词,把y变为i再加es;如:study---studies
3)以字母o, s, x, sh, ch, 结尾的动词,要加es。如:do---does, go---goes
3..现在分词:在动词后加ing。
1)一般情况下直接加ing;如:wait---waiting
2)以不发音的e结尾,去掉e再加ing;如:have---having, make---making
同上:come, take, live, like, bake, wake, hate ,love, bite, shake, write ,close
3)以重度音节结尾而末尾只有一个元音字母+一个辅音字母的动词,双写这个辅音字母再加ing。
如:cut---cutting, begin---beginning
在小学阶段大约有以下几个单词需要双写这个辅音字母再加ing
put,,cut,set,hit,let,run,swim,skip,hop,sit,clap,get,wrap,dig,regret,plan,win,begin,for get
动词的过去式变化分为规则变化和不规则的变化。
规则的动词见下表:
要变换一个字母:(改i为a)drink---drank swim--swam sing--sang sit--sat give--gave begin--began ring--rang
2. 只需要变换一个字母:(改i为o)write--wrote ride--rode drive—drove win--won
3. 只需要变换一个字母:build---built send---sent spend---spent come---
came become---became fall---fell hang---hung get---got run---ran
4. 有相同的字母:
teach---taught think---thought fly---flew sleep---slept wake---woke catch---
caught buy---bought
draw---drew sweep---swept speak---spoke sell---sold bring---brought
throw---threw feel---felt break---broke tell---told grow---grew stand---
stood understand---understood
5. 过去式与原型相同:put cut set let read hit hurt
二、时态
小学阶段所学的时态主要是:一般现在时、现在进行时、一般过去时和一般将来时。
1. 一般现在时:表示现阶段经常、习惯性的动作或状态、特征、客观真理。常用的时间状语有:often, always, sometimes, usually, every day, and soon。一般现在时的构成:动词原形;当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词加-s或-es。如下:
①We/They/I/You+动词原形
②He/She/It+动词+s或(es)
问句:Do/Does(he, she, it)+动词原形(do)…
Be+主语……Yes,
主语+do/does./No,主语+don’t/doesn’t
答语: I am. I’m not. Yes, he/she/it is. No, he/she/it isn’t we/you/they are. we/you/they aren’t.
例如:I always go to school by bike. She often gets up at five thirsty.
We play basketball on the playground. Does he go to school on foot every day? No, he doesn’t.
2. 现在进行时:表示正在进行或发生的动作。
常与这些词搭配:now, look, listen或根据上下文做题。
现在进行时的构成:
①I am
肯定句:②He/She/It is +动词+ing
③We/They/You are
否定句在be动词后面加not,问句把be动词提前。
例如:He is playing basketball now. They aren’t singing a song. What are they doing now?
3. 过去进行时:表示在过去的某一时刻正在进行或发生的动作。
过去进行时的构成:
①I was
肯定句:②He/She/It+动词+ing
③We/They/You were
否定句在be动词后加not,问句把be动词提前。
例如:He was walking at 6 yesterday morning.
I was not walking at 6 yesterday morning. I was running.
4. 一般过去时:表示过去某一时间发生的事,存在的状态或过去发生地动作。
常用的时间状语有:yesterday, yesterday morning/afternoon/evening/,evening, last
week/morning/Sunday/month/year/…,in 2006
一般过去时没有单数和复数之分。
一般过去时的构成:
肯定句:(主语)I/we/you/she/he/it/they+动词过去式
否定句:主语+didn’t+动词原形(do)
问句:Did+主语+动词原形(do)
例如:I walked in the street yesterday. He didn’t go to school.
Tom had a big dinner last week. She ate an ice cream yesterday.
Did she send emails to your sister last night? No, she didn’t.
5. 一般将来时:表示将要发生的动作或状态。
常用的时间状语:next week/month/year/Sunday…,tomorrow, tomorrow morning/afternoon/evenin g…一般将来时的构成:
肯定句:①(主语)I/we/you/she/he/it. They +will/shall+动词原形。
②be going to+动词原形
否定句:主语+will not(won’t)+动词原形(do)
主语+be not+ going to+动词原形
问句: Will+主语+going to+动词原形(do)…
Be+主语+going to+动词原形?
