
人教版2017高一英语选修8全册教案WORD
Unit 1 A land of diversity
Period 1 Reading
Teaching goals
Enable the students to talk about things about the USA.
Help the students learn the huge diversity of races and cultures in America, especially in California. Teaching important and difficult points
Learn the huge diversity of races and cultures in California.
Teaching methods
Fast and careful reading; asking and answering activity; individual, pair or group work.
Teaching aids
A map, a blackboard and a computer
Teaching procedures
Step 1 Warming up.
Ask the students to describe what they learn about the USA.
Group work: look at the map of the USA with your group. Write on the map the names of as many of the following as you can. Compare your names with other groups.
Step 2 Pre-reading
Ask the students to tell things about California including its location, size, population, economy, history etc. What do you learn about California?
Show the students some pictures and encourage students not only to say what each picture is about but how each one relates to California.
Step 3 Fast reading
Read through the passage and get the main idea.
Reading comprehension.
Ask the students the following questions:
When you look at the title, what so you think of ?
A land of differences. California is a land of great differences —differences in climate, in landscape and attitude.
2) Why is the USA called a melting pot?
There are many immigrants to the USA and there are many cultures and nationalities. So it is a place in which people, ideas, etc of different kinds gradually get mixed together.
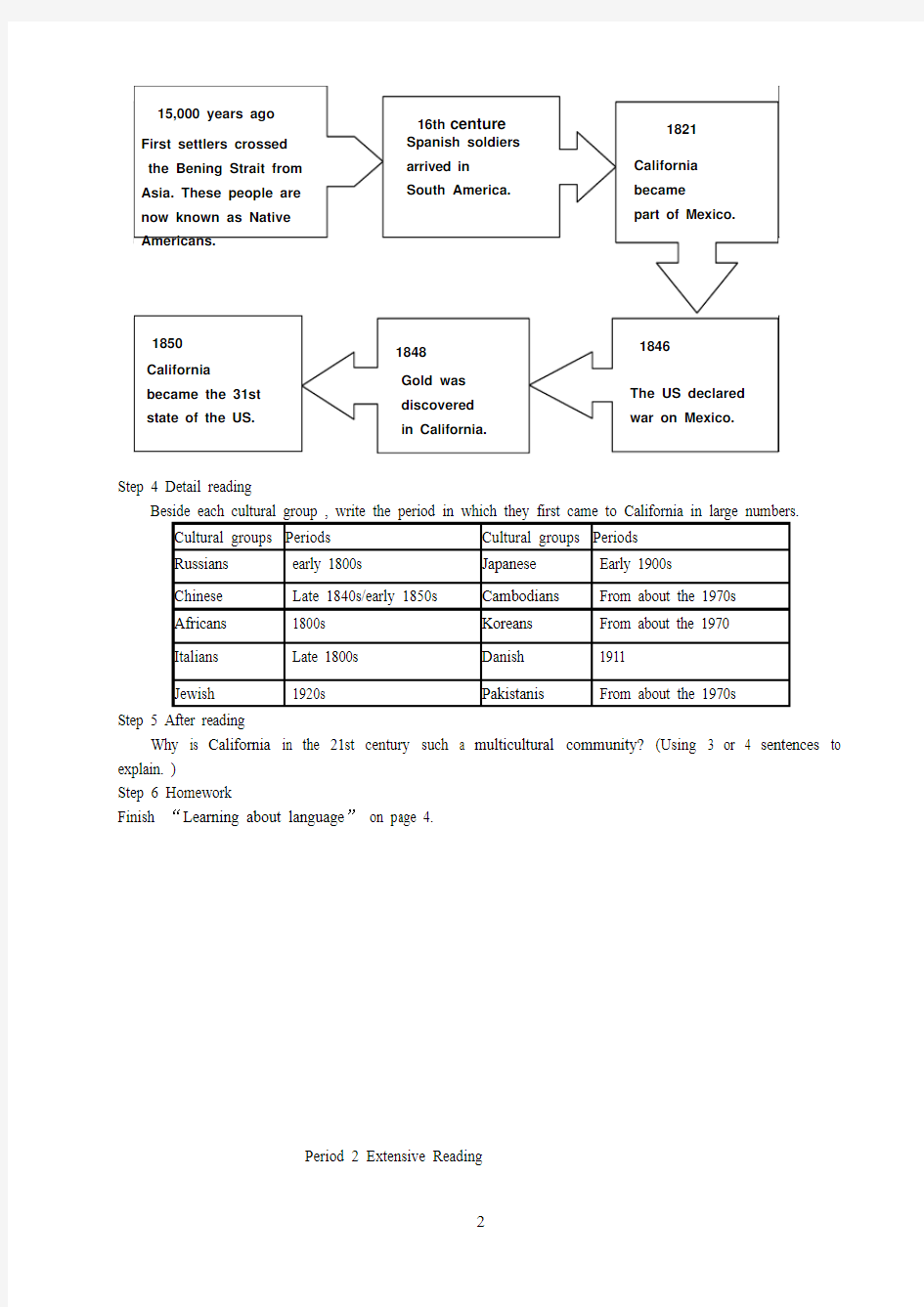
Beside each date note down an important event in Californian history.
