
第一章:
1.1What is the purpose of a database?数据库的目的
The purpose of a database is to help people track(跟踪监测) of things.
1.2What is the most commonly used type of database?最常见的数据库类型
The most commonly used type of database is the relational database.
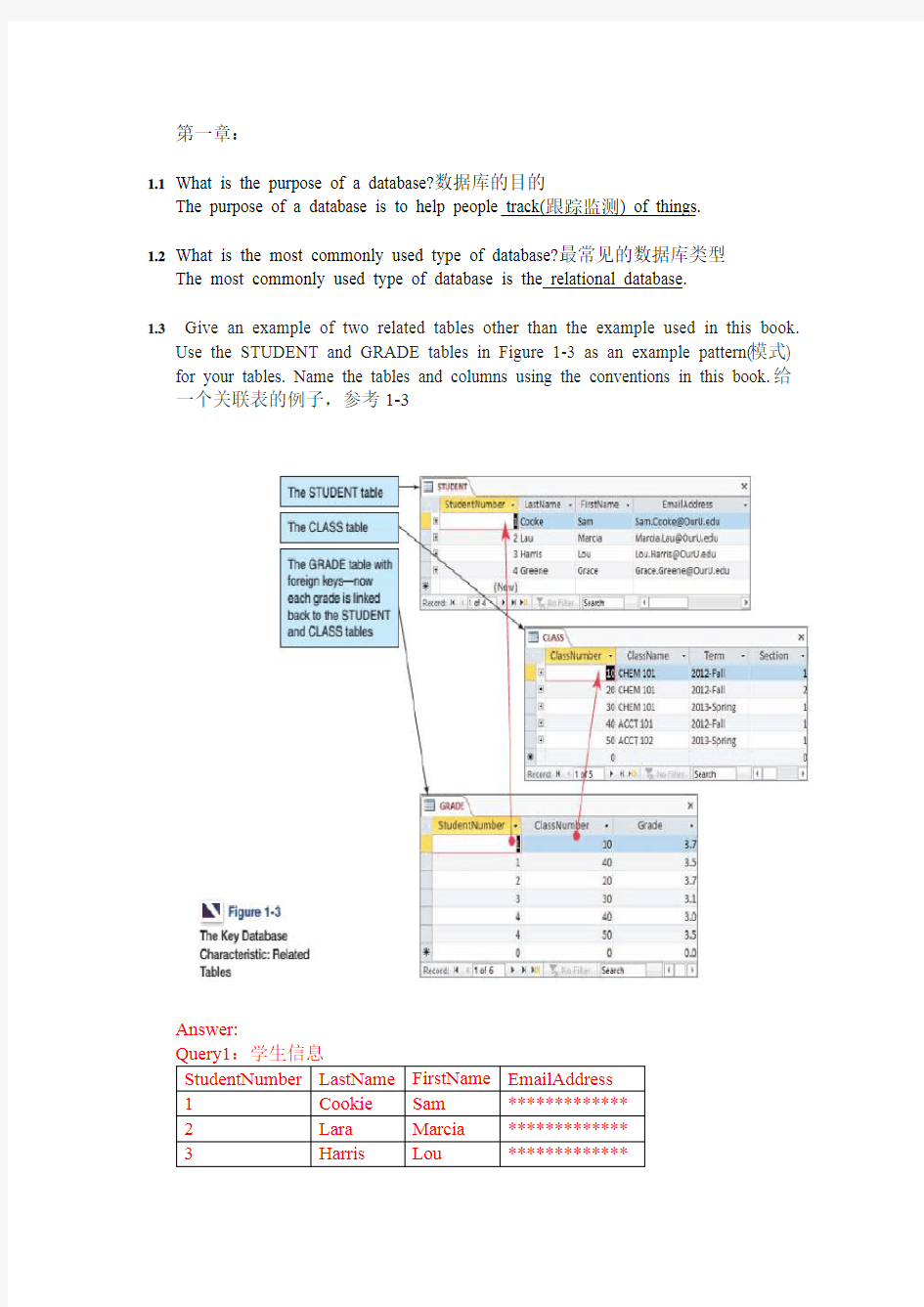
1.3Give an example of two related tables other than the example used in this book.
Use the STUDENT and GRADE tables in Figure 1-3 as an example pattern(模式) for your tables. Name the tables and columns using the conventions in this book.
给一个关联表的例子,参考1-3
Answer:
1.4For the tables you created in Review Question 1.3, what are the primary keys of
each table? Do you think that any of these primary keys could be surrogate(代理) keys?每张表的主码?这些主码可以是代理码吗?
Query1: StudentNumber
Query2: StudentNumber, RoomNumber
Yes, both.
1.5 Explain how the two tables you provided in Review Question 1.3 are related. Which table contains the foreign key, and what is the foreign key?
The primary key of Q1 were added to the Q2 with a primary key of StudentNumber to uniquely identify each row.
In Q2 StudentNumber and RoomNumber each now serves as a foreign key.
1.6 Show your two tables from Review Question 1.3 without the columns that represent the relationships. Explain how the value of your two tables is diminished(减少) without the relationships.在你的表中去掉代表关系的列,解释没有关系的表的value如何减少?
1.7 Define the terms data and information. Explain how the two terms differ.定义术语data和information,解释它俩的不同。
Answer: Data are recorded facts and numbers.
We can define information as:
Knowledge derived from data.
Data presented in a meaningful context.
Data processed by summing, ordering, averaging, grouping, comparing or other similar operations.
1.8 Give an example of information that could be determined using the two tables you provided in your answer to Review Question 1.3.
Anna Smith lives in 4-454 which the rent is 1300.
1.9 Give examples of a single-user database application and a multiuser database application other than the ones shown in Figure 1-5.举例子,单用户和多用户的数据库应用,除表1-5之外。
single-user: Cloud Service
multi-user: File Management System
1.10 What problem can occur when a database is processed by more than one user?
当数据库被不止一个用户处理会导致什么问题?
Answer: When more than one user employs a database application, these is always the chance that one user's work may interfere with other's.
1.11 Give an example of a database application that has hundreds of users and a
very large and complicated database. Use an example other than one in Figure 1-5.
举一个有成百上千个用户和一个庞大而复杂数据库的数据库应用,除表1-5以外。
Answer: Selection lesson system
选课系统
1.12 What is the purpose of the largest databases at e-commerce companies such
as https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,?
像亚马逊这样的电商公司有着最大的数据库的目的是什么?
Answer: The largest database are those that track customer browser behavior. (用来记录用户的浏览行为)
1.13 How do the e-commerce companies use the databases discussed in Review Question 1.12?
电商公司如何使用数据库?
Answer: E-commerce companies use Web activity databases to determine which items on a Web page are popular and successful and which are not.
1.14 How do digital dashboard and data mining applications differ from transaction processing applications?
数字仪表板和数据挖掘应用程序在事务处理应用上有何不同?
Answer: Digital dashboard and other reporting systems assess past and current performance. Data mining applications predict future performance.
1.15 Explain why a small database is not necessarily simpler than a large one.
解释为什么一个小的数据库不一定比大的数据库简单?
Answer: Supposed we have 2 company which are different in sales but have similar database. Though the difference in sale, both have the same kinds of data, about the same number of tables of data, about the same level of complexity in data relationships. Only the amount of data varies from one to the other. Thus, although a database for a small business may be small, it is not necessarily simple. (一句话,麻雀虽小五脏俱全)
1.16 Explain the components in Figure 1-7.解释图1-7的成分要素
A database system is defined to consist of five components:users, the database application,Structured Query Language (SQL), the database management system (DBMS), and the database.
a. Users employ a database application to keep track of things. They use forms to read, enter, and query data, and they produce reports to convey information.
b. A database application is a set of one or more computer programs that serves as an intermediary between the user and the DBMS.
c. Structured Query Language (SQL), an internationally recognized standard language that is understood by all commercial DBMS products, in database processing and the fact that database applications typically send SQL statements to the DBMS for processing.
d. The database management system (DBMS) is a computer program used to create, process, and administer the databas
e.
e. The database is a collection of related tables and other structures.
1.17 What are the functions of application programs?
应用程序的功能是什么?