例如:Pat will go to Shenzhen next week.
注:如果句中含有will, shall, should, would, can, could, may, mast等情态动词,其后面的动词一律接动词
第八章日常交际用语
日常交际用语主要有以下几种:
1. 打电话:(Making telephone calls)
1) Hello!、 Hello! This is Tom.
2) Hello! May/Can I speak to……Is that……speaking/This is ……speaking. I am afraid he is out./Hold on, please. I’ll get him./May I take a message for him?
2. 看病:(seeing the doctor)
1) What’s wrong with you/What’s the matter with you/What’s your trouble
2) I have got a bad cold./I have a headache./I have got a pain here./I feel
bad/terrible.
3. 购物:(shopping)
1) What can I do for you/Can I help you/May I help you
2) I’d like……
3) How much is it/How much does it cost
4) How much/How many……do you want?
5) What size/colour do you like?
6) I’ll take/have it. Here is the money.
4. 问路及应答:(Asking the way and responses)
1) Excuse me, where is the……
/Excuse me. Can you tell me the way to……
Excuse me. Can you tell me how can I get to……
2) Go aright down this street/road. Go along the road. Turn left/right at the
first/second crossing. It’s far from there. You can take the bus. It’s
beside/near/between……
3) I am sorry. I don’t know. I am new here. You can ask the policeman.
5. 谈论天气:
1) What is the weather like today/What was the weather like yesterday in Shenzhen
2) It’s cold/hot/rainy. It was cool/wet/dry. It’s raining/snowing.
6. 就餐:(Taking meals)
1) What would you like? What would you like to eat/drink? Would you like something to eat/drink? What do you want to eat/drink?
2) I’d like a glass of juice./I’d like some dumplings.
3) Help yourself to some……
4) Would you like some more……
5) No, thank you.
7. 致谢、道歉及应答:
1) Thank you./Thanks a lot./Many thanks.
2) You are welcome./Not at all./That’s all right./It’s my pleasure./That’s OK.
3) Excuse me./Sorry./I’m sorry.
小学英语基础知识汇总 Document serial number【KKGB-LBS98YT-BS8CB-BSUT-BST108】
第一章名词 一、名词可分为:1.专有名词和普通名词 2.可数名词和不可数名词 1.专有名词和普通名词 1)专有名词:是指特定的人、地方、事物、机构的专有名称。开头的字母必须大写。如:Tom, Martin, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, China, Sunday, October, Chinese等。 2)普通名词:是指不属于特定的人名、地名、事物、概念的名词都是普通名词。 它分为四类:个体名词、集体名词、物质名词、抽象名词。 ①个体名词:用来表示单个的人或事物。如:hospital, policeman, house, tree, cat, dog等。 ②集体名词:用来表示一群人或一些事物的总称。如:family, class, group, people, police, army等。 ③物质名词:表示无法分为个体的物质。如:water, air, tea, sugar, butter, rice 等。 ④抽象名词:表示动作、状态、品质或其他抽象概念。如:happiness, health, life, manners, love等。 2.可数名词和不可数名词 1)可数名词:一般地说,个体名词和集体名词是可以计数的,所以称之为可数名词, 有单数和复数形式。如: a city---two citiesa bird---three birdsa book---ten books 可数名词复数形式的构成:
②不规则变化:英语里有一部分名词的复试形式是不规则的。 a)改变元音字母,发音也随之发生变化。如:man---menwoman---womenpolicewoman---policewomenpostman---postmenpoliceman---policemen foot---feettooth---teethgoose---geese 注意:man和woman用作定语时,也有单复数变化。如:a man teacher---two men teachers a woman nurse---three women nurses b)有些名词单数和复数相同。如:a sheep---two sheepa fish---three fisha deer---two deeran aircraft---four aircraft c)有些名词通常以复数形式出现,如:scissors(剪刀) trousers(裤子) clothes(衣服) glasses(眼镜) shorts(短裤) d)表示“某国人”的名词单数和复数形式因习惯不同而有不同的形式。这类词通常分为三类。 ·单数和复数相同:如:a Japanese---two Japanesea Chinese---two Chinese ·词尾加s:如:a German---two Germansan American---two Americans ·变man为men:如:an Englishman---two Englishmenan Frenchwoman---two Frenchwomen e)其他形式。如:a child---two childrenan ox---three oxena mouse---four mice 2)不可数名词:物质名词和抽象名词一般是不可数的,所以称之为不可数名词。如:water, milk, oil, soil, ink, bread, juice等。 它们通常只有单数形式。但是在具体的情况下也可以用作可数名词。