Step 4 Detail reading
Step 5 After reading
Why is California in the 21st century such a multicultural community? (Using 3 or 4 sentences to explain. )
Step 6 Homework
Finish “Learning about language”on page 4.
Period 2 Extensive Reading
Teaching aims: 1. Improve Ss‘ ability of reading
2. 德育目标:了解美国多元文化,进一步培养学生跨文化交际意识,为终身学习奠定良好基础。PART I READING (P8)
Step 1. Fast reading: SB P7 PART 1.
Step 2. Careful reading: Read George‘s diary and answer the 5 questions on Page9 PART 2
Step 3. Pay attention to the main words, phrases and sentences(根据学生实际由集体备课确定)
PART II READING TASK(WB P51)
Step 1. Fast reading to find the main topic of each paragraph:
Step 2. T explains some difficult points.(由集体备课确定)
Step 3. Homework :read the passage fluently and recite some parts.
Period 3 Grammar
Teaching aims
Enable the students to use the Noun Clauses as the subject, object, predicative and oppositive.
Help the students learn how to use the Noun Clauses.
Teaching important and difficult points
Differ the noun clauses.
Teaching methods
Analysis and have some discussions.
Teaching procedures
Step 1 Preparation
Ask the students to underline the noun clauses in the following sentences. Then tell what types of noun clauses they are.
1)Whether native Americans arrived in California 15,000 years ago or 14,000 years ago is not important. Subject clause(主语从句)
2)The fact that they arrived a long time before Europeans is what matters.
Appositive clause(同位语从句) & Predicative clause(表语从句)
3)I believe that the native Americans were treated badly when the first Europeans came. Object clause(宾语从句)
Step 2 Discussion
Step 3 Analysis
1.高考考查热点:
1)名词性从句的语序(陈述句语序);
2)几对重要关联词的区别:whether\if, what\that, what\whatever, who\whoever, etc;
3)it用作形式主语或形式宾语代替主语从句或宾语从句;
4)根据具体情景选用适当的关联词。
2.根据例句,讨论:
1)whether\if的区别
I. Please tell me if/whether you will go to the lectures tomorrow.
II. It all depends on whether the sky will clear up.
III. The question is whether the film is well worth seeing.
IV. Whether he will be well tomorrow I‘m not sure.
V. Whether it is true remains a problem.
A.引导宾语从句,位于及物动词后
B.引导宾语从句,位于介词后
C.引导宾语从句,放句首
D.引导表语从句,主语从句或同位语从句
whether: A, B, C, D
if: A
2)What\that的区别
I. I think that it is unnecessary for me to speak louder.
II. His mother is satisfied with what he has done.
III. That he was able to come made us happy.
IV. This is what makes us interested.
V. The reason was that Tod had never seen the million-pound note before.
3)who\whoever; what\whatever的区别
I. The spoken English competition is coming. Who will attend the meeting hasn‘t been decided yet.
II. I believe whoever takes part in the competition will try his best.
III. Can you tell me what you would like to order?
IV. Whatever happens, don‘t be surprised.
4)常见的it作形式主语的结构
I. It is a fact that he won the match.
II. It is necessary that we do study the English.
III. It is known to all that light travels in straight lines.
1)Exs.3&4, Students Book P5
2)Make sentences using noun clauses as the subject, object, predicative and appositive.
Step 5 Homework
1. Review what we have learnt today.
2. Translate sentences:
1)显而易见, 英语很重要.(主语从句) 2)玛利认为他会帮助她.(宾语从句)
3)我从来未到过那儿这事实是真的.(同位语从句)
4)问题是我们下一步该怎么做.(表语从句)
Period 4 Listening and speaking
Teaching goals
Train their listening and speaking abilities.
eaching important and difficult points
Help the students to talk about position, space and direction and illustrate ways that listeners indicate that they are listening to the speaker.
Teaching methods
Pair work and group work, discussion and cooperation
Teaching aids
A recorder, a computer, and a blackboard
Teaching procedures
Step1 Listening
The first time the students listen to the tape they are expected to listen for the gist only. Read Ex1 on page 6 with students so that they know what to listen for and play the recording right through without stopping.
4 Geographic areas of California
2 Wher e George‘s tour started
3 California not as George expected
1 Where George is now
5 Californian people
Read the postcard on page 6 with students and ask them to recall the missing information. Then play the tape right through while students listen for the missing details. Play it twice if necessary and then check answers by playing the tape again and stopping when the missing details are given.
Dear Sam,
I‘m here in Joshua Tree National Park, in the___southeastern_
part of California. Have been traveling around the state of
__california___ for three weeks now. Very different from what
I have seen in ___American movies____ . Not everyone is ___rich__
and not everyone lives near the __beach_____. First traveled
southeast through rich farmland then to the central part.