Answer:
? Create and process forms
? Process user queries
? Create and process reports
? Execute application logic
? Control application
1.18 What is Structured Query Language (SQL), and why is it important? Structured Query Language (SQL) is an internationally recognized standard language. Because it nearly can be understood by all commercial DBMS products, in database processing, database applications typically send SQL statements to the DBMS for processing. (在数据库方法中,数据库应用向DBMS发送SQL语句)
1.19 What does DBMS stand for?
Database management system
1.20 What are the functions of the DBMS?
? Create database、Create tables
? Create supporting structures
? Read database data
? Modify (修改)(insert, update, or delete) database data
? Maintain database structures
? Enforce rules
? Control concurrency(并发控制)
? Provide security
? Perform backup and recovery (备份与恢复)
1.21 Name three vendors of DBMS products.
MySQL,Microsoft SQL Server,IBM
1.22 Define the term database.(数据库一词的定义)
A database is a self-describing collection of integrated tables.
1.23 Why is a database considered to be self-describing?
A database is self-describing because it contains a description of itself. Thus, databases contain not only tables of user data, but also tables of data that describe that user data.
1.24 What is metadata(元数据)? How does this term pertain(属于) to a database? databases contain not only tables of user data, but also tables of data that describe that user data. Such descriptive data is called metadata because it is data about data.(元数据是描述数据的数据)
1.25 What advantage is there in storing metadata in tables?
You can examine(调查) metadata to determine if particular tables, columns, indexes, or other structures exist in a database.
可以通过调查元数据得知某些特定的结构是否存在于数据库中
1.26 List the components of a database other than user tables and metadata. 除了用户表和元数据以外的其他数据库组件。
? Indexes
? Stored procedures
? Triggers
? S ecurity data
? Backup/recovery data
1.27 Is Microsoft Access a DBMS? Why or why not?
No, Microsoft Access is not just a DBMS. Because it is a personal database system: a DBMS plus an application generator. Although Microsoft Access contains a DBMS engine that creates, processes, and administers the database, it also contains form, report, and query components that are the Microsoft Access application generator.(应用程序生成器)
1.28-1.35了解就好,太偏太细,感觉不会考
1.28 Describe the components shown in Figure 1-15.
Components of a Microsoft Access Database System
Microsoft Access contains a DBMS engine that creates, processes, and administers the database, it also contains form, report, and query components that are the Microsoft Access application generator.
1.29 What is the function of the application generator in Microsoft Access?
The application generator consists of applications components that create and process forms, reports, and queries.
1.30 What is the name of the DBMS engine within Microsoft Access? Why do we rarely hear about that engine?
The current DBMS engine within Microsoft Access is called the Access Database Engine (ADE). ADE is a Microsoft Office specific version of Microsoft‘s Joint Engine Technology (JET or Jet) database engine. But you seldom hear about Jet because Microsoft does not sell Jet as a separate product. ADE是Jet引擎的一个版本,很少听说是因为Jet不是一个独立销售的产品
1.31 Why does Microsoft Access hide important database technology?
Because it is an effective strategy for beginners working on small databases
1.32 Why would someone choose to replace the native Microsoft Access DBMS engine with SQL Server?
You would do this if you wanted to process a large database or if you needed the advanced functions and features of Microsoft SQL Server.
1.33 Name the components of an enterprise-class database system.
1.34 Name and describe the four categories of database applications that would use an enterprise-class database system.
client/server applications:the application program is a client that connects to a database server. Client/server applications often are written in programming languages such as https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,, C++, or Java.
e-commerce applications:run on a Web server
reporting applications:publish the results of database queries on a corporate portal or other Web site.
XML Web services applications:use a combination of the XML markup language and other standards to enable program-to-program communication.
1.35 How do database applications read and write database data?
All of these database applications get and put database data by sending SQL statements to the DBMS.
1.35How do database applications read and write database data?(数据库应用程序是如何读写数据库数据的?PPT: First class P23)
Answer:the application program first queries the DBMS for data (again using SQL). The application then formats the query results as a report. (首先在DBMS中使用SQL查询数据,然后将查询结果作为报表显示)
1.36Name the five DBMS products described in this chapter, and compare them in terms of power, features, and difficulty of use.(列出本章中5个DBMS产品,并比较他们的功效、特性和使用的难易程度PPT:second class p39)
Answer: Microsoft Access, MySQL, SQL Server, DB2, and Oracle Database.(这已经是按比较顺序来的了)
1.37List several consequences of a poorly designed database.(列出几个数据库设计不良的后果)
Answer:
(1)They may require application developers to write overly complex and contrived SQL to get –wanted data.(开发人员需要编写过于复杂的SQL来获取数据)(2)they may be difficult to adapt to new and changing requirements.(很难适应新的不断变化的需求)
(3)they may fail in some other way.(或其他)
1.38Explain two ways that a database can be designed from existing data.(解释两种可以用现有数据设计的数据库PPT: second class p13)
Answer:
(1)The first type of database design involves databases that are constructed from existing
(2)A second way that databases are designed is for the development of new information systems.(p17)
1.39 What is a data warehouse? What is a data mart?(什么是数据仓库?什么是数据集市)
Answer:data from an operational database, such as a CRM or ERP database, may be copied into a new database that will be used only for studies and analysis. Such databases are used in facilities called data warehouses and data marts. (笔记)
1.40Describe the general process of designing a database for a new information system.(描述为一个新的信息斯通设计数据库的一般过程)
Answer:(1)create data model from application requirements
( 2)transform data model into database design (PPT: second class p12)
1.41 Explain two ways that databases can be redesigned.(解释两种数据库重设计的方式PPT:third class p19或12)
Answer:
(1)In the first, a database is adapted to new or changing requirements. This
process sometimes is called database migration. In the migration process, tables may be created, modified, or removed; relationships may be altered; data constraints may be changed; and so forth.
(2)The second type of database redesign involves the integration of two or more
databases. This type of redesign is common when adapting or removing legacy systems. It is also common for enterprise application integration, when two or more previously separate information systems are adapted to work with each other.
1.42What does the term database migration mean?(数据库迁移是什么意思)
Answer:The process of a database is adapted to new or changing requirements.
1.43Summarize the various ways that you might work with database technology.(总结你可能使用数据库技术的不同方式)
Answer:
In our career, we may work with database technology as either a user or as a database administrator.
(1)As a user, you may be a knowledge worker who prepares reports, mines data, and does other types of data analysis or you may be a programmer who writes applications that process the database. (作为用户时)
(2)Alternatively, you might be a database administrator who designs, constructs, and manages the database itself. Users are primarily concerned with constructing SQL statements to get and put the data they want. Database administrators are primarily concerned with the management of the database.(作为数据库管理员时)
1.44 What job functions does a knowledge worker perform?(知识工作者(意会……)工作职能是什么)
Answer:preparing reports, mining data, and doing other types of data analysis.
1.45 What job functions does a database administrator perform?(数据库管理员的工作职能是什么)
Answer:designing, constructing, and managing the database itself.
1.46 Explain the meaning of the domains(域)in Figure 1-23.(解释图中的域的意思)(这题找不到= =)
Answer:
Knowledge workers
Programmers
Database administrators
1.47 What need drove the development of the first database technology?
Answer:The need for data integration drove the development of the first database technology.
1.48 What are Data Language/I and CODASYL DBTG?
Answer:Data Language/I (DL/I) used hierarchies or trees (see Appendix G) to represent relationships.
This subcommittee developed a standard data model that came to bear its name—the CODASYL DBTG model. It was an unnecessarily complicated model. This data relationship used data structures called networks.
1.49 Who was E. F. Codd?
ANSWER: E.F.Codd was a little-known IBM engineer published a paper in the Communications of the ACM3 in which he applied the concepts of a branch of m athematics called relational algebra to the problem of ―shared data banks,‖ as databases were then known. The results of this work are now the relational model for databases, and all relational database DBMS products are built on this model.
1.50What were the early objections to the relational model?(最早的关系模型的反对是什么)
Answer:Early objections included (1) too theoretical for practical implementation, (2) too slow, and(3) so much storage would be required that the model would never be useful in thecommercial world
1.51 Name two early relational DBMS products.
ANSWER: Oracle Database, DB2.
1.52 What are some of the reasons for the success of Oracle Database?
(数据库成功的原因是什么?)
ANSWER:
Oracle Database achieved success for many reasons, one of which was that(1)it would run on just about any computer and just about any operating system. (2)Oracle Database had, and continues to have, an elegant and efficient internal design.
1.53 Name three early personal computer DBMS products.
ANSWER:
dBase, R:base, Paradox.
1.54 What happened to the products in your answer to Review Question 1.53? ANSWER:
dBase was the most successful of the early products, but another product, R:base, was the first to implement true relational algebra and other operations on the PC. Later, another relational DBMS product named Paradox was developed for personal computers. Eventually, Paradox was acquired by Borland.