如:food---foods(各种食物)fruit---fruits(各种水果) tea---teas(各种茶叶)gas---gases(各种气味) 如果需要表示名词的具体数量时,可用以下的短语写: a glass of juicea piece of papera slice of breada bottle of oil a box of ……a bowl of ……a dish of ……a pair of …… a kind of ……a kilo of ……a kilogram of ……a basket of …… a bag of ……a full of ……a basin of ……a cup of …… a packet of ……a lot of …… 而有些物质名词和抽象名词的单复数含义不同,如: people(人民/人们) peoples(民族)water(水) waters(海/潮水) paper(纸) papers(报纸/试卷/文件)custom(习惯) customs(海关) time(时间) times(次数/倍/时代)brain(头脑) brains(脑力/智力) arm(胳膊) arms(武器)snow (雪snows(积雪)cloth(布) clothes(衣服)
个性化教学辅导教案 学员姓名:任课教师:所授科目:英语
一般疑问句:Be 主语其它。 如:-Are you a student -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not. 非凡疑问句:疑问词一般疑问句。如:Where is my bike 2.行为动词的变化。 否定句:主语don't( doesn't ) 动词原形( 其它)。如: I don't like bread. 当主语为第三人称单数时,要用doesn't构成否定句。如: He doesn't often play. 一般疑问句:Do( Does ) 主语动词原形其它。如: - Do you often play football - Yes, I do. / No, I don't. 当主语为第三人称单数时,要用does构成一般疑问句。如: - Does she go to work by bike - Yes, she does. / No, she doesn't. 动词s的变化规则 1.一般情况下,直接加-s,如:cook-cooks, milk-milks 2.以s. x. sh. ch. o结尾,加-es,如:guess-guesses, wash-washes, watch-watches, go-goes 3.以“辅音字母y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:study-studies 用括号内动词的适当形式填空。 1. He often ________(have) dinner at home. 2. Daniel and Tommy _______(be) in Class One. 3. We _______(not watch) TV on Monday. 4. Nick _______(not go) to the zoo on Sunday. 5. ______ they ________(like) the World Cup 6. What _______they often _______(do) on Saturdays 7. _______ your parents _______(read) newspapers every day 8. The girl _______(teach) us English on Sundays. 9. She and I ________(take) a walk together every evening. 10. There ________(be) some water in the bottle. 11. Mike _______(like) cooking. 12. They _______(have) the same hobby. 13. My aunt _______(look) after her baby carefully. 14. You always _______(do) your homework well. 15. I _______(be) ill. I’m staying in bed. 16. She _______(go) to school from Monday to Friday. 17. Liu Tao _______(do) not like PE. 18. The child often _______(watch) TV in the evening. 19. Su Hai and Su Yang _______(have) eight lessons this term. 20. -What day _______(be) it today -It’s Saturday 三、现在进行时 1.现在进行时表示现在正在进行或发生的动作,也可表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。 2.现在进行时的肯定句基本结构为be+动词ing. 3.现在进行时的否定句在be后加not。 4.现在进行时的一般疑问句把be动词调到句首。 5.现在进行时的非凡疑问的基本结构为: 疑问词不达意be 主语动词ing 但疑问词当主语时其结构为: 疑问词不达意be 动词ing 动词加ing的变化规则
小学英语基础知识测试英语试题 一、选出不同类的一项。(10 分) ( ) I. A. was B. are C. where ( ) 2. A. reach B. peach C. catch ( ) 3. A. Chinese B. Australian C. Sydney ( ) 4. A. thirty B.thirsty C. dirty ( ) 5. A. never B. clever C. always 二、英汉词组互译。(20分) 1 一些好习惯___________________ 2 hit the ball hard _____________________ 3 健康的饮食___________________ 4 eat a few eggs __________________ 5 某一天______________________ 6 so many balls ____________________ 7 当心_________________ 8 put his things in order_______________ 9 马路安全__________________ 10 follow the rules__________________ 三、选择填空。.(10分) ()1. From then on, Sam and Tina_________ good friends. A. become B. becomes C. became ()2. What is your cousin’s bad ? A. habits B. habit C. a habit ()3. Does Tom learn English_________? Yes, he often ________English books after dinner. A. good; reads B. well; reads C. well; looks ()4. The lion cried_________. ‘________can I get out?’ A. sadly; what B. sadly; How C. sad; How ()5.This is my new house. Let me ________you ________ it.
