
翻译:
1、GIS is a system of hardware,software aad procedures to facilitate the manipulation,analysis,modeling,representation and display of geo—referencedcomplex problems regarding planning and management of resollrces,
翻译:gis是一个由硬件、软件和程序组成的系统,便于管理、处理、分析、模拟、表现并显示地理参照数据,从而解决规划和资源管理的复杂问题。
2、GIS technology,integrates common database operations such as query and statistical
analysis with the unique visualization and geographical analysis benefits offered by maps.These
abilities distinguish GIS from other information systems and make it valuable to a wide range of
public and private enterprises for explaining events,predicting outcomes,and planning strategies(ESRI).
翻译:地理信息系统技术将诸如查询和统计分析的常见的数据库操作和地图特有的可视化功能和地理分析优势集成起来。这些功能是区分地理信息系统和其他信息系统的关键,并且对于众多的公共和私营企业用于事件解析,结果预测和战略规划十分有价值(ESEI)。
3、Projection is a fundamental component of mapmaking.A projection is a mathematical
means of transferring information from the earth’s three—dimensional,curved surface to a twodimensional medium--paper or a computer screen.Mathematically speaking,map projectionsare transformations of geographic coordinates(1atitude,longitude)into the Cartesian(x,y)coordinate space of the map.
翻译:投影是地图制作的一个基本要素,同时也是将信息从地球的三维曲面上传递到纸张或电脑屏幕二维介质上的一种数学手段。从数学上来讲,地图投影就是将地理坐标(纬度,经度)转换为地图的笛卡儿空间坐标(x,Y)。
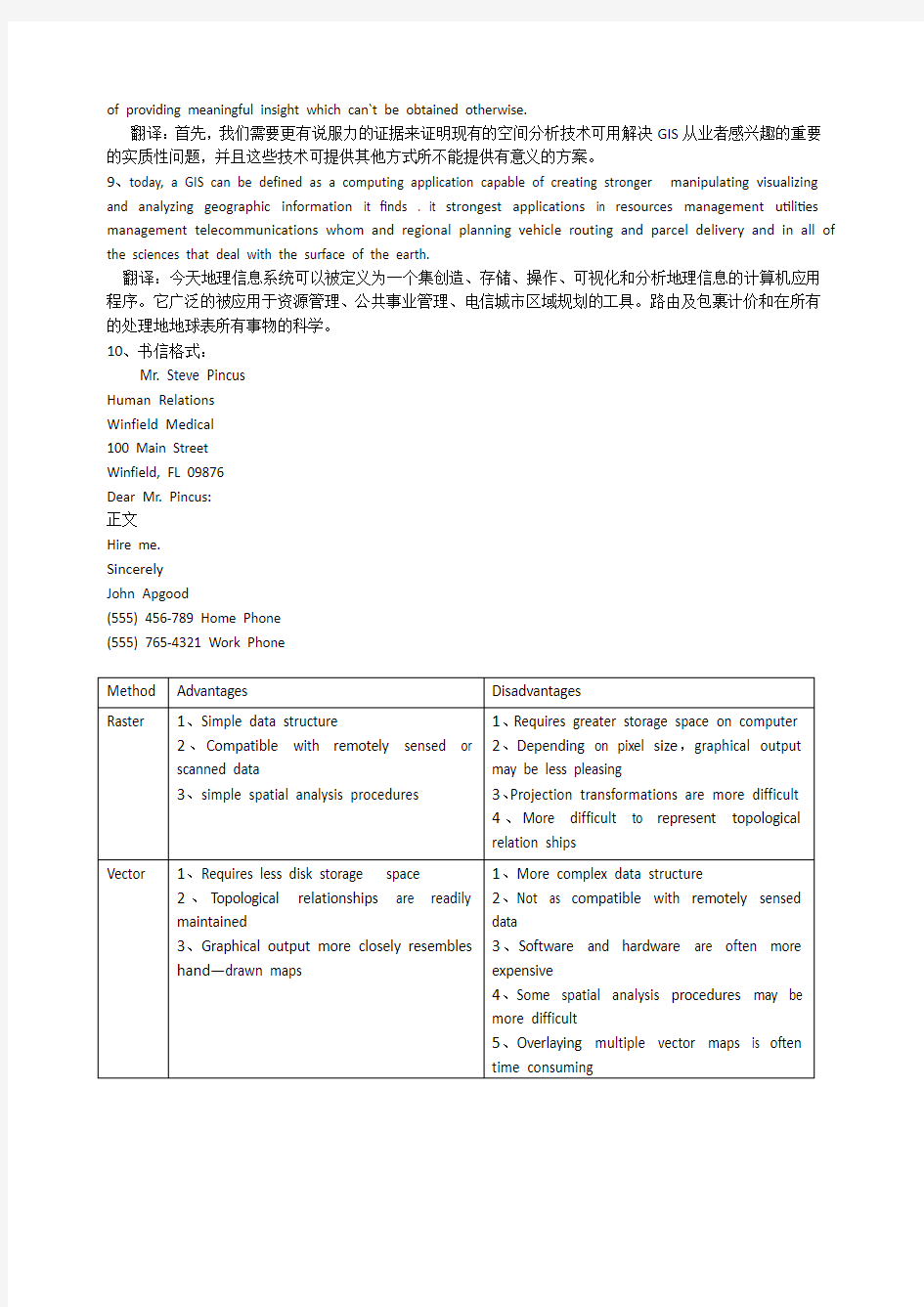
4、A raster based system displays,locates,and stores graphical data by using a matrix orgTid of cells such as squares,triangular,or hexagonal cells,or even irregular triangles orpolygons,which are tessellated to form geographical representations.
翻译:基于栅格数据的系统采用栅格单元有正方形、三角形或六角形形成了地理表征。栅格矩阵或栅格单元显示、定位存储地理数据,这些,甚至不规则三角形或多边形,这些单元嵌合在一起形成了地理表征。
5、A vector based system displays graphical data as points,lines or curves,or areas withattributes.Cartesian coordinates (i.e.x and Y) and computational algorithms of thecoordinates define points in a vector system.Lines or arcs are a series of ordered points.Areasor polygons are also stored as ordered lists of points,but by making the beginning and endpoints the same node the shape is closed and defined.