Microsoft Access killed R:base and Paradox, and then Microsoft bought a dBase ―work-alike‖ product called FoxPro and used it to eliminate dBase
1.55 What was the purpose of OODBMS products? State two reasons that OODBMS products were not successful.(面向对象数据库管理系统产品的目的是什么?陈述OODBMS产品均未成功的两个原因)
ANSWER:
These products were designed to make it easy to store the data encapsulated in OOP objects
There were two reasons for their lack of acceptance. First, using an OODBMS required that the relational data be converted from relational format to object-oriented format. By the time OODBMS emerged, billions upon billions of bytes of data were stored in relational format in organizational databases. No company was willing to undergo the expensive travail of converting those databases to be able to use the new OODBMS.
Second, object-oriented databases had no substantial advantage over relational databases for most commercial database processing. As you will see in the next chapter, SQL is not object oriented. But it works, and thousands of developers have created programs that use it. Without a demonstrable advantage over relational databases, no organization was willing to take on the task of converting their data to OODBMS format.
1.56 What characteristic of HTTP was a problem for database processing applications?
ANSWER:
HTTP is a stateless protocol; a server receives a request from a user, processes the request, and then forgets about the user and the request. Many database interactions are multistage. A customer views products, adds one or more to a shopping cart, views more products, adds more to the shopping cart, and eventually checks out. A stateless protocol cannot be used for such applications.
1.57 What is an open source DBMS product? Which of the five DBMS products that you named in answering Review Question 1.36 is historically an open source DBMS product?(什么是一个开源的数据库管理系统产品?)
ANSWER:
the MySQL DBMS 答案待商榷
1.58 What has been the response of companies that sell proprietary DBMS products to the open source DBMS products? Include two examples in your answer. ANSWER:
One interesting outcome of the emergence of open source DBMS products is that companies that typically sell proprietary (closed source) DBMS products now offer free versions of their products. For example, Microsoft now offers SQL Server 2008 R2 Express (www.microsoft. com/express/Database), and Oracle Corporation makes its Oracle Database 10g Express Edition available for free.
1.59 What is XML? What comment did Bill Gates make regarding XML?(什么是XML?比尔盖茨对此做了什么评论?)
ANSWER:
XML means Extensible Markup Language.
Bill Gates said that ―XML is the lingua-franca of the Internet Age.‖
1.60 What is the NoSQL movement? Name two applications that rely on NoSQL databases.
ANSWER:
It‘s the work is really on databases are often based on XML.
Two applications that rely on NoSQLdatabases: Facebook and Twitter.
第二章
2.1 What is a business intelligence (BI) system?
ANSWER:
Application refers to the collection of commercial information, the integration, analysis and the technical reports.
2.2 What is an ad-hoc query?
ANSWER:
ad-hoc SQL queries is how SQL is used to ―ask questions‖ about the data in the database.
2.3 What does SQL stand for, and what is SQL?
ANSWER:
SQL stand for Structured Quqery Language. SQL is not a complete programming language, like Java or C#. Instead, it is called a data sublanguage, because it has only those statements needed for creating and processing database data and metadata.
2.4 What does SKU stand for? What is an SKU?
ANSWER:
SKU stand for stock-keeping unit. SKU is a unique identifier for each particular item that Cape Codd sells或SKU is an integer value that identifies a particular product sold by Cape Codd.
2.5 Summarize how data were altered and filtered in creating the Cape Codd data extraction.
ANSWER:
the ORDER_ITEM table stores an extract of the items purchased in each order. There is one row in the table for each item in an order, and this item is identified by its SKU.
The OrderNumber Column in ORDER_ITEM relates each row in ORDER_ITEM to the corresponding OrderNumber in the RETAIL_ORDER table. SKU identifies the actual item purchased by its stock-keeping unit number. Further, the SKU column in ORDER_ITEM relates each row in ORDER_ITEM to its corresponding SKU in the SKU_DATA table
2.6 Explain, in general terms, the relationships among the RETAIL_ORDER, ORDER_ITEM,and SKU_DATA tables.
ANSWER:
The RETAIL_ORDER table has data about each retail sales order, the ORDER_ITEM table has data about each item in an order, and the SKU_DATA table has data about each stock-keeping unit (SKU)
2.7 Summarize the background of SQL.
ANSWER:
SQL was developed by the IBM Corporation in the late 1970s. It was endorsed as a national standard by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986 and by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
2.8 What is SQL-92? How does it relate to the SQL statements in this chapter? ANSWER:
Subsequent versions of SQL were adopted in 1989 and 1992. The 1992 version is sometimes referred to as SQL-92, or sometimes as ANSI-92 SQL. 缺少第二问答案2.9 What features have been added to SQL in versions subsequent to the SQL-92?
什么样的功能已被添加到SQL版本SQL-92后续
ANSWER: All the new versions of SQL support for Extensible Markup Language (X ML) and there are many other common language features.最重要的功能是添加了对XML语句的支持
这是ppt里面复制的话:Each of these added new features or extended existing SQL features, the most important of which for us is SQL support for Extensible
Markup Language (XML).
2.10 Why is SQL described as a data sublanguage?
ANSWER: Because it has only those statements needed for creating and processing d atabase data and metadata. You can use SQL statements in many different ways.
You can submit them directly to the DBMS for processing. You can embed SQ L statements into client/server application programs. You can embed them into Web pages, and you can use them in reporting and data extraction programs. Yo u also can execute SQL statements directly from Visual https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html, and other d evelopment tools.
百度翻译:它被称为一个数据子语言,因为它只有那些创建与数据库数据处理和元数据需要的报表。你可以在许多不同的方式使用SQL语句。您可以直接提交给数据库管理系统处理。您可以嵌入SQL语句为客户端/服务器应用程序。您可以将它们嵌入到网页中,并且您可以使用它们来报告和数据提取程序。你还可以执行SQL语句直接从Visual Studio .NET等开发工具。
2.11 What does DML stand for? What are DML statements?
ANSWER: DML stand for Data Manipulation Language, which is a category of SQL. Data manipulation language (DML) statements, which are used for querying, insertin g, modifying, and deleting data.
2.12 What does DDL stand for? What are DDL statements?
ANSWER: DDL stand for Data definition language, which is a category of SQL. Data definition language (DDL) statements, which are used for creating tables, relationshi ps, and other structures
2.13 What is the SQL SELECT/FROM/WHERE framework?
ANSWER: The basic form of SQL queries uses the SQL SELECT/FROM/WHERE f ramework.
In this framework:
? The SQL SELECT clause specifies which columns are to be listed in the query result s.
? The SQL FROM clause specifies which tables are to be used in the query.
? The SQL WHERE clause specifies which rows are to be listed in the query results. SQL查询的基本形式采用SQL选择/从/框架。在这个框架中:
?SQL SELECT子句中指定的列将查询结果中的列。
?FROM子句中指定的SQL表用于查询。
?SQL WHERE子句指定哪些行是查询结果中的列。
(2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13解释那些东西都是ppt的原话)
2.14 Explain how Microsoft Access uses SQL.(ppt:第四课p4之后不造咋概括。。答案写的也有点奇怪,,不是很懂)
ANSWER: Every time you process a form, create a report, or run a query Microsoft Access generates SQL and sends that SQL to Microsoft Access‘ internal ADE DBMS engine. To do more than elementary database processing, you need to uncover the SQL hidden by Microsoft Access. Further, once you know SQL, you will find it easier to write a query statement in SQL rather than fight with the graphical forms, buttons.
2.15 Explain how enterprise-class(企业级)DBMS products use SQL.(ppt 第五课应该都是。。。同上一题懵逼。。。)
ANSWER: Enterprise-class DBMSs such as Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2, Oracle Database 11g, Oracle MySQL 5.5, and IBM DB2 require that you know SQL. With these products, all data manipulation is expressed using SQL.
The Cape Codd Outdoor Sports sale extraction database has been modified to include
two additional tables, the Inventory table and the Warehouse table. The table schemas for these tables, together with the Retail Order, Order Item, and SKU_ Data tables, are as follows:
RETAIL_ORDER (OrderNumber, StoreNumber, StoreZip, OrderMonth, OrderYear, OrderTotal)
ORDER_ITEM (OrderNumber, SKU, Quantity, Price, ExtendedPrice)
SKU_DATA (SKU, SKU_Description, Department, Buyer)
WAREHOUSE (WarehouseID, WarehouseCity, WarehouseState, Manager, Squarefeet)
INVENTORY (WarehouseID, SKU, SKU_Description, QuantityOnHand, QuantityOnOrder)
The five tables in the revised Cape Codd database schema are shown in Figure
2-24. The column characteristics for the Warehouse table are shown in Figure 2-25,
and the column characteristics for the Inventory table are shown in Figure 2-26. The data for the Warehouse table are shown in Figure 2-27, and the data for the Inventory table are shown in Figure 2-28.