设计意图:小学英语新课程标准强调指出:英语教学要重视对学生实际语言运用能力的培养,强调课程从学生的学习兴趣、生活经验和认识水平出发,倡导体验、实践、参与、合作与交流的学习方式和任务型的教学途径,发展学生的综合语言运用能力。也就是说,要通过适合儿童年龄、心理和生理特点的生动活泼的课堂活动,把学习英语与用英语做事情联系起来,创设良好的语言环境和语用环境,使学生在愉快和自信的情绪中,保持积极的学习态度,在大量的语言实践中形成语感,养成良好的英语学习习惯。 这是我们贯彻―新课程标准‖,运用―新课程标准‖教学的关键所在。 我将本课教学分为以下几个环节: 一、课前寻找、激发兴趣 本课涉及的生词不多,但它和我们的生活息息相关,一提出问题就收到了意想不到的效果,同学们马上就想知道平常我们口中称呼的爸爸、妈妈、爷爷、奶奶的英语叫法。我没有告诉他们答案,让他们自己去找。象dad(爹地), mom(妈咪)这些称呼在他们接触英语前都从港台电视上所熟知。上课时百分之百的同学会说dad(爹地), mom(妈咪),大多数同学会说(uncle)安可,(aunt)安娣。从一开始就刺激了同学们强烈的好奇心,使他们产生强烈的求知欲。 二、歌曲导入、初步感知 唱英语歌是学习英语的一种好方法。课前一首歌,可以使学生精神饱满,思想集中,做好上课准备。课中一首歌,不仅能减轻学生的心理负荷,减少疲劳,又使学生在轻松愉快的气氛中学会新词、新句型。课外几首歌,有利于开展第二课堂活动,以巩固所学知识。例:教学本课时,我们以歌曲导入,播放―Boy and Girl‖:―I‘m a boy and you are a girl. I‘m a girl and you are a boy. Do you want to be my friend?‖根据歌词中提到的boy, girl出示男孩,女孩的图片,并让说到该性别单词的学生站起来大声说。在这种活泼欢快的气氛中,在这种互动的形式下,既训练了学生―听‖的能力,又让他们初步感知了有关他们性别的英语单词。 三、近交流,借物练说 用―振救大行动‖的游戏进行比赛,男女同学各一组,老师走到一个同学前问―Are a boy/girl?‖如果他/她回答正确了,就可以从―鳄鱼‖嘴里挽救回他们组的一个人[把这些虚拟的人和鳄鱼都画大黑板上],否则就被―鳄鱼‖吃掉。 在学生充分练说的基础上,让几组同桌同学试说,要求其他同学认真听,听他们说得是否符合要求,培养学生良好的听说态度和习惯。练说内容层层深入,范围逐步扩大,为学生提供自主学习和相互交流的机会及充分表现和自我发展的空间,让学生能在掌握新知的基础上,做到新旧结合,从而培养―说‖的能力。 四、课外延伸,学以致用 小学英语的最终目的是使学生掌握以交际为目的的最初步运用英语的能力。为让学生能把课上所学的知识运用到实际生活中去,我们在课后尽量让学生用英语与老师和同学作交流,如开展―英语一分钟讲坛‖,让学生谈论学校、老师、家庭及个人爱好等。用英语Asking the questions、Greetings、Conversations及用英语道谢、告别。让学生在日常生活中恰当地自然地运用英语,真正做到学以致用。 教学目标(Teaching aims): 1、Let‘s learn 能听、说、认读本课有关家庭成员的主要单词man: brother,,father(dad), grandfather(grandpa); woman: sister, mother(mom), grandmother(grandma) 2、Let‘s sing 本部分是通过学唱英文歌曲,巩固所学单词,培养学生的学习兴趣。 教学难点/重点(Teaching keys):
小学英语基础知识必备第一部分:基础知识 1.字母:26个字母的大小写 ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz 2.语音:元音的发音 五个元音字母:AEIOU 12个单元音: 前元音:[i:] [?] /e/ [?] 中元音:[?:] [?] 后元音:[ɑ:] [?] [?:] [u :] [?] [?] 双元音(8个) 合口双元音(5个)[ai] [ei] [au] [?u] [?i] 集中双元音(3个)[i?][ε?][u?] 3.词汇:词汇量,近反义词 4.句子:大小写,标点符号 第二部分:语法知识 一.名词:名词单复数,名词的格 (一)名词单复数 一般情况,直接加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds 以s. x. sh. ch结尾,加-es,如:bus-buses, box-boxes, brush-brushes, watch-watches 以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries 以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,如:knife-knives 不规则名词复数: man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen, mouse-mice
child-children, foot-feet, tooth-teeth, fish-fish, people-people, Chinese-Chinese, Japanese-Japanese 不可数名词的复数就是原型:paper, juice, water, milk, rice, tea (二)名词的格 有生命的东西的名词所有格: a) 单数后加’s 如: Lucy’s ruler my father’s shirt b) 以s 结尾的复数名词后加’如: his friends’bags c) 不以s 结尾的复数后加’s children’s shoes 并列名词中,如果把’s加在最后一个名词后,表示共有, 如: Tom and Mike’s car 汤姆和迈克共有的小汽车 要表示所有物不是共有的,应分别在并列名词后加’s Tom’s and Mike’s cars 汤姆和麦克各自的小汽车 (2)表示无生命东西的名词通常用“of +名词”来表示所有关系:如: a picture of the classroom a map of China 第二部分:语法知识 二.