They grow everything here including __cotton, nuts, vegetables_____
and fruit. Cattle too. Then traveled further ____southeast______ into
mountains and ____desert_____.Californians are very friendly,
and they are from many different ___races_____ and cultures.
Every culture has its own ____music__, ___festivals_____, food and art.
Most interesting. Wish you were here. Give my love to Paula.
George
Tell the students that when they listen to this time they are to focus on what Christie, who is mainly listening, says. Play the tape and stop after each thing that Christie says so that students can write down her words
Step 2 Speaking
With a partner hold a telephone conversation about a place you have visited recently.
Sit back to back with your partner so you can‘t see each other.
Partner A: Talk about where the place is , what the climate is like, what you thought about the people, and any other interesting things you saw or did.
Partner B: Encourage your partner to talk by asking questions and making comments.
3. Swap roles. Partner B tells Partner A about his\her visit.
Step 3 Homework
Write a short passage about the place they have visited recently.
Period 5 Using Language
Teaching goals
Target language
Useful words and expressions: luggage, tram, apparently, slip, bakery, ferry, hire, seagull, immigration, team up with, mark out, take in, a great many.
Teaching important and difficult points
Improve the students‘ reading ability (skimming and scanning).
enable the students to grasp the useful words and expressions.
Teaching methods
Reading, discussion, cooperative learning
Teaching procedures:
Step 1 Lead-in
Look at George’s photos. Then quickly read George’s diary. Write the days he saw these things under the photos.
Read George’s diary more slowly and answer the questions.
1.Why did Andrew Hallidie invent the cable car system?
2. Where did George eat lunch on his first day in San Francisco?
3. Why did George hire a car? Why do you think he joined up with Terri and Peter?
4. Name three things that visitors can do in Chinatown.
5. What is Alcatraz Island famous for?
3. Read George’s diary again. Put the mark”^‖ in the places where George has left out some words. Discuss with others in your class: Why did George leave out some words when he wrote his diary?
Step 2 Language points
Team up with: make an effort in cooperation with; work together with与……协力从事,合作
Translate:
He teamed up with an experienced worker in the project.
2.hire 解雇
fire 租,雇佣
1)You are _fired___, because you are so lazy for the work.
理解
4)Don‘t let yourself be taken in by these politicians.欺骗
Take off 拆开,拆散
Take on 贬低, 贬损名誉等
Take apart 从事,对…..产生兴趣,打听,占用空间或时间
Take away from 脱下,脱去,起居,休假,离开
Take up 开始雇佣,露出,承担,接受
Step 3 Pair work and consolidation.
Make sentences with the new words learned in this lesson.
Step 4 Homework
Read the passage again
Prepare for the diction of the useful words and expressions of this unit
3. Prepare for the writing of the next lesson.
Unit 2 Cloning
Period 1 Warming Up, Pre-reading, Reading & Comprehending
Teaching Goals:
1. To arouse Ss‘ interest in learning about cloning
2. To learn about the procedure of animal cloning and the life of Dolly the sheep
3. To develop Ss‘ some basic reading skills.
Teaching Procedures:
Step 1. Leading-in
Purpose: To activate Ss and arouse them to want to know about cloning.
Look at the following pictures and have a free talk.
1.Do you know the name of the most famous sheep and how it is different from other sheep?
Suggested Answer:
Its name is the Dolly sheep. It was cloned while the others were born naturally. It is the copy of another sheep.
2.What is cloning?
Suggested Answer:
Cloning is a way of making an exact copy of another animal or plant.
Step 2. Warming Up
Purpose: To lead Ss to the topic of this unit through the discussion
To get Ss to look at the pictures and discuss how they differ
Suggested Answer:
The first picture shows ―identical dogs‖. The smaller of the two dogs must be a man-made clone of the larger one. The other picture is about human twins. They are identical in sex and appearance and are good examples of natural clones.
Step 3. Pre-reading
Purpose: To arouse S s’ interest in the text and encourage Ss to predict the content of the text.
Get students to discuss what the passage talks about and how they understand the meaning of the title “Cloning : Where is it leading us?”
Ask Ss to talk about the following questions.
(1) What is cloning?
(2) How is a clone produced?
(3) What‘s the function of cloning?
(4) What‘s the effect of the cloning?
Suggested Answers:
A clone is a group of cells or organisms that are genetically identical and have been produced asexually from the same original cell. They include natural and man-made clones
he cloning of plants is simple and relatively easy. It can bee done by taking cuttings (man-made cloning) or letting the plant produce its own runners (natural cloning) . The cloning of animals is more complicated. It was not achieved until 1996 and is fully explained in the first reading.
It is possible to use cloning to cure serious illnesses, and help infertile people have babies.
People may want to clone themselves so they can live forever. People may want to clone dead children. People may want to clone their favorite pets.
Step 4. Fast reading
Purpose: To get Ss to get some useful information.
1. Ask Ss to listen to the text and try to get the main idea of the text.
2. Ask Ss to read the text quickly and answer the following questions.
Suggested Answer: (1) How many female sheep participate in the cloning of a new sheep?