If at all possible, you should run your SQL solutions to the following questions against an actual database. a Microsoft access database named Cape-Codd.accdb is
available on our Web site (https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,/kroenke) that contains all the tables and data for the Cape Codd Outdoor Sports sales data extract database. also
available on our Web site are SQL scripts for creating and populating the tables for the
Cape Codd database in Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle Database, and MySQL.
2.16 There is an intentional flaw in the design of the INVENTORY table used in these exercises. This flaw was purposely included in the INVENTORY tables so you can answer some of the following questions using only that table. Compare the SKU and INVENTORY tables, and determine what design flaw is included in INVENTORY.Specifically, why did we include it?
比较SKU和INVENTORY表,INVENTORY中有个设计缺陷,说明为什么会产生这个缺陷
不懂。。。。。
Use only the Inventory table to answer Review Questions 2.17 through 2.39: SELECT 查找列(去除重复用DISTINCT)
FROM 表名
WHERE 从行的角度选择满足条件的行
GROUP BY 分组
HA VING 从分组的角度选择满足条件的分组
ORDER BY 根据指定的列对结果集进行排序,默认升序,降序需要使用DESC 关键字
2.17 Write an SQL statement to display SKU and SKU_Description.
SELECT SKU,SKU_Description
FROM INVENTORY;
2.18 Write an SQL statement to display SKU_Description and SKU.
SELECT SKU_Description,SKU
FROM INVENTORY;
(2.17、2.18和搜的那份答案不一样)
2.19 Write an SQL statement to display WarehouseID.
SELECT WarehouseID
FROM WAREHOUSE;
2.20 Write an SQL statement to display unique WarehouseIDs.
SELECT WarehouseIDs
FROM WAREHOUSE;
2.21 Write an SQL statement to display all of the columns without using the SQL asterisk(*) wildcard character.
SELECT WarehouseID, WarehouseCity, WarehouseState, Manager, SquareFeet FROM WAREHOUSE.
SELECT WarehouseID.SKU,SKU_Description,QuantityOnHand,QuantityOnHand FROM INVENTORY;
2.22 Write an SQL statement to display all of the columns using the SQL asterisk (*) wildcardcharacter.
SELECT *
FROM WAREHOUSE.
SELECT *
FROM INVENTORY;
2.23 Write an SQL statement to display all data on products having a QuantityOnHand
greater than 0.
SELECT *
FROM INVENTORY
WHERE QuantityOnHand>0;
2.24 Write an SQL statement to display the SKU and SKU_Description for products havingQuantityOnHand equal to 0.
SELECT SKU,SKU_Description
FROM INVENTORY
WHERE QuantityOnHand=0;
2.25 Write an SQL statement to display the SKU, SKU_Description, and WarehouseID forproducts that have a QuantityOnHand equal to 0. Sort the results in ascending order byWarehouseID.
SELECT SKU,SKU_Description,WarehouseID
FROM INVENTORY
WHERE QuantityOnHand=0
ORDER BY WarehouseID;
2.26 Write an SQL statement to display the SKU, SKU_Description, and WarehouseID for products that have a QuantityOnHand greater than 0. Sort the results in descending
order by WarehouseID and in ascending order by SKU.
SELECT SKU, SKU_Description,WarehouseID
FROM INVENTORY
WHERE QuantityOnHand> 0
ORDER BY WarehouseID DESC,SKU ASC;
2.27 Write an SQL statement to display SKU, SKU_Description, and WarehouseID for all products that have a QuantityOnHand equal to 0 and a QuantityOnOrder greater than
0. Sort the results in descending order by WarehouseID and in ascending order by SKU.
SELECT SKU, SKU_Description,WarehouseID
FROM INVENTORY
WHERE QuantityOnHand = 0 AND QuantityOnOrder> 0
ORDER BY WarehouseID DESC,SKU ASC
2.28 Write an SQL statement to display SKU, SKU_Description, and WarehouseID for all products that have a QuantityOnHand equal to 0 or a QuantityOnOrder equal to 0. Sort the results in descending order by WarehouseID and in ascending order by SKU.
SELECT SKU, SKU_Description,WarehouseID
FROM INVENTORY
WHERE QuantityOnHand = 0 OR QuantityOnOrder = 0
ORDER BY WarehouseID DESC,SKU ASC;
2.29 Write an SQL statement to display the SKU, SKU_Description, WarehouseID, and
QuantityOnHand for all products having a QuantityOnHand greater than 1 and less than 10. Do not use the BETWEEN keyword.
SELECT SKU, SKU_Description,WarehouseIDQuantityOnHand
FROM INVENTORY
WHERE QuantityOnHand>1 AND QuantityOnHand< 10
ORDER BY WarehouseID DESC,SKU ASC;