冠词:不定冠词,定冠词种类: (1)不定冠词:a / an a unit / an uncle 元音开头的可数名词前用an : an egg / an apple / an orange / an eraser / an answer / an ID card / an alarm clock / an actor / an actress / an e-mail / an address / an event / an example / an opera / an houran old man / an interesting book / an exciting sport / an action movie / an art lesson / (2)定冠词:the the egg the plane 2. 用法: 定冠词的用法: 特指某(些)人或某(些)物:The ruler is on the desk. 复述上文提到的人或物:He has a sweater. The sweater is new. 谈话双方都知道的人或物:The boys aren’t at school.
人教部编版小学英语1到6年级十大基础语法知识总结 小学英语形容词性物主代词 1、形容词性物主代词8个: My your his her its our your their 我的你的他的她的它的我们的你们的他(她、它)们的 2、形容词性物主代词的特点: 1)译成汉语都有"的" eg:my 我的their 他们的 2)后面加名词:eg:my backpack his name 3)前后不用冠词 a an the This is a my eraser(错误) That is your a pen(错误) It's his the pen(错误) 3、I(物主代词)my you(物主代词)your he (物主代词)her we (物主代词) our 注:在变物主代词时,把原题所给的词加上的,再译成 单词就可以了。 小学英语名词性物主代词 1、名词性物主代词和形容词性物主代词一样有8个: Mine yours his hers its ours yours theirs 我的你的他的她的它的我们的你们的他(她、它)们的 2、名词性物主代词的特点:
1)译成汉语都有"的" 2)后面不加名词 3)名词性物主代词=形容词性物主代词+名词 Eg:1、the pen is mine 钢笔是我的(mine=my pen) 小学英语单数的句子变成复数的句子 把单数的句子成复数的句子很简单:变法是把能变成复 数的词变成复数,但a或an要把去掉。特殊疑问词、形容词、国家及地点通常不变。 Eg:把下列句子变成复数 1, I have a car ----we have cars 2, He is an American boy. ----They are American boys 3, It is a car ----They are cars 4,This is an eraser ----These are erasers 5,That is a backpsck -----Those are backpacks 6,I'm an English teather ------We are English teathers 7,It's a new shirt---- They are new shirts 8,He's a boy ----They are boys 9,She's a singer ------They are singers 10,What'sthis in English?---- What are these in English? 小学英语名词单复数 名词有单数和复数两种形式
小学英语初学者基础测 试题 公司内部档案编码:[OPPTR-OPPT28-OPPTL98-OPPNN08]
一:选出下列不同于其他的发音的单词。(5) 1.A pear B here C where D dear 2.A apple B head C bed D letter 3.A hot B door C watch D body 4.A old B most C out D hope 5.A chicken B child C sure D chip 二:单项选择题(20) 1.Thank you________your help. A with b for c at 2.I see ______elephant in the zoo today. A the b a c / 3.There _________ a book,two pens and three boxes in the room. A is b are c am 4.She _______like the song,but I can sing the song. A don’t b isn’t c doesn’t 5.Every day,our teacher will play ____basketball,but I play____ violin. A the, a b a,the c the,the d /,the 6.I often go to the park ______my friends. A and b with c about 7.____________two books on the table. A there have b there is c there are
小学英语字母课堂教学设计
小学英语字母课堂教学设计 昆明市晋宁区晋城第四小学陈永娇 一、小组讨论 1、小学英语字母教学的内容有哪些?字母教学的目标是什么? 字母教学包括26个字母的读音,辩认和书写三项内容。小学英语字母教学的目标是在教师的指导下,让学生达到能认字母的音和形,能读准字母,能按正确的笔顺和规格书写,能按顺序背诵和默写字母,同时能初步掌握字母在单词中的发音,为进一步学习单词的读音和拼读打下基础。 2、小学英语字母教学有哪些基本环节?可以用什么方法和手段进行教学? 教学环节主要有:Warming up-----Presentation----Practice------Consolidatio n-----Homework Warming up 阶段是充分调动孩子的学习兴趣,吸引他们注意力;Presentation 阶段主要是让学生接触语言目标,感知语音与语意;Practice 阶段主要是让学生通过一些简单活动