翻译:基于矢量数据的系统用点、线或曲线、面及其属性显示图形数据。笛卡儿坐标(即光和Y)和坐标计算算法确定矢量系统中的点、线或弧段是一系列有序点。面或多边形也是用一系列有序点储存的,但是起始节点和结束节点相同以闭合和确定图形。
6、Geo-referencing describes the process of locating an entity in“real world”coordinates,establishing a relation between raster or vector images to map projections or coordinate systems.
翻译:空间参照描述了定位实体在“真实世界”的坐标及确立栅格或矢量影像与地图投影或坐标系统关系的过程。
7、Map projections are systematic transformations that allow the orderly representation ofthe earth’S spherical gratieule on a flat map.Mathematically speaking,map projections aretransformations of geographical coordinates(1atitudelongitude)into the Cartesian(x,Y)co—ordinate space of the map.
翻译:地图投影是一种系统转换,即将地球球面上的方格网有序地表示在平面地图上。从数学上来讲,地图投影是地理坐标(纬度,经度)到地图笛卡儿(x,Y)坐标空间的转换。
8、first of all ,we need to demonstrate more convincingly that existing spatial analysis techniques can be used to address important substantive problems of interest to GIS practitioner and that such techniques are capable
of providing meaningful insight which can`t be obtained otherwise.
翻译:首先,我们需要更有说服力的证据来证明现有的空间分析技术可用解决GIS从业者感兴趣的重要的实质性问题,并且这些技术可提供其他方式所不能提供有意义的方案。
9、today, a GIS can be defined as a computing application capable of creating stronger manipulating visualizing and analyzing geographic information it finds . it strongest applications in resources management utilities management telecommunications whom and regional planning vehicle routing and parcel delivery and in all of the sciences that deal with the surface of the earth.
翻译:今天地理信息系统可以被定义为一个集创造、存储、操作、可视化和分析地理信息的计算机应用程序。它广泛的被应用于资源管理、公共事业管理、电信城市区域规划的工具。路由及包裹计价和在所有的处理地地球表所有事物的科学。
10、书信格式:
Mr. Steve Pincus
Human Relations
Winfield Medical
100 Main Street
Winfield, FL 09876
Dear Mr. Pincus:
正文
Hire me.