环境与材料科学技术的前沿进展 刘艳艳武汉理工大学资源与环境工程学院 资源与环境已成为当今世界发展的主题。经济与资源、环境之间的和谐发展日益广泛受到关注。如何合理利用资源、保护环境,同时促进经济的增长,这对相应学科的科学与技术提出了高要求,也已成为全球化的重要议题。2015环境与材料科学技术学术研讨会在武汉理工大学资源与环境工程学院院长宋少先教授的主持下拉开帷幕。出席开幕式的人员包括圣路易斯波多西自治大学校长ManuelVilla、武汉理工大学副校长康灿华、圣路易斯波多西自治大学物理研究所所长JoséLuisArauzLara、武汉理工大学新材料研究所所长余家国教授等,还包括武汉理工大学资环学院、理学院、化生学院、材料复合新技术国家实验室等单位百余名师生参加。研讨会主题是“环境与材料科学技术”,会议旨在为中墨两国合作搭建潜在的平台,为环境、材料、能源等多方领域交流最新研究成果提供一个交流的机会。研讨会主题围绕环境、材料、能源、地理空间科学与技术等领域进行了交流,包括1场大会报告与4组分会场报告,双方与会代表共进行37场次报告,展示了双方各自最新研究成果,探讨了环境、材料与能源等领域的发展趋势,为日后合作发展提供了机会。本研讨会获得了中国教育部、武汉理工大学以及圣路易斯波多西自治大学的大力支持。武汉理工大学康灿华副校长在研讨会开幕式上发言,希望利用本次机会充分展示该校在环境与材料科学技术领域的研究成果和特色,推动该校在该领域学科建设的发展并提升国际影响。ManuelVilla校长介绍了圣路易斯波多西自治大学的学校历史、学科结构及对外合作项目,希望两校在科研合作与学生交流等方面开展深入合作,为双方优秀学者和学生搭建良好的学术交流平台。武汉理工大学余家国教授在大会报告中介绍了用于生产太阳能燃料的石墨烯光催化材料的研究进展与发展趋势。利用太阳能转化制备太阳能燃料目前被认为是解决未来全球能源与环境问题的主要策略之一。其中利用光催化水产氢和还原二氧化碳制甲烷已经成为利用太阳光制备太阳能燃料的重要且有前景的方法,可以实现清洁、经济以及再生等生产。通常基于TiO2光催化产氢强烈依赖于触媒类型与数量,这是因为仅有TiO2不具备很高的光催化性能,需要添加Pt作为触媒,这样才能增强TiO2的光催化产氢性能,然而Pt更是稀有且昂贵的材料。因此,便宜且来源丰富的材料便成了触媒的另外选择。比如基于石墨烯的纳米复合材料作为光催化剂具备增强光催化产氢和二氧化碳还原的能力,能将太阳能转化成化学能。余家国教授对在基于石墨烯的纳米复合材料在光催化产氢和二氧化碳还原方面的设计与制造研究成果进行了介绍与分享。 圣路易斯波多西自治大学的MagdalenoMedi-na-Noyola教授作了题为“StructuralRelaxiationandAgingofGlassesandPhysicalGels:aNon-equilibriumStatisticalThermodyn amicTheory的大会报告。有一项关于非均衡液体不可逆过程的非均衡统计热力学理论被用来表述淬火液体结构与动力学的非稳态演变,该理论提出一个方案:演变时间是一个基础的变量。该方案为类玻璃材料在高填充率下的老化行为以及低密度的类凝胶材料的形成过程,方案设计符合通用情况,也符合各系统下的分子内作用过程。比如硬体系和Lennard-Jones简单液体等具体模型体系都能很好地解释这个预计方案。其定性定量准确度可以通过对比模拟和实验结果进行评估。武汉理工大学资源与环境工程学院张一敏教授作了题为“VanadiumExtractionfromVanadium-bearingCarbonaceousShaleinChina”的大会报告。钒作为
电子信息科学与技术专业本科培养计划 Undergraduate Program for Electronic Information Science and Technology 一、业务培养目标 ⅠEducational Objectives 本专业培养电子信息科学与技术高级专门人才,具备电子信息科学与技术的基础理论和基本知识,接受严格的科学实验训练和科学研究初步训练,有较强的创新意识,能够在电子、信息、计算机及相关领域和行政部门从事科学研究、教学、科技开发、产品设计、生产技术或管理的工作。 This program aims at training advanced and special talents in the field of electronic information science and technology and electronic science and technology, who should receive basic trainings on scientific experiment and research, master basic theory, knowledge and skills in electronic information science and technology, and are capable of jobs about researching, teaching, sci-tech development, engineering design or management in fields of electronics, information, computer and governmental administration. 二、业务培养要求 ⅡEducational Requirements 本专业学生主要学习电子信息科学与技术的基础理论和技术,受到科学实验与科学思维的训练,具备本学科及相关领域的应用研究与技术开发的能力。 毕业生应具备以下几方面的知识和能力: 1.掌握数学、物理等方面的基础理论和基本知识; 2.掌握电子信息科学与技术、计算机科学与技术等方面的基础理论、专业知识与技能; 3.了解相近专业的一般原理和知识; 4.熟悉国家电子信息产业政策及国内外有关知识产权的法律法规; 5.了解电子信息科学与技术的理论前沿、应用前景和最新发展动态,以及电子信息产业发展状况; 6.掌握资料查询、文献检索及运用现代信息技术获取相关信息的基本方法,具有初步的电子设计、 科学实验、论文撰写及学术交流的能力; 7.具有较强的外语综合应用能力,特别是听说能力。在今后工作和社会交往中能用外语进行口头 和书面的信息交流,能熟练地进行外文阅读,有一定的科技外语能力; 8.具有较强的创新意识。 Students of this program are mainly required to acquire basic theory and technology of electronic information and technology, receive basic trainings on scientific experiment and thinking, and have competency for scientific research and technological development. The graduates are also required to obtain the knowledge or abilities as follows: 1.Mastering basic theory and knowledge of both physics and mathematics; 2.Mastering basic principles and professional knowledge of electronic information science and technology together with computer science and technology; 3.Understanding common theory and knowledge of related fields; 4.Understanding policies of national IT industry as well as laws and regulations about intellectual property right both at home and abroad; 5.Acquiring advanced theory, application prospect and latest development of electronic information science and technology; 6.Acquiring abilities for literature retrieval, information inquiry and data obtaining; having competencies for preliminary electronic design, scientific experiment, paper writing and academic exchange;
《中间件及软件组件》复习题 任课老师:祁明龙 时间:第一周——第八周 2012-4-8 1.什么Remote Method Invocation? 2.什么是POJO? 3.什么是EJB? 4.什么是Stateless Session Bean? 5.什么是Stateful Session Bean?与SLSF的区别是什么? 6.什么是EJB容器?试举出两个以上的产品。 7.什么是WEB容器?试举出两个以上的产品。 8.什么是JDBC API?它的标吧是什么?试举出三个以上的类。 9.JDBC-ODBC桥的数据源URL的格式是什么? 10.试说明MySql URL jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/students每部分的含义。 11.一个Java接口要转变成RMI接口,需要继承什么接口?捕获什么异常? 12.一个Java Bean要能“序列化”,需要实现什么接口? 13.一个java.sql.ResultSet对象能序列化吗? 14.一个java.util.ArrayList对象能序列化吗? 15.一个java.util.ArrayList对象和java.util.List使用方法的差别是什么? 16.什么是JNDI? 17.jdk1.x的RMI JNDI 命名目录服务器是什么? 18.RMI/IIOP命名目录服务器是什么? 19.Java CORBA命名目录服务器是什么? 20.Jboss是什么服务器?带WEB服务器吗?带JNDI服务器吗? 21.GlassFish是什么服务器?带WEB服务器吗?带JNDI服务器吗? 22.什么CORBA? 23.什么IIOP? 24.什么是Stub, Skelton,他们的作用是什么? 25.什么是CORBA的POA? 作用是什么? 26.什么是IDL? 27.在jdk1.x(x>5)把一个IDL文件映射成Java目标代码的编译器及其主要选项 是什么? 28.什么是中间件?试举出若干重要的技术? 29.DCOM是中间件技术吗? 30.Microsoft Dot Net Framework是中间件技术吗? 31.什么是企业信息处理的异构性? 32.什么是Java Annotation? 33.EJB2.0与EJB3.0的区别是什么? 34.什么是一个EJB 部署描述符?是个符号吗? 35.标注@Stateless是做什么用的? 36.对于GlassFish EJB Container来说,标注 @Stateless(mappedName=”ejb/StudentBean”)属性值mappedName指的是什么? 37.标注@PersistenceContext(unitName=”MyEJBApp-ejbPU”) 属性值unitName