Three sheep.
Suggested Answer: (2) How many major uses does cloning have and what are they?
Cloning has two uses. One is to produce commercial quantities of plants and do research on new plants species and medical research on animals.
Step 5. Intensive reading
做《优化方案》和报纸。
Purpose: To get Ss to get a brief understanding of the text.
1. Ask Ss to read the text carefully and then decide which statements are true or false.
(1) Cloning is a new topic.
(2) When a gardener takes cuttings from growing plants to make new ones, we say the new ones are natural cloning.
(3) Cloning animals is as complicated as cloning plants.
(4) Dolly the sheep was the first successful clone of a mammal
(5) Scientists were very excited to find that Dolly`s illnesses were more appropriate to a much older animal.
(6) People `s opinions on cloning were different.
Suggested Answers:
(1) F (2) T (3) F (4) T (5) F (6) T
外研版高中英语必修8 全册教学设计教案
目录 Module 1 Deep South Period II Module 1 Deep South Period III Module 1 Deep South Period IV Module 1 Deep South Period V Module 1 Deep South Period VI Module 1 Deep South Period Ⅰ Module 1《Deep South》 Module 2 The Renaissance--cultural corner and task Module 2 The Renaissance--function and grammar Module 2 The Renaissance--reading and vocabulary 1 Module 2 The Renaissance--reading practice Module 2 The Renaissance--Vocabulary and writing Module 2 The Renaissance--word list and introduction Module 3 Foreign Food--function and grammar Module 3 Foreign Food--reading and vocabulary Module 3 Foreign Food--reading practice Module 3 Foreign Food--vocabulary and writing Module 3 Foreign Food--word list and introduction Module 4 Which English--Cultural corner Module 4 Which English--Grammar Module 4 Which English--Introduction Module 4 Which English--Listening Everyday English Speaking Module 4 Which English--Reading and Vocabulary Module 4 Which English--Reading Practice Module 4 Which English--Speaking-Reading and Vocabulary (2)-Writing-Task Module 5 The Conquest of the Universe-- Introduction Reading and speaking Module 5 The Conquest of the Universe-- Listening Everyday English Speaking Module 5 The Conquest of the Universe-- Reading and Vocabulary Module 5 The Conquest of the Universe--Grammar Module 5 The Conquest of the Universe--Reading and Vocabulary (2) Writing Task Module 5 The Conquest of the Universe--Reading Practice Module 6 《War and Peace-grammer》 Module 6《The Tang Poems-Introduction》 Module 6《The Tang Poems-Language Points》 Module 6《The Tang Poems-Reading and writing》
必修1 第一单元ANNE’S BEST FRIEND Do you want a friend whom you could tell everything to, like your deepest feelings and thoughts? Or are you afraid that your friend would laugh at you, or would not understand what you are going through? Anne Frank wanted the first kind, so she made her diary her best friend. Anne lived in Amsterdam in the Netherlands during World War II. Her family was Jewish so they had to hide or they would be caught by the German Nazis. She and her family hide away for two years before they were discovered. During that time the only true friend was her diary. She said, “I don’t want to set down a series of facts in a diary as most people do, but I want this diary itself to be my friend, and I shall call my friend Kitty.” Now read how she felt after being in the hiding place since July 1942. Thursday 15, June, 1944 Dear kitty, I wonder if it’s because I haven’t been able to be outdoors for so long that I’ve grown so crazy about everything to do with nature. I can well remember that there was a time when a deep blue sky, the song of the birds, moonlight and flowers could never have kept me spellbound. That’s changed since I came here. …For example, when it was so warm, I stayed awake on purpose until half past eleven one evening in order to have a good look at