Sincerely
John Apgood
(555) 456-789 Home Phone
(555) 765-4321 Work Phone
albers equal—area conic projection 阿尔伯斯等积圆锥投影
Cartesian coordinates笛卡儿坐标continuous fields连续字段
coordinate systems坐标系统
data capture 数据获取
data integration数据集成
data output数据输出
data structures数据结构
datum基准面
developable Sulfate 投影面
digital elevation models(DEM) 数字地面模digital terrain model(DTM)数字高程模型discrete objects离散对象
ellipsoid椭球体
exhaustive enumeration穷举法
geodesy大地测量学
geoids大地水准面
geo—referenced data地理参照数据geo—referencing空间参照
gnomonic projection心射切面投影
gravity万有引力
hierarchical file层次文件
information retrieval 信息检索
Lambert azimuthally equal—area projection 朗伯等积方位投影
map projections地图投影
network analysis网络分析
orthographic projections正射投影
overlay叠置
polar coordinate极坐标
projection and registration投影与匹配raster data格数据
relational file关系文件
run—length encoding行程长度编码
spatial data model空间数据模型topological modeling拓扑建模
vector data矢量数据
Address matching 地址匹配
Annotation feature 注释要素
Associated attribute 关联属性
Attribute 属性
Base map 底图
Buffer 缓冲区
Cartography 绘图
Cartology 地图学Census 人口统计
Central projection 中心投影
Cigitization 数字化
Contour line 等高线
Convert 转换
Coordinates 坐标
Cybercity 数字城市
Data conversion 数据转换
Data table 数据表
Database 数据库
Digital elevation model 数字高程模型dem
Digital orthoimagery 数字正射影像
Digital terrain model 数字地面模型
Entity 实体
Environment System Research Institute ESRI
美国环境系统研究所
External table 外部表格
Feature 要素
Feature 要素,特征
Geographic feature 地理要素
Geographic/spatial information 地理信息、空间信息Georeferenced Coordinate referencing system
地理参考
Hierarchical 层次
Imagery 影像
Layer 图层,数据层
Map legeng 地图图例
Map projection 地图投影
Mapping 制图
Network feature 网络要素
Network 网络
Object 目标,对象
Proximity 领域分析
Qualitative 质的
Quantitative 量的
Query 查询
Reference 相关的
Relational database 关系数据库
Relational 关系
Retrieval 检索
Spatial attribute 空间属性
Spatial data 空间数据
Statistical analysis 统计分析
Thematic MAP 专题地图
Theme 主题,图层
Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO EARTH Major Concept (I) The planets in our solar system, including Earth, began to form out of a rotating disk of gas and dust about 4.6 billion years ago. Related or supporting concepts: The present view of the beginning of the solar system suggests that a cloud of gas and dust was flattened into a disk by rotation. The density of the matter in the disk was greatest at its center and decreased toward the edges. The sun formed at the center of the disk where the temperature was highest and the planets formed at greater distances away from the center. The compositions of the planets differ because of a natural sorting of elements in the cloud with distance from the center. The temperature of the early Earth was probably quite high due to: a. the gravitational capture of particles that released heat on impact, b. the increased pressure on the interior of the planet as it continued to grow, and c. the capture of radioactive elements that gave off heat when they decaye d. During the first few hundred million years, the internal temperature rose high enough to melt iron and nickel. These heavy metals sank to form the core of the planet and displaced lighter material that rose to form chemically differentiated shells. Major Concept (II) Earth’s oceans originated early in the planet’s history. There are two proposed sources of the water in the oceans. Related or supporting concepts: The oldest sedimentary rocks found that required water for their formation are 3.9 billion years old. This suggests that there are been oceans on Earth for roughly 4 billion years. Traditionally scientists have believed that the water in the oceans and atmosphere originated in Earth’s mantle and was brought to the surface by volcanism. Most magmas contain from 1% to 5% dissolved gas by weight, most of which is water vapor. If we assume that the current rate of release of water vapor in volcanic eruptions has remained essentially constant for the past 4 billion years, then the volume of water expelled(put out) during that time would be roughly 100 times the volume of today’s oceans. A relatively new proposal is that a significant amount of water is added to Earth from space when small icy comets(彗星)enter Earth’s atmosphere. The early atmosphere did not have any oxygen. The oxygen released from the interior of the planet would have combined with metals at the surface to produce oxides. It wasn't until large amounts of oxygen were produced after plants formed that it began to accumulate in the atmosphere. Major Concept (III)