1、党的十八大主题是:高举中国特色社会主义伟大旗帜,以邓小平理论、“三个代表”重要思想、科学发展观为指导,解放思想,改革开放,凝聚力量,攻坚克难,坚定不移沿着中国特色社会主义道路前进,为全面建成小康社会而奋斗。 2、(1)完善海洋立法,调整海洋政策和海洋战略,制定《南海开发管理法》,做好南海海域及资源战略性长远规划。 (2)对南海海洋资源进行可持续的经济开发活动。 (3)建立一支强大的海军,加强对南海争议海域的实际控制。 (4)建立“海上信息高速公路”,加强海上执法力量、海上保卫力量和海洋管理部门的管理协作,建立高效协调机构。 (5)通过海洋教育,弘扬海洋文化,培养全民族的海洋观念和海权意识,增强南海海权意识。 南海对我国政治、经济、安全等方面具有重大的意义,保护好在南海的海洋权益,是事关国家利益安全的极大问题,维护我国南海海洋权益,任重而道远。 3、一、加强和改善宏观调控,促进经济持续健康发展。 二、夯实农业基础,保障农产品供给。 三、加快调整产业结构,提高产业整体素质。 四、积极稳妥推进城镇化,着力提高城镇化质量。 五、加强民生保障,提高人民生活水平。 六、全面深化经济体制改革,坚定不移扩大开放。 4、新型大国关系是以相互尊重、互利共赢的合作伙伴关系为核心特征的大国关系,是崛起国和既成大国之间处理冲突和矛盾的新方式。 中美新型大国关系是一条历史上的大国从来没有走过的路。在新时期,中美走上这条路是必要的,走好这条路自然也不乏挑战。 发展中美新型大国关系,需要创新思维,需要相互信任,需要平等互谅,需要积极行动,需要厚植友谊。 在新形势下,走好中美新型大国关系之路,应着重处理好三个问题: 第一,美国如何看待中国的战略意图? 第二,美国如何实施“再平衡”战略? 第三,双方如何发掘合作共赢潜力? 构建新型大国关系,短期内应当立足现状,着力于守住中美关系的底线和大局。 构建新型大国关系,需要理性分析中美关系背后的利益结构,把握这一结构变化的动态。构建新型大国关系,从长期看应推动中美关系从增量合作转向内生合作。 5、生态文明建设的主要特征 1 在价值观念上,强调尊重自然、顺应自然、保护自然。 2 在指导方针上,坚持节约优先、保护优先、自然恢复为主。 3在实现路径上,着力推进绿色发展、循环发展、低碳发展。 4在目标追求上,努力建设美丽中国。为人民创造良好生活生产环境,为全球生态安全做出贡献。 5在时间跨度上,需要长期艰巨的建设过程。既要补上工业文明的“必修课”,又要走好生态文明的“跨越路”
普通全日制本科生辅修管理办法 为了满足社会对人才的需要,培养全面发展的复合型人才,根据《普通高等学校学生管理规定》,对我校普通全日制本科生实行辅修专业、辅修第二专业学士学位、辅修双学位制度,允许学生在学好一个主修专业的基础上,自愿参加本校或武汉大学、华中科技大学、华中师范大学、中南财经政法大学、华中农业大学、中国地质大学另一个专业的辅修学习。为了加强辅修管理,保证辅修质量,特制定本办法。 一、报名条件 凡进校后前二个学期所修专业必修课程考核成绩合格,学有余力,且学习能力较强,在校期间未受过处分(或处理)者均可参加校内辅修学习;符合以上条件,且必修课平均学分绩达到80分以上者,可申请参加校外辅修学习。 二、学分及学位 修读第二专业学士学位是指主修专业与攻读的第二专业属于同一学科门类,修读双学位是指主修专业与攻读的第二专业分别为不同的学科门类。修读第二专业学士学位、双学位总学分为50学分左右;辅修专业总学分为25学分以上。修满规定课程的全部学分,通过论文答辩(毕业设计),且符合学校授予学士学位要求者,在获得第一学士学位的基础上由学校授予相应的辅修学士学位;修满25学分(含25学分)以上者,由学校颁发辅修专业证书。 三、报名与交费 1.每年十二月份由教务处公布本校开设的辅修专业和校外各学校开设的辅修专业。 2、学生辅修需按要求交纳辅修费。校内辅修学生每学期按本学期所修学分交纳辅修费用,校外辅修学生每学年交纳一次辅修费用。 四、教学管理 (一)校内辅修教学管理 1.辅修专业所在学院负责制定辅修培养计划报教务处批准。教务处根据开课需要从开课学院择优聘用教师任课。 2.辅修专业的课程学习与主修专业的课程学习同时进行,从学生进校后第四学期开始,到学生进校后第八学期为止。 3.修读辅修课程不及格者,参加学校安排的重考。每门课程最多只能重考两次。学生在修读辅修专业过程中,如辅修课程累计三门不及格(重考及格算通过),终止其继续修读辅修专业。
学号: 题目数据库系统综合实验 学院计算机科学与技术 专业 班级 姓名 指导教师施继珉 年月日
项目管理系统数据库综合实验 1.概述 1.1任务描述 本系统旨在协助用户管理自己的项目,通过综合管理项目信息及用户基本情况,以达到高效,快速,迅捷,准确的掌握全方面信息,大大降低了人工管理的复杂度,其简单的操作界面和强大的数据库操作功能带给管理者和使用者很大的经济效益。 协助用户管理自己的项目。项目管理系统可以登记项目的详细信息,从不同的角度对项目进行统计,监控项目的进度,对项目进行维护,安排项目的人员调度。 1.2可行性分析 目前,随着IT技术的进步和高等院校规模的逐步扩大,许多日常工作都是围绕一个个项目展开的,且项目管理工作日益复杂,项目信息数据库也日益庞大,早期的人工管理方式已经不能适应高校发展的要求。 本系统旨在协助用户管理自己的项目,通过综合管理项目信息及用户基本情况,以达到高效,快速,迅捷,准确的掌握全方面信息,大大降低了人工管理的复杂度,其简单的操作界面和强大的数据库操作功能带给管理者和使用者很大的经济效益。 根据学过的各方面的知识,先修课程:高级语言程序设计、数据结构、操作系统、软件工程等,实现项目管理数据库一般要求。 1.3系统目标 (1)实用性原则:真正项目管理者,工程管理的实际流程,设计出实用的项目 管理系统。 (2)可靠性原则:必须为项目管理者提供信息安全的服务,以保证工程项目信 息不被泄露。 (3)友好性原则:本系统面向的用户是工程管理人员和用户,所以系统操作上 要求简单、方便、快捷,便于用户使用。 (4)可扩展性原则:采用开发的标准和接口,便于系统向更大的规模和功能得 进一步完善和发展,所以要实现可扩展性。
2006 1解释概念 1生产函数2交易方程3边际消费倾向4资本边际效率5潜在产量6国际收支平衡 2简答题 1论述国民生产总值与国内生产总值的异同 1“国民收入决定是宏观经济分析的一条线索”,你是否同意这种观点,为什么?3论述新古典增长模型及其意义和局限性 4什么是货币政策,其主要手段有哪些? 3论述题 试述“古典”AD—AS模型与凯恩斯主义AD—AS模型的差异,说明这种差异表明了什么问题,并结合实际对上一理论作一简要的评论 2007 1解释概念 1生产函数2凯恩斯革命3消费者剩余4货币政策5帕累托最优6 BP曲线 2简答题 1为什么说完全竞争市场能够实现资源的最优配置?对这一市场的研究有何理论和实际意义? 2厂商为了实现最大的利润,应该以怎样的要素组合进行生产? 3什么是国民生产总值(GNP)和国内生产总值(GDP)。二者异同何在? 4试述新古典宏观模型的基本观点和政策主张。 3论述题 试述市场经济条件下市场和ZF的关系。 2008 1解释概念 1垄断竞争2萨伊定理3国际收支平衡4一般均衡5产品转换曲线6资本边际效率 2简答题 1用消费者行为理论说明需求曲线为什么向右下方倾斜 2凯恩斯主义AD—AS模型和新古典主义AD—AS模型有何差异?这种差异说明了什么问题? 3追求最大利润的厂商必须按照什么原则来进行生产?为什么? 3判断并简要说明理由 1完全竞争能实现资源配置的帕累托最优,因而ZF无需干预微观经济活动。 2要求价格理论就是收入分配理论
4论述题 用宏观经济理论并结合实际说明在什么样的情况下ZF要实行紧缩性的货币政策,其政策手段有哪些? 2009 1解释概念 1寡头垄断2规模经济3国际收支平衡表4道德风险5自然失业率6哈罗德-多马模型 2简答题 1经济学中有哪些成本概念?它们在经济分析中能起到哪些作用? 2什么是市场失灵?纠正市场失灵的基本思路和主要对策有哪些? 3试述理性预期概念的含义,由来及其意义 4试述市场经济条件下收入分配的原则和方法。 3判断并简要说明理由 完全竞争市场能实现资源的优化配置,因而完全竞争厂商都是竞争力和控制力较强的企业。 4论述题 什么是充分就业,价格稳定和经济增长?充分就业,价格稳定和经济增长之间是何关系?它们之间是否存在矛盾?试用宏观经济学理论对此加以解释和说明,并论述当前保增长,防通胀政策的意义。 2010(回忆版) 解释概念只记得2个了。。。1潜在产量2国际收支平衡 2简答题 1什么是外部性?怎样纠正外部性? 2财政政策有什么作用,局限有哪些? 3新古典宏观模型有哪些基本观点,对它怎样评价 4凯恩斯革命的主要内容有哪些极其意义。 3判断并说明理由 有人说在完全竞争厂商的停止营业点厂商不亏不赢,利润为零 4论述题 为什么说微观经济学就是“价格理论”,试述各个市场价格的决定及作用2013武汉理工大学经济学院复试专业课 一、简答题 边际递减规律赫俄模型垄断原因贸易保护主义内涵及主要表现形式银行经营三原则及相互关系cpi和ppi指什么上下波动反映了什么经济状况 二、论述题
武汉理工大学教室使用管理规定 (经2016年第14次校长办公会审议通过) 第一条为规范、有序合理地使用学校的教室资源,切实保障学校正常教学活动,为师生创造良好的学习、工作环境,根据学校实际,制定本规定。 第二条学校的教室(研究生教学专用教室除外)统一由教务处调配使用,包括普通教室、多媒体教室、语音室、制图教室、设计教室等。无教务处出具的教室使用通知单,任何单位和个人(包括班级、社团等)不得擅自使用教室。 第三条所有教室优先保证本校全日制本科生教学、考试、自习使用。在不影响正常教学活动的前提下,可以有条件地满足部分学生活动的需要。 第四条任课教师应严格按照课表安排的教室和时间上课,不得擅自调整。如因特殊原因需要调整的,按《武汉理工大学本科教学教师调(停)课管理规定》办理相关手续。 第五条未经教务处批准,任何单位或个人不得擅自将任何教室占用或改作他用。若造成课桌椅及其它设施损失的,必须在限期内按原教室规格修复。任何单位或个人在开课计划外使用教室,必须先向教务处申请办理教室借用手续。未办理手续擅用的,一经发现,即暂停该单位当学期借用教室的资格。
第六条教师上课临时需用教室,可由教师本人直接到教务处办理审批手续。如委托他人办理,则需要填写《武汉理工大学教室使用申请表》。 第七条学校各单位需利用教室开会或组织学术讲座等,应事先填写《武汉理工大学教室使用申请表》到教务处办理审批手续。 第八条每周日晚上学院晚点名教室由教务处和学工部统筹安排,不单独办理借用。 第九条为维护正常教学秩序,学生社团、协会及学生班级在教室开展集体活动,只能利用周五晚上、周六全天、周日白天进行,且应至少提前一天办理手续。学生活动不得跨教学周借用教室。 活动组织者应填写《武汉理工大学教室使用申请表》,经主管部门(学工部、校团委或各学院)负责人审核签字,到教务处办理审批手续。 第十条为保证教学效果,学校只在指定时间段提供部分多媒体教室供学生活动使用。活动由学工部负责审核,并在教务处办理借用手续。其他多媒体教室、活动桌椅教室、语音室仅供教学使用。 第十一条教室借用经审批后,由教务处开出《教室使用通知单》。申请人应尽快将通知单送达教服中心(多媒体教室)