进行机械操练;Consolidation 阶段是让学生在一些真实意义活动中运用语言目标。 可以运用儿歌、复习等方式来导入教学;运用实物、图片、卡片、动画等呈现;通过游戏来操练;运用儿歌、律动复习或巩固。 二、教学过程与实施 1、Warming-up 歌谣引入法:比如学生十分熟悉的《ABC song》。复习导入法:复习就知引出新知。 律动导入法:字母操 2、Presentation 运用卡片、图片、动画等方法来呈现字母的形,示范准确发音,并示范正确书写顺序。让学生对字母能够认读和书写,还要掌握在单词中的正确发音,做到字母不离词。 故事教授法;直接教学法;多媒体教学吸引法;游戏教学法;音标衬托法(将字母与其能常发音的音标相结合,以音标衬托字母,以字母带动音标。) 3、Practice 字母操练我们可以采用游戏的形式。例如: 1. “What's missing?”游戏
Introduction to basic knowledge of primary school Chinese teaching Longshan primary school Hong-mei liu Everybody is good! Here is my pleasure to share with you my views on basic knowledge of primary school Chinese teaching. The development of anything from quantitative change to qualitative change, and from qualitative to quantitative change new. Primary school Chinese teaching, students to understand Chinese characters one by one, reach a certain amount, can read; Reading reaches a certain amount, can the composition. As the ancients cloud: "qian fu can read, could give." Primary school Chinese basic knowledge including pinyin, read, write, and so on aspects. To break through the primary school Chinese basic knowledge of the difficulties, we must also take corresponding measures in practice: A, stimulate students interest One is to make the students like their teacher. So there's a phrase said "a successful teacher, itself is a textbook". I think it is a successful teacher's standard, we should all efforts to push yourself to this realm. In the face of students, we should let our students have confidence in their teacher, admire his teacher. We can in their own personality, accomplishment and love to let the students like himself. Like teacher, like class, like on the subject, resulting in a very strong interest in learning. The second is to get the basic knowledge of classroom to life. Students can concentrate to the observing time generally can't more than thirty minutes, it must make good use of the precious time in class, improve the efficiency of their classroom. Especially the language basic knowledge learning is boring, more should make the classroom to life. We should use of textbooks, give students the opportunity to play, let them become a real master. I often and students together play a role, in this way, students can help themselves by the movements of the rich expression and interesting to understand the text, understand the meaning of them. Second, I will also according to the content and characteristics of Chinese basic knowledge teaching, to carry out some activities, such as looking for wrong character, tone of voice, speech sounds