引言Introduction 人文地理学,作为科学王国中一支较小的学科,尽管常常不被人们关注和重视,然而它却是一支最具活力的学科,它的研究主题——社会的空间组织和人与环境的关系——为许许多多形式的研究和朝气蓬勃的地理学者提供了机遇和挑战。在最近30年来,西方人文地理学可以说是百家争鸣、百花齐放。人文地理学家不断地接受他们以前很少遇到的其它学科的新思想、新观念,这样就给人文地理学的发展带来无限的生机。 Human geography is such a subject full of vitalities despite of being neglected sometimes.Its research themes, the social-spatial structure and the relationship between human and environments, have brought opportunities and challenges to both various forms of research and geographers.In recent 30 years, the western human geography has so many variegated theories and ramifications.Human geographers have kept absorbing new ideas and opinions from many other subjects, which gives tremendous vital force to the development of human geography. 一、人文地理学的性质 Characters of human geography 1、地理学形成及分化 Formation and differentiation of geography 地理学(geography)是希腊语中关于地球和书写两个词复合词,主要研究人类生活空间的地球表面(Haggett,1990)。 Geography mainly studies the earth sphere that people live in. 大学地理学的发展一开始就受到自然科学和人文社会科学两大类学科分化的影响,研究自然环境的地理学称为“自然地理学”,研究人工环境的称“人文地理学”。 Geography studied in university had ramifications about “physical geography”and “human geography”because its development had been affected by the differentiation of natural science and social science from the beginning. 随着科学的进步和社会需求的出现,地理学的定义也在不断地发生变化。通过英国和美国地理学家学会研究组对大多数地理学系课程和学科体系的调查发现,1990年代的地理学主要由人文地理学、自然地理学、混合人文和自然地理学和其它领域四个方面所组成。 With the development of sciences and the emergence of social demands, the definition of geography has been evolving continuously. As shown in a survey about the curriculum and the subject system of geography, in the 1990s, geography was consisted of four branches: human geography, physical geography, human- physical geography together with other geography fields. 2、人文地理学的发展 Progress of human geography 18世纪后期到19世纪早期,德国和法国的人文地理学萌芽 From late 1800s to early 1900s, human geography germinated in German and France. 1918-1939,两次世界大战之间,处在早期调查阶段 From 1918 to1939, the progress of human geography was in the period of early survey. 二战后,主要从1960年代起,人文地理学与其他社会科学互动与接轨,实现了从区域描述到诠释人与社会、人与环境、及人与地点或地方关系的转变。 After the world War II, especially from the 1960s, human geography had interacted and linked up with other social sciences. It changed into interpreting the relationship between human
一、英英释义 ?Vertical line ?Contour ?Leveling 二、词汇汉译英 地理信息系统地图学 等高线 大地水准面高程电子测绘仪 经纬仪 十字丝 放样 照准部 水准测量 全站仪 方位角 准确度 卫星测距 三、词汇英译汉 Geomantic Geodesy Photogrammetry Aerial photograph Field work Horizontal survey Latitude Plumb line Mean sea level Tacheometry Level staff Vertical circle Counter clockwise Topography Level surface Stadia hair Prism Precision Random error GPS receiver 四、句子英译汉
1.It is processed and manipulated with state-of-the-art information technology using computer software and hardware. 2.It has applications in all disciplines which depend on spatial data. 3.Once the positions and attributes of geographic entities(实体) have been digitized and stored in computer memory, they are available for use by a wide variety of users. https://www.doczj.com/doc/e38359635.html,nd surveys are the oldest type of survey and have been performed since earliest recoded history. 5.Construction surveys are made for purposes of locating structures and providing required elevation points during their construction. 6.To judge the exact horizontal line, we should move tape up and down along the plump line and we will find the changes of reading in the tape. 7.If the distance is longer than the length of tape, then we can divide the distance into several segments and get the total distance by plus each segment together. 8.Since different tapes have different starts of zero of the tapes, it is important to judge where the zero of the tape begins. 9.Vertical Line is a line that follows the direction of gravity as indicatedby a plumb line. 10.A spirit level is used to fix the line of sight of the telescope.