武汉理工大学理学院 院学字[2011]10号 关于表彰2010-2011学年校园文化建设先进个人的决定 各学生班: 在2010-2011学年,我院广大学生响应校园文化建设号召,积极参加体育、文艺活动,在校内外各项文艺体育比赛和汇演中均取得了优异的成绩和做出了突出的贡献,同时也展现了我院学生良好的精神风貌和拼搏精神,涌现出了成绩显著的优秀个人和为了集体的荣誉勇于拼搏的先进典型。为了进一步加强理学院校园文化建设,促进我院学生体育、文艺活动的开展,激发学生的爱校爱院热情,学院决定,向在2011年校广播提早比赛中获得三等奖的王晶等62名同学、在2011年湖北省大学生武术比赛和2011年武汉理工大学校创业策划大赛中获奖的蔡裕坤同学、在武汉理工大学第八届校运会中取得好成绩的朱栋等37名同学以及在武汉理工大学纪念建党九十周年文学征文中获奖的殷本俊等6名同学授予"校园文化建设先进个人"荣誉称号,同时给予院级通报表扬。 希望受表彰的同学戒骄戒躁、再接再厉,号召全院学生向他们学习,勇于进取,不断创新,取得更大成绩。 附件: 理学院2011年校广播体操比赛获奖队员名单 理学院2011年湖北省大学生武术比赛获奖名单 理学院2011年武汉理工大学校创业策划大赛获奖名单 理学院校第八届运动会理学院优秀学生运动员名单 理学院纪念建党九十周年文学征文获奖名单 武汉理工大学理学院 二〇一一年十二月二日 发至:各学生班 抄送:学工部、校团委、研究生院 理学院2011年校广播体操比赛获奖队员名单 三等奖(62人) 王晶余攀懿先倚懿梁璋琦陈保利王艳李晨晨王昆鹏 蒙志轩胡恒恒刘文端夏洋刘云龙赵玉林绕松李云强 高建徐鹏徐晨李盛全罗博伟黎永光胡波陈亮 石玉刘超赵雄王开宏周伟黄振雄陈海龙魏天伟 刘辉刘乾峰靳乾乾管飞尹晨暄陈超佳陈云静林晨 肖莹霞李婷关小云郑娟高颖兰江珊詹维娜黎燕燕 刘思奕陈黛悦卫晓丹罗聪麻青映陈丽丹龙静赵巧云 李娇娇吴汨涓张亚茜黄露露袁顺昌杨帆
《数据库应用基础》大作业 课程名称数据库应用基础 开课学院计算机科学与技术学院指导教师姓名佘名高 学生姓名 学生专业班级 2013-2014 学年第二学期
一、假定一个数据库包括下述信息: 学生的信息:学号、姓名、单位、选修的课程名 课程的信息:课程号、课程名、学时、任课教师号 教师的信息:教师号、姓名、职称、所在单位 单位的信息:单位名、电话 1.上述实体中存在如下联系: (1)一个学生可以选修多门课程,一门课程可以为多个学生选修 (2)一个教师可以讲授多门课程,一门课程可以有多个教师讲授 (3)一个单位可以有多个教师和学生,而一个教师或学生仅属于一个单位2.根据上述情况和假设,试作如下设计: (1)构造满足需要的E-R图 (2)将E-R图转换为等价的关系模型并指出每个关系的关键字 学生(学号、姓名、单位、选修的课程名) 课程(课程号、课程名、学时、任课教师号) 教师(教师号、姓名、职称、单位名) 单位(单位名、电话) 选修(学号、课程号) 讲授(课程号、教师号) 所属1(学号、单位名) 所属2(教师号、单位名) 注:下划线为关键字 3.画出该数据库模式导航图。
二、假定一个学生成绩管理数据库ScoreDB包括下述信息: 学生表Student结构 课程表Course结构 课程表Course数据 学生选课表SC数据
用SQL语言完成如下操作: 1.查询全体学生的学号、姓名和所修专业。 select Sno,Sname,Sdept from Student; 2.检索年龄在19岁以上学生的学号、姓名和性别。 select Sno,Sname,Ssex from Student where Sage>19 ; 3.查询计算机软件专业男同学的学号和姓名。 select Sno,Sname from Student where Sdept is “计算机软件” ; 4.查询选修了C301课程的学生的学号和成绩,查询结果按成绩降序排序。 select Student.Sno,SC.Grade from Student,SC,Course where Student.Sno=SC.Sno and https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,ame=”C301” order by SC.Grade desc; 5.查询每个学生及其选修课程的情况。 select Student.*,SC.* from Student ,SC,Course where Student.Sno=SC.Sno; 6.查询所有学生(姓名)选修的课程名和成绩。 select Student.Sname,https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,ame, SC.Grade from Student ,SC,Course where Student.Sno=SC.Sno and https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,o=https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,o; 7.查询所有比“李明”大的学生的姓名和年龄。 select Sname, Sage from Student where and Sage>any (select Sage from Student where Sname=”李明”); 8.求选课在3门以上并且成绩及格的学生,并统计平均成绩,按总成绩降序排列。 select Sno,avg(Grade) from SC where Grade>=60 group by Sno having count(*)>3 order by Sum(Grade) desc; 9.查询选修了"计算机网络技术"课的学生姓名。 select Student.Sname from Student,Course where Student.Sno=SC.Sno and https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,o=https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,o and https://www.doczj.com/doc/d212192421.html,ame=”计算机网络技术”;
武汉理工大学普通全日制本科学生学籍管理规定 第一章总则 为了全面贯彻执行党的教育方针,保障学校正常的教学秩序,树立良好的学风,不断提高教育质量,培养德、智、体、美全面发展的高素质人才,根据《中华人民共和国高等教育法》和《普通高等学校学生管理规定》,结合我校实际,特制定本管理规定。 第二章入学与注册 第一条按国家招生规定录取为武汉理工大学的新生,必须持武汉理工大学入学录取通知书和学校规定的有关证件,按期到校办理入学手续。因故不能按期入学者,应及时向学校请假,假期不得超过两周;未经请假或请假逾期者,除因不可抗力等正当事由以外,视为放弃入学资格。 第二条按国家招生规定,学校在三个月内对入学新生进行复查。复查合格者,予以注册,取得学籍。复查不合格者,由学校区别情况,予以处理,直至取消入学资格。凡属弄虚作假、徇私舞弊者,一经查实,取消入学资格或学籍,予以退学。情节恶劣者,将提请有关部门处理。 第三条新生进行复查患有疾病者,经学校指定的二级甲等以上医疗单位和学校医院证明,短期治疗(不超过一年)可以达到健康标准者,经本人申请,由学院报学生工作部(处),学校批准,可准许保留入学资格一年。保留入学资格者,不具有学籍。 1.保留入学资格的学生,应回家或回原单位治疗,离校期间不享受在校学生的待遇,自通知办理离校手续之日起,半个月内无故不办理离校手续者,则取消其入学资格。 2.保留入学资格的学生,在下一届新生入学前向学校提出入学申请报告,并出具二级甲等以上医疗单位诊断证明和学校医院复查合格证明,经批准后方可办理入学手续,入学手续与当年新生相同。复查不合格或逾期不办理入学手续者,取消入学资格。 第四条学校实行二学期制,每学年分秋季、春季二个学期。已取得学籍的学生须按学校规定时间到校办理注册手续,每学期注册一次。每学年秋季学期开学时缴齐本学年专业学费后方予注册。 因故不能如期注册者,应当履行请假手续,暂缓注册。 未按学校规定缴纳学费或者其他不符合注册条件的不予注册。 家庭经济困难的学生可以申请贷款或者其他形式资助,办理有关手续后注册。 未经请假逾期两周不注册者作退学处理,取消其学籍(不可抗力等正当事由除外)。 第三章学制与学习年限
武汉理工大学广泛征求《一流大学一流学科建设 实施方案》意见 1月5日至6日,武汉理工大学在会议中心104组织召开《武汉 理工大学一流大学一流学科建设实施方案》征求意见会,校领导刘伟、张清杰、王乾坤、康灿华、刘祖源、陈文,各学院院长、独立建制科 研院所主任、院士、学科首席教授、二级教授、中青年学术骨干代表、学校有关职能部门主要负责人参加. 会上,研究生院学科建设处负责人介绍了学校一流大学一流学科 建设实施方案的具体情况,并对近期工作安排进行了说明.理学院院 长翟鹏程、化生学院院长孙涛垒、中国应急管理研究中心主任宋英华、数字传播工程中心主任刘永坚分别介绍了协同创新团队建设的 思考和经验. 与会人员直奔主题、畅所欲言、各抒己见,围绕方案的建设模式、建设领域、建设指标等方面进行深入交流与研讨,提出建设性的意见 与建议. 校党委书记刘伟对与会教授代表提出的意见和建议给予充分肯定,感谢大家为学校发展所作的重要贡献.他指出,“在目前激烈竞争的 态势下,我们能否在新一轮建设中抓住机遇、赢得先机、实现跨越发展,事关学校的未来,必需统一思想,转变观念,立即行动起来.”他强调,学校一流大学一流学科建设实施方案应把握好几个方面:在建设 模式上,各职能部门和教学科研单位要做好统筹协调,要充分以项目 为驱动,以创新研究中心为依托,充分调动和发挥广大教师的积极性;在建设领域上,要瞄准国际学术前沿、国家重大发展战略和三大行业 转型升级的重大需求,结合教授们提出的意见进一步完善相关内容;
在建设指标上,要进一步体现多元化,既要体现学科的差异性,也要考 虑指标的合理性,同时要注重体现国际标准. 校长张清杰在总结讲话时指出,教授们着眼学校发展大局,对一些问题分析的很深刻,发言十分恳切,学校将会认真吸纳并进一步对方 案进行修改和完善.对于学校一流大学一流学科建设,他强调,要充满 自信,在看到当前存在问题的同时,也应看到学校近年来在队伍建设、科学研究、人才培养等方面所取得的显著成绩;要凝聚共识,在国家 实施一流大学一流计划这一重大历史机遇面前,有所作为、不负众望,为理工大的未来发展负责,进一步转变观念,崇尚创新、锐意改革,以 一流学科建设牵引学校各项事业的发展;要突出重点,在实施一流大 学一流学科计划建设过程中,突出国际学术前沿和行业重大需求,突 出一流团队、一流科研、一流人才培养和一流文化等目标,突出不同 学科或学科不同方向的深度融合,突出特色和重大创新,突出管理体 制创新.张清杰校长希望大家以此次会议为契机,以改革创新的精神, 高举一流学科建设的旗帜,引领学校发展实现新跨越.