人教版高中英语选修十单词表 unit1 1. venture['vent??]n.(有风险的)商业、企业 2. web[web]n.(蜘蛛等的)网查看详细 3. Scottish['sk?ti?]adj.苏格兰的;苏格兰人的; 4. suffering['s?f?ri?]n.苦楚;受难 5. gall-bladder[ɡ?:l'bl?d?]n. 胆囊 6. strengthen['stre?θn]vt.加强;巩固 7. endurance[in'dju?r?ns]n.忍耐;持久;耐(性)
8. hut[h?t]n.小屋;棚屋 9. stove[st?uv]n.炉子 10. unbearable[,?n'bε?r?bl]n.无法忍受的;承受不住的 11. cosy['k?uzi]adj.舒适的;安逸的 12. block out[bl?k aut]封闭 13. breathless['breθlis]adj.喘不过气来的 14. rotten['r?tn]adj.腐烂的;变质的 15. blacken['bl?k?n]vt.使变黑 16. circumstance['s?:k?mst?ns]n.环境;详情;境况
17. blast[bl?st]n.一阵(风);一股(气流) 18. hoarse[h?:s]adj.嘶哑的 19. bless[bles]vt.祝福;保佑 20. selfish['selfi?]adj.自私的 21. hook[h?k]n.钩;吊钩vt.钩住;入迷 22. aboard[??b?:d]adv.&perp.在船(飞机) 23. seasickness['si:siknis]n. 晕船 24. anyhow['enihau]adv.无论如何 25. steward[stju?d]n.(轮船、飞机等)乘务员;膳
一、词汇拓展 1.适应,改编v.____________;适应,改编本n.____________;能适应的adj.___ __________ 2.误会n. &v.________;(过去式)________;(过去分词)________;错误的adj.________ 3.恐怖,恐惧n.__________;可怕的,恐怖的adj.__________;可怕地adv.__________ 4.犹豫,踌躇v._________________;犹豫,迟疑n.________________ 5 编排,分类v._____________;编排,分类n._____________ 6.使作呕,反感,厌恶v.________;使人反感的adj.________;感到反感的adj.________ 7. ___________ n. 舒适; 安慰vt. 安慰_____________ adj. 不舒服的; 不安的 8. _______n. 羊毛; 毛线; 毛织品_______ adj. 毛纺的; 纯毛的 9. ________ adj. 经典的n. 经典著作_______ adj. 古典的, 典雅的, 经典的 二、短语(从Reading 1 和 Reading 2 中找出以下短语) 1. (某人)冒充…____________________ 2. 结识,与…相见___________________ 3. 惊愕地_________________________ 4. 一般来说________________________ 5. 就…来说,从…角度 ______________ 6. 带…进来________________________ 7. 几天前 _________________________ 8. 带走,拿走_____________________ 9. 需要 _____________________ 10.透露身份,显露(本来面目)____________ 11. 伪装, 乔装 _________________ 12. 毫不犹豫 ____________________ 13. 把..误认为 _________________ 14. 要是…怎么办 ________________ 15. 优于… _____________________ 16. 打赌 ________________________ 17. 注定… _____________________ 18. 使…相信… ___________________ 19.采取有效措施 _____________________ 20. 根据…把..分类 ________________ 21. (声音、画面)逐渐模糊_____________ 22.用…的声音___________________ 23.自以为是 _______________________ 24. 移交 ______________________ 三、语言点 1. adaptation n. 改编本;适应性 adaptation to 对……的适应 adapt vt.使适应(合);修改,改编 vi. (to)适应 adapt oneself to 使适应;使适合 1)这部戏剧是一部短篇小说的改编本。 ___________________________________________________________. 2)动物对环境的适应是相当慢的。 ___________________________________________________________. 3)He tried hard to______________________(使自己适应) the new conditions. 4)He made a quick ____________________(适应) the new environment. 5)When they moved to Canada, the children _____________(适应) the change very well. 2. hesitate vi. 犹豫;踌躇 (1)hesitate to do sth.迟疑做某事,不愿做某事 hesitate about/in/at/over (doing) sth.(做)某事犹豫不决 hesitate about+疑问词+to do sth.做某事犹豫不决 (2)hesitation n.踌躇,犹豫 without hesitation毫不犹豫地 have no hesitation in doing sth.毫不犹豫地做某事
选修8 Unit 1 大课文多样性的土地 加州 加州是美国第三大洲,但是人口最多。它也有不同的是最多元文化国家在美国,有吸引了来自世界各地的人们。的习俗和语言的移民活在新居。这个文化多样性并不令人惊讶当你知道他的历史加州。本土美国人 什么时候到的第一批人我们现在知道的加利福尼亚,没有人真的知道。然而,很可能在加利福尼亚居住美国印地安人是至少一万五千年前。科学家们认为这些定居者穿过白令海峡在北极到美国的一种方法中存在的陆地桥在史前时期。在16世纪,欧洲人到来之后,当地人中蒙受了重大损失。数千人的死亡或被迫成为奴隶。另外,许多人死于这种疾病所带来的欧洲人。然而,从一些这些可怕的时代,今天还有更多的美国人住在加州比任何其他国家。 西班牙 在18世纪,加州被西班牙。名西班牙士兵初到南美洲,在16世纪早期当他们攻打当地人,把他们的土地。两个世纪以后,西班牙人定居在大部分南美和沿西北海岸的我们现在所称的美国。第一个西班牙去加州,大多数都是虔诚的教徒。他们的部门是要教导天主教给当地人。1821年,墨西哥取得了他们的从西班牙独立。加州的一部分则成了墨西哥。1846年美国宣战墨西哥和战争结束后获美国、墨西哥不得不给加州