game solitaire, etc., these activities can sometimes influence the teaching process, but students in activities to cultivate the study interest, also improves the ability of learning. Second, pay attention to teaching methods One is focusing the difficulty, the breakthrough "pinyin". Chinese phonetic knowledge is the foundation of students to learn the language, and learn the language. How to let the students can learn this seemingly boring knowledge lively and interesting, but also a good grasp of, I communicate with school teachers often, and learn from their experience in teaching, to make students learn easily, learn more solid. Chinese pinyin is the tool that helps literacy, reading and learning mandarin. Students learning difficulties are often characterized by flat become warped lingual regardless, im read not to come out, and lateral nasal is difficult to distinguish. To these questions can be used with the aid of the Chinese characters sound learning pinyin and categorized resolution method. 2 it is to know a word to recognize more words, the breakthrough "literacy". As soon as possible in order to improve the efficiency of the literacy teaching, make students master the 3500 or so commonly, in the literacy teaching, we can make full use of the characteristics of lenovo literacy, let the students to master Chinese characters, and guide students to lenovo, through has carried off some commonly used Chinese characters, teach students reading (teaching we referred to as "more than a word with the word"). Here is the main method is: to familiar with life: born by a familiar
小学英语必备基础知识 基础知识 1.字母:26个字母的大小写 ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz 2.音标:48个音标 3.词汇:词汇量,近反义词 4.句子:大小写,标点符号 语法知识 一、名词:名词单复数,名词的格 (一)名词单复数 1.一般情况,直接加-s,如:book-books, bag-bags, cat-cats, bed-beds 2.以s. x. sh. ch结尾,加-es,如:bus-buses, box-boxes, brush-brushes, watch-watches 3.以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i, 再加-es,如:family-families, strawberry-strawberries 4.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v, 再加-es,如:knife-knives 5.不规则名词复数: man-men, woman-women, policeman-policemen, policewoman-policewomen, mouse-mice,child-children, foot-feet, tooth-teeth, fish-fish, people-people, Chinese-Chinese, Japanese-Japanese 不可数名词的复数就是原型:paper, juice, water, milk, rice, tea (二)名词的格 (1) 有生命的东西的名词所有格: a) 单数后加’s 如: Lucy’s ruler my father’s shirt b) 以s 结尾的复数名词后加’如: his friends’ bags c) 不以s 结尾的复数后加’s children’s shoes l并列名词中,如果把’s加在最后一个名词后,表示共有, 如: Tom and Mike’s car 汤姆和迈克共有的小汽车 l要表示所有物不是共有的,应分别在并列名词后加’s Tom’s and Mike’s cars 汤姆和麦克各自的小汽车 (2)表示无生命东西的名词通常用“ of +名词”来表示所有关系:如: a picture of the classroom a map of China 二、冠词:不定冠词,定冠词种类: (1)不定冠词:a / an 元音开头的可数名词前用an : an egg / an apple / an orange / an eraser / an answer / an ID card / an alarm clock / an actor / an actress / an e-mail / an address / an event / an example / an opera / an houran old man / an interesting book / an exciting sport / an action movie / an art lesson / (2)定冠词:the 定冠词的用法:
《小学英语课程标准》试题 一、填空(共10分) 1.基础教育阶段英语课程的总体目标是培养学生的综合语言运用能力。 2.基础教育阶段英语课程目标的各个级别均以学生语言技能、语言知识、情感态度、学习策略和文化意识五个方面的综合行为表现为基础进行总体描述。 3.语言技能包括听、说、读、写四个方面的技能以及这四种技能的综合运用能力。 4.新课程的最高宗旨和核心理念是一切为了学生的发展 5.学习策略指学生为了有效地学习和发展而采取的各种行动和步骤。英语学习的策略包括认知策略、调控策略、交际策略和资源策略等。 6.3一6年级英语教学评价的主要目的是激励学生的学习兴趣和积极性。评价形式应具有多样性和可选择性。评价应以形成性评价为主,以学生平时参与各种教学活动的表现和合作能力为主要依据。 7.英语课程在目标设定、教学过程、课程评价和教学资源的开发等方面都突出以学生为主体的思想。 8.从3年级开设英语课程的学校,5、6年级完成二级目标; 9.《标准》以学生“能做某事”的描述方式设定各级目标要求。教师应该避免单纯传授语言知识的教学方法,尽量采用“任务型”的教学途径。 10.教师要充分利用现代教育技术,开发英语教学资源,拓宽学生学习渠道,改进学生学习方式,提高教学效果。 二、判断正误 1.小学英语教学要创建以活动课为主的教学模式,充分利用听、做、说、唱、玩、演的方式,鼓励学生积极参与,大胆表达,侧重提高学生对英语的感受和初步用英语进行听、说、唱、演的能力,到了五、六年级也要发展初步的读写能力。(√) 2.小学英语教学的目标共分两段,一级的目标类别是语言技能方面的听做、说唱、读写、视听;二级语言技能的目标是听、说、读、写、玩、演、视听。此外,二级还有语言知识目标———语音、词汇、语法、功能、话题、情感态度目标、基本学习策略目标、文化意识目标。(√) 3.小学英语语言技能二级读的目标中,要求能认读所学词语;能根据拼读的规律读出简单的单词;能借助图片读懂简单的故事或小短文,并养成按意群阅读的习惯。(√)4.小学英语教学中要使用听、做、画、说、唱、背、玩、演、读、写诸种技巧和活动。但这些技巧要根据学生的学习需要与可能去选择搭配,不是用得越多越好。(√)5.小学英语教师必须转变角色,和小学生成为朋友。这要求教师首先改变教者的专断态度,即使在学习英语中,也要谦逊地把学生看作朋友;其次要有自信,自信能使小学生成为自己的朋友,肯和自己谈心。(√) 6.如果以听为训练的中心,用做和画帮助听,则做和画要比听稍后一点,要让学生先听音。(√) 7.玩、演的目的是听、说英语和记忆英语材料,最好在玩、演之后再读,以判断玩、演之中使用英语的正误,增加用、记英语的效果。(√) 8.现代化教学手段(媒体)对小学英语教学极为有效,传统教学手段则缺乏生气,如果学校缺乏现代化教学手段,教师只好用一张嘴、一本书、一枝粉笔进行教学。(╳) 三、选正题:下面每题四个备选答案中有一个正确答案,请选出。 1.小学英语教学的重点是___D___ 。A.组织课堂教学活动B.培养学生自学英语的能力C.帮助学生模仿√D.培养学生用英语进行交流的能力和兴趣 2.小学英语教材要有利于培养学生的学习兴趣与语感,了解英语国家的文化、习俗,学生对异国文化的正确态度。教材还要培养学生____C__ 和做事情的能力,提高他们的思维能力和认识世界的能力。 A.学习能力B.自我管理能力√C.用英语进行交流D.创新能力
小学英语基础知识 一、小学英语形容词性物主代词 1、形容词性物主代词8个: My your his her its our your their 我的你的他的她的它的我们的你们的他(她、它)们的2、形容词性物主代词的特点: 1)译成汉语都有"的" 如: my 我的 their 他们的 2)后面加名词:如: my backpack his name 3)前后不用冠词 a an the This is a my eraser(错误) That is your a pen(错误) It's his the pen(错误) 3、I(物主代词)my you(物主代词)your he (物主代词)her we (物主代词) our 注:在变物主代词时,把原题所给的词加上的,再译成单词就可以了。 二、小学英语名词性物主代词 1、名词性物主代词和形容词性物主代词一样有8个: GAGGAGAGGAFFFFAFAF
Mine yours his hers its ours yours theirs 我的你的他的她的它的我们的你们的他(她、它)们的2、名词性物主代词的特点: 1)译成汉语都有"的" 2)后面不加名词 3)名词性物主代词=形容词性物主代词+名词 如:the pen is mine 钢笔是我的(mine=my pen) 三、小学英语单数的句子变成复数的句子 把单数的句子成复数的句子很简单:变法是把能变成复数的词变成复数,但a或an要把去掉。特殊疑问词、形容词、国家及地点通常不变。 Eg:把下列句子变成复数 1, I have a car ---- we have cars 2, He is an American boy. ---- They are American boys 3, It is a car ---- They are cars 4,This is an eraser ---- These are erasers 5,That is a backpsck ----- Those are backpacks 6,I'm an English teather ------ We are English teathers GAGGAGAGGAFFFFAFAF