第一章: 1.1What is the purpose of a database?数据库的目的 The purpose of a database is to help people track(跟踪监测) of things. 1.2What is the most commonly used type of database?最常见的数据库类型 The most commonly used type of database is the relational database. 1.3Give an example of two related tables other than the example used in this book. Use the STUDENT and GRADE tables in Figure 1-3 as an example pattern(模式) for your tables. Name the tables and columns using the conventions in this book. 给一个关联表的例子,参考1-3 Answer:
1.4For the tables you created in Review Question 1.3, what are the primary keys of each table? Do you think that any of these primary keys could be surrogate(代理) keys?每张表的主码?这些主码可以是代理码吗? Query1: StudentNumber Query2: StudentNumber, RoomNumber Yes, both. 1.5 Explain how the two tables you provided in Review Question 1.3 are related. Which table contains the foreign key, and what is the foreign key? The primary key of Q1 were added to the Q2 with a primary key of StudentNumber to uniquely identify each row. In Q2 StudentNumber and RoomNumber each now serves as a foreign key. 1.6 Show your two tables from Review Question 1.3 without the columns that represent the relationships. Explain how the value of your two tables is diminished(减少) without the relationships.在你的表中去掉代表关系的列,解释没有关系的表的value如何减少? 1.7 Define the terms data and information. Explain how the two terms differ.定义术语data和information,解释它俩的不同。 Answer: Data are recorded facts and numbers. We can define information as: Knowledge derived from data. Data presented in a meaningful context. Data processed by summing, ordering, averaging, grouping, comparing or other similar operations. 1.8 Give an example of information that could be determined using the two tables you provided in your answer to Review Question 1.3. Anna Smith lives in 4-454 which the rent is 1300. 1.9 Give examples of a single-user database application and a multiuser database application other than the ones shown in Figure 1-5.举例子,单用户和多用户的数据库应用,除表1-5之外。 single-user: Cloud Service
[武汉理工大学] 关于鉴湖校区生态环境 调查报告 姓名:[XXX] 班级:[规划1201班] 2014.12.24
目录 一、绪论 (1) 二、调查问卷结果及分析 (1) 三、实地考察结果及分析 (8) 四、调查结论 (11) 五、总结及建议 (11)
一、绪论 调查时间:2014.12.18—2014.12.23 调查地点:武汉理工大学鉴湖校区 调查对象:武汉理工大学鉴湖校区在校生、校区生态环境 调查方式:问卷调查、实际考察、网络搜集 调查安排:根据鉴湖校区的实际情况,以及在鉴湖生活的经历,小组讨论决定分别从以下几个部分对其生态环境状况进行调查: 1、地理位置:土地利用现状(教学楼、宿舍、超市等建筑或设施的布局,有无图书馆、医务室)、交通情况。——网络搜集,集体 2、人口分布:人口总数及类型。——网络搜集,集体 3、植被状况:校园绿化面积、植被类型、植物种类及数量。——网络搜集、实际考察、问卷调查,四人 4、垃圾处理:垃圾桶的种类及数量、垃圾桶周围有无垃圾。——实际考察,两人 5、水体情况:水体质量(生活用水质量、鉴湖水质)、排水设施(道路排水设施、雨天积水情况)。——实际考察、调查问卷,两人 6、噪声污染:对学生生活的影响。——网络搜集、问卷调查,两人 7、空气质量:武汉市总体空气状况、植被对空气的进化。——网络搜集,集体 小组成员中有九人进行外业调查,分工如上面的调查安排,根据各个分小组的调查,最终统计相应的数据,对鉴湖校区的整体生态情况进行评价,并给出相应建议。 二、调查问卷结果及分析 此次我们共发放调查问卷90份,实际回收有效调查问卷90份,调查男女生比例2:1,填写调查问卷的学生多居于学海宿舍楼,周围
理工大学数据库系统原理总复习题(完整版含答案) 1. Questions 1.1What is the purpose of a database? ANSWER:The purpose of a database is to help people track of things. 1.2What is the most commonly used type of database? ANSWER: the most commonly used type of database is the relational database. 1.7 Define the terms data and information. Explain how the two terms differ. ANSWER: Data are recorded facts and numbers. we can now define information as: ●Knowledge derived from data. ●Data presented in a meaningful context. ●Data processed by summing, ordering, averaging, grouping, comparing or other similar operations. 1.10 What problem can occur when a database is processed by more than one user? ANSWER: When more than one user employs a database application, these is always the chance that one user's work may interfere with other's.
[实践]武汉理工大学选课操作手册武汉理工大学 选课手册(学生) 一(登录 打开浏览器,在浏览器的地址栏中输入: 进入教务处网站首页,如图1-1-1所示 图1-1-1教务处网站首页在右侧处找到“学分制选课系统”,如图1-1-2所示 图1-1-2 点击“学分制选课系统“进入选课登录页面,如图1-1-3所示
图1-1-3登录页面 输入用户名和密码,选择“学生身份“,登陆到系统,如图1-1-4所示,第一次登陆需要用户绑定手机,以便系统今后发送通知短信以及自助找回密码(系统很多功能依赖于绑定手机请确保手机号码的正确,如果手机号码丢失请及时修改否则会影响到很多提示信息无法发送至手机)。 图1-1-4手机与邮箱验证输入手机号点击“发送短信验证码“按钮,稍等片刻手机会收到系统发送的验证码短信,将手机收到的验证码填入“手机验证码”中,并填写完“邮箱地址”,点击“确定”按钮即可进入选课系统,如图1-1-5所示。
图1-1-5选课系统 二(选课操作流程 1选课过程(以专业选课为例) 1.1专业选课 点击“专业选课”按钮,如图2-1-1所示,系统会显示培养计划中该学期可以选的课程,如图2-1-2所示 图2-1-1 然后,选择要选修的一门课程,点击该课程,系统会显示该课程的开课情况,如图2-1-3 所示。
图 2-1-2课程列表此时,学生可以点击课程名称查看课程简介,点击想要选修课程的课程名称,如图2-1-3所示 图2-1-3课程简介和课程咨询列表查看课程信息及学生对该课程的咨询信息(课程咨询操作请看 2.1节) 也可以点击教师姓名,查看教师简介以及之前老生对该教师的评语,如图2-1-4所示