到美国。然而,仍有强烈的西班牙影响国家。这就是为什么今天超过40的加州人说西班牙语作为第一或第二语言。 俄罗斯人 在19世纪初,俄罗斯的猎人,这些原本,开始去阿拉斯加定居在加州。在那里的今天是大约2.5万美籍俄裔住在旧金山市区和郊区。 黄金生产商 1848年1月24日,美墨战争后不久,有人在加州发现了黄金。快速致富的梦想吸引了来自世界各地的人们。最近的,因此第一个到达,是来自美国人民和来自美国。然后从欧洲和亚洲的冒险者随之而来。事实上,一些达到了他们的梦想成为富足。一些死亡或回到家,但是大多数住在加利福尼亚使自己的生活不顾大的困难。他们就住在新城镇或在农场工作。在加州成为31日当选美国的联邦州在1850年,已经是一个多元文化的社会。 晚来者 尽管中国移民开始到在淘金热期间,他们的建筑……(文件丢失)从西方的铁路网络到东海岸带来了更大的编号到加州十九世纪六十年代。今天,美藉华人住在加州的所有部分,尽管大部分选择呆在“唐人街”的洛杉矶和旧金山。 意大利人等其他移民,主要渔民还酿酒师,到达了加州在十九世纪。在1911年移民建立了镇来自丹麦的自己,今天仍然继续他们的丹麦文化。到了二十世纪二十年代电影产业被确立在美国加利福尼亚州的好莱坞。因此本行业的繁荣——吸引了欧洲人包括许多犹太民族主
高中英语外研版选修八单词表 polar adj. 极地的(SH8 M1 P1) penguin n. 企鹅(SH8 M1 P1) explorer n. 探险者(SH8 M1 P1) Antarctica n. 南极洲(SH8 M1 P2) annual adj. 每年的(SH8 M1 P2) rainfall n. 降水量;降雨量(SH8 M1 P2) state n. 状态;状况(SH8 M1 P2) depth n. 深度(SH8 M1 P2) gravity n. 重力,地心引力(SH8 M1 P2) inhospitable adj. 荒凉的,不适宜居住的(SH8 M1 P2) extreme adj. 极端的,极度的(SH8 M1 P2) flower v. 开花(SH8 M1 P2) moss n. 藓;苔藓(SH8 M1 P2) algae n. 藻类(植物)(SH8 M1 P2) lichen n. 地衣(SH8 M1 P2) adapt to (使)适应(SH8 M1 P2) trap v. 储存,留存(SH8 M1 P2) meteorite n. 陨石(SH8 M1 P2) extraterrestrial adj. 天外的,地球外的(SH8 M1 P2) mass n. 块,堆,团(SH8 M1 P3) balance v. 使平衡(SH8 M1 P3) exploration n. (对某地区的)勘查(SH8 M1 P3) set foot on 进入,到达(SH8 M1 P3) rivalry n. (不断的)竞争(SH8 M1 P3) treaty n. (国家或政府间的)条约,公约(SH8 M1 P3) commercial adj. 商业的(SH8 M1 P3) nuclear adj. 核的,核能的(SH8 M1 P3) test n. 试验(SH8 M1 P3) radioactive adj. (具有)放射性的(SH8 M1 P3) promote v. 促进,增进(SH8 M1 P3) via prep. 经由,取道(SH8 M1 P7) trap v. 使陷入困境(SH8 M1 P7) lifeboat n. 救生船(SH8 M1 P7) crew n. (全体)船员(SH8 M1 P7) voyage n. (乘船的)旅行,航行(SH8 M1 P8) drift v. 漂流,漂泊(SH8 M1 P8) ceremonial adj. 正式的(SH8 M1 P11) glacier n. 冰川;冰河(SH8 M1 P11) magnetic adj. 磁的,磁性的,磁场的(SH8 M1 P11) glare n. 刺眼的光(SH8 M1 P11) intense adj. 强烈的(SH8 M1 P11) sunglasses n. 太阳镜;墨镜(SH8 M1 P11)
人教版《英语选修10》(普通高中课程标准实验教科书)单元词汇、音标、词义。Unit 1 venture/'vent??/n.(有风险的)商业、企业vi.vt.冒险;敢于去web/web/n.(蜘蛛)网 Scottish adj.苏格兰(人)的;苏格兰英语的 suffering/'s?f?ri?/n.苦楚;受难 gall-bladder n.胆囊 strengthen/'stre?θ?n/vt.加强;巩固 Perce Blackborow珀斯.布莱克鲍罗 Sir Ernest Shackleton欧内斯特.沙克尔顿爵士 endurance/in'dju?r?ns/n.忍耐;持久;耐(性) hut/h?t/n.小屋;棚屋 stove/st?uv/n.炉子 unbearable/?n'b??r?bl/adj.无法忍受的;承受不住的 cosy/'kouzi/adj.舒适的,安逸的 block out封闭 breathless/'breθlis/adj.喘不过气来的 rotten/'r?tn/adj.腐烂的;变质的 blacken/'bl?k?n/vt.使变黑 circumstance/'s?:k?mst?ns/n.环境;详情;境况 blast/blɑ:st/n.一阵(风);一股(气流) hoarse/h?:s/adj.嘶哑的 bless/bles/vt.祝福;保佑 selfish/'selfi?/adj.自私的 Tom Orde-Lees汤姆.奥德.利兹 hook/huk/n.钩;吊钩vt.钩住;迷上 aboard/?'b?:d/adv.在船(飞机、车等)上;上船(飞机、车等) seasickness n.晕船 anyhow/'enihau/adv.无论如何 steward/stju?d/n.乘务员;膳务员 crush/kr??/vt.碾碎;粉碎;(使)变形 mourn/m?:n/vi.哀悼;忧伤 urgent/'?:d??nt/adj.急迫的;紧急的 bedding/'bedi?/n.被褥;草垫 Hussey赫西 banjo/'b?nd??u/n.班卓琴;五弦琴 vital/'vaitl/adj.生死攸关的;重要的
Unit four Pygmalion The First Period Warming up 一.Aims: Teaching goals 教学目标 1. Target language目标语言: 重点词汇和短语adaptation, plot, professor, Pygmalion 2. Ability goals能力目标 Enable the students to talk about the Greek story Pygmalion 二.Contents: Ask Students to look at a group of three pictures and try to describe them in their own words. T: Yes, today we are going to learn about a Greek story Pygmalion. First, look at the pictures on page 28. Please work in pairs and work out the story. S1: Let me try. Pygmalion was a very gifted artist. He spent a long time making a stone statue of a beautiful woman. It was so beautiful that he couldn’t help loving it and wanted it to be his wife. T: What problems do you think they will have? S1: Maybe they can’t understand ea ch other, because they come from different world. S2: It’s very hard for Pygmalion to understand his wife, because his wife is made form a stone. She doesn’t know the words, behavior, anything about him.… Step III Discussion Make a brief introduction about Shaw. T: George Bernard Shaw, Irish dramatist, literary critic, a socialist spokesman, and a leading figure in the 20th century theater. Shaw was a freethinker, defenders of women’s rights, and advocate of equality of income,. In 1925 he was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature. Shaw accepted the honor, but refused the money. He was a very humorous playwright. Here is a story about him. One day, Shaw took part in a grand party, in which he met the then Prime Minister Churchill. Churchill was very fat at that time whereas Shaw was very thin. Churchill said to Shaw very sharply, “When people see you, they will know how poor your country is”. And then Shaw answered very quickly, “When people see you, they will know the reason why our country is so poor.” Fro m it we can see how witty Shaw is!
选修8 Unit 1 A land of diversity-Reading CALIFORNIA California is the third largest state in the USA but has the largest population. It also has the distinction of being the most multicultural state in the USA, having attracted people from all over the world. The customs and languages of the immigrants live on in their new home. This diversity of culture is not surprising when you know the history of California. NATIVE AMERCANS Exactly when the first people arrived in what we now know as California, no one really knows. However, it is likely that Native Americans were living in California at least fifteen thousand years ago. Scientists believe that these settlers crossed the Bering Strait in the Arctic to America by means of a land bridge which existed in prehistoric times. In the 16th century, after the arrival of the Europeans, t he native people suffered greatly. Thousands were killed or forced into slavery. In addition, many died from the diseases b rought by the Europeans. However, some survived these terrible times, and today there are more Native Americans living in California than in any other state. THE SPANISH In the 18th century California was ruled by Spain. Spanish soldiers first arrived in South America in the early 16th century, when they fought against the native people and took their land. Two centuries later, the Spanish had settled in most parts of South America and along the northwest coast of what we now call the United States. Of the first Spanish to go to California, the majority were religious men, whose ministry was to teach the Catholic religion to the natives. In 1821, the people of Mexico gained their independence from Spain. California then became part of Mexico. In 1846 the United States declared war on Mexico, and after the war won by the USA, Mexico had to give California to the USA. However, there is still a strong Spanish influence in the state. That is why today over 40 of Californians speak Spanish as a first or second language. RUSSIANS In the early 1800s, Russian hunters, who had originally gone to Alaska, began settling in California. Today there are about 25,000 Russian-Americans living in and around San Francisco. GOLD MINERS In 1848, not long after the American-Mexican war, gold was discovered in California. The dream of becoming rich quickly attracted people from all over the world. The nearest, and therefore the first to arrive, were South Americans and people from the United States. Then adventurers from Europe and Asia soon followed. In fact, few achieved their dream of becoming rich. Some died or returned home, but most remained in California to make a life for themselves despite great hardship. They settled in the new towns or on farms. By the time California elected to become the thirty-first federal state of the USA in 1850, it was already a multicultural society.
高中英语外研版选修八单词表 Moudle 1 Polar penguin explorer Antarctica annual rainfall State depth gravity Inhospitable extreme flower Moss algae lichen adapt to trap meteorite extraterrestrial mass balance exploration set foot on rivalry treaty commercial nuclear test radioactive promote via trap lifeboat crew voyage drift ceremonial glacier magnetic glare intense sunglasses sun-cream severe eyesight sunburnt minus numb frost clothing portable pure millimeter abnormal sunrise sunset absence daylight tiresome depressing isolated aircraft platform powder minimum modest luxury cosy dormitory canteen stock laundry discourage in case of emergency conventional drill snap tricky fragile battery ecology delicate privilege trader spice jewel befriend tale legendary reliability obscure intimate inhabit spaghetti insight inspiration
高中英语学习材料 ***鼎尚图文理制作*** 第九周交通通讯与旅游 周一 1. A 解析:词义推测题。根据下句文字信息The nearest town, Garissa, is hundreds of kilometers away from these villages. 可知。 2. B 解析:推理判断题。A、C、D属于错误推断, 肯尼亚北部道路条件恶劣, 骆驼是较有效的运输图书的工具。 3. C 解析:与传统图书馆不同的地方在于驼背上的流动图书馆用骆驼把书带给人们。B、D 为错误陈述, A是与传统图书馆的相同之处。 周二 1. D 解析:推理判断题。根据全文内容, 尤其是文章最后一句The museum is a good way to learn about the interesting life of him. 2. C 解析:推理判断题。根据第二句He also loved words and writing. B根据这一段的第一句可知为错误判断。D的叙述没有错误, 但对于此段的写作目的而言角度太小。 3. C 解析:细节认定题。根据第四段中Porter was accused of financial wrongdoing at the bank and lost his job. Fearing a trial, he fled the country. 可知。 4. A 解析:排列顺序题。根据文章中时间顺序可知。 5. B 解析:推理判断题。A、D可以根据文章的最后一段排除。根据第一段欧·亨利出生时间和Beginning in 1893, he lived here. 以及第二段信息可知C为错误推理。 周三 1. D 解析:信件可以被欣赏, 被读, 被“重新读”。前三项都与本句内容不符。 2. C 解析:根据前一个分句中的内容可知几乎不费力气就可以用信件保持“友谊”。 3. A 解析:上文叙述的是信件的益处, 本段则用作者与哥哥重归于好的例子进行证明, 由此可知是“例证”。 4. C 解析:本段中间部分提到两人之间存在误解, 由此可知两个人在几年前相处得不好。get along相处融洽。 5. B 解析:根据本句后半部分中的内容可知两个人在小的时候关系非常密切, 只是随着年龄
Unit 3 Inventors and inventions The First Period Reading Teaching goals教学目标 1. Target language目标语言 a. 重点词汇和短语 patent, distinguish, product, power, perfume, cube, abrupt, abruptly, convenient, expectation, monitor, passive, criterion, valid, application, file, rod, call up, now and then, set about, in case 2. Ability goals Enable the students to describe the problem of the snakes and what has been done by the writer to solve the problem. 3. Learning ability goals Help the students to learn how to retell the story and how to meet the requirements of getting a patent. 4. Emotional goals Make the students try to be good at discovering some useful things and realize that it’s not easy to get a patent. Teaching important points 教学重点 To get the main idea of the whole passage and each parts. Teaching difficult points 教学难点 Learn how to meet the requirements of getting a patent. Teaching methods 教学方法 Reading and Task-based activities. Teaching procedures & ways教学过程与方式 Step Ⅰ warming up Deal with the part of warming up and ask the students to find out the definitions of discovery and an invention, and their differences. An invention is something that is created by a human being, such as the lightning rod. To the contrary, a discovery merely makes known something that already existed in nature, such as the discovery on the New Continent by Columbia. Step Ⅱ Pre-reading
人教版高中英语选修8 课文及翻译 选修8 Unit 1 A land of diversity-Reading CALIFORNIA California is the third largest state in the USA but has the largest population. It also has the distinction of being the most multicultural state in the USA, having attracted people from all over the world. The customs and languages of the immigrants live on in their new home. This diversity of culture is not surprising when you know the history of California. NATIVE AMERCANS Exactly when the first people arrived in what we now know as California, no one really knows. However, it is likely that Native Americans were living in California at least fifteen thousand years ago. Scientists believe that these settlers crossed the Bering Strait in the Arctic to America by means of a land bridge which existed in prehistoric times. In the 16th century, after the arrival of the Europeans, the native people suffered greatly. Thousands were killed or forced into slavery. In addition, many died from the diseases brought by the Europeans. However, some survived these terrible times, and today there are more Native Americans living in California than in any other state. THE SPANISH In the 18th century California was ruled by Spain. Spanish soldiers first arrived in South America in the early 16th century, when they fought against the native people and took their land. Two centuries later, the Spanish had settled in most parts of South America and along the northwest coast of what we now call the United States. Of the first Spanish to go to California, the majority were religious men, whose ministry was to teach the Catholic religion to the natives. In 1821, the people of Mexico gained their independence from Spain. California then became part of Mexico. In 1846 the United States declared war on Mexico, and after the war won by the USA, Mexico had to give California to the USA. However, there is still a strong Spanish influence in the state. That is why today over 40 of Californians speak Spanish as a first or second language. RUSSIANS In the early 1800s, Russian hunters, who had originally gone to Alaska, began settling in California. Today there are about 25,000 Russian-Americans living in and around San Francisco. GOLD MINERS In 1848, not long after the American-Mexican war, gold was discovered in California. The dream of becoming rich quickly attracted people from all over the world. The nearest, and therefore the first to arrive, were South Americans and people from the United States. Then adventurers from Europe and Asia soon followed. In fact, few achieved their dream of becoming rich. Some died or returned home, but most remained in California to make a life for themselves despite great hardship. They settled in the new towns or on farms. By the time California elected to become the