Uuit1 What is Geomatics? (什么是测绘学) Geomatics Defined(测绘学定义) Where does the word Geomatics come from?(Geomatics-测绘或地球空间信息学,这个名词是怎么来的呢?) GEODESY+GEOINFORMATICS=GEOMATICS or GEO- for earth and –MATICS for mathematical or GEO- for Geoscience and -MATICS for informatics. (大地测量学+地理信息学=GEOMATICS测绘学或者 geo代表地球,matics代表数学,或者 geo代表地球科学,matics 代表信息学) It has been said that geomatics is many things to many people.(据说测绘学这个词对不同的人有不同的理解) The term geomatics emerged first in Canada and as an academic discipline; it has been introduced worldwide in a number of institutes of higher education during the past few years, mostly by renaming what was previously called “geodesy” or “surveying”, and by adding a number of computer science- and/or GIS-oriented courses.(这个术语【term术语】作为一个学科【academic discipline学科】第一次形成【emerge】于加拿大;在过去的几年里被全世界的许多高等教育研究机构所熟知,通常是以前的“大地测量学”或“测量学”在引入了许多计算机科学和GIS方向【或“基于GIS”】的课程后重新命名的。) Now the term includes the traditional surveying definition along with surveying steadily increased importance with the development of new technologies and the growing demand for a variety of spatially related types of information, particularly in measuring and monitoring our environment.(随着新技术的发展和不断增长的对空间关系的信息类型的需求,尤其是在测量和监测我们的环境方面【环境监测】,现在,传统测量学定义连同【along with】日益【steadily稳定的】增长的测量的重要性一起包含在这个术语里了。【逗号后面的句子修饰demand】) Increasingly critical are areas of expanding populations, appreciating land values, dwindling natural resources, and the continuing stressing of the quality of our land, water and air from human activities.(日益增长的危机来自人口扩张,地价上涨,资源紧缩【紧张】,还有由于人类活动引起的土地、水、空气质量的持续的压力【由人类活动带来的土地、水、空气质量的恶化】 As such, geomatics bridges wide arcs from the geosciences through various engineering sciences and computer sciences to spatial planning, land development and the environmental sciences.(这样,测绘学在地球科学,各种工程学【engineering sciences工程学】,计算机科学,空间规划,土地开发和环境科学相互之间架起了广泛的桥梁。) Now the word geomatics has been adopted by several international bodies including the International Standards Organization(ISO),so it is here to stay.(现在geomatics 这个词已经被包括ISO【国际标准化组织】在内的数个国际机构【international bodies】所采用, 因此它就这样被普遍接受【be here to stay 习惯用语“被普遍接受”】 The term “surveyor” is traditionally used to collectively describe those engaged in the above activities. (surveyor这个词按惯例用来总指(这换成“总称”较好)【collectively全体的】那些从事上述活动的人。) More explicit job descriptions such as Land Surveyor, Engineering Surveyor or
A a horizon 腐殖堆积层 aa lava 块熔岩 abandoned field 撩荒地 abandoned lands 撩荒地 abandoned mine 废弃矿山 abandoned shoreline 旧岸线 aberration 像差 abiogenesis 自然发生 abiotic factor 非生物因素 ablation 水蚀 ablation moraine 消融冰碛 abnormality 反常 aboriginal 土着的 abrasion 海蚀 abrasion platform 浪蚀台地 abrasion shore 浪蚀海岸 abrasion surface 浪蚀面 abrasion terrace 海蚀阶地 abrasive 研磨剂 abrupt slope 陡坡 abrupt textural change 质地突变 abscissa 横坐标 absolute age 绝对年龄 absolute age determination 绝对年代测定absolute age of groundwater 地下水绝对年龄absolute altitude 绝对高度 absolute amplitude 绝对振幅 absolute chronology 绝对年代 absolute convergence 绝对收敛 absolute dating 绝对年代测定 absolute error 绝对误差 absolute extremes 绝对极值 absolute geochronology 绝对地质年代学absolute geopotential 绝对重力势 absolute gravity 绝对重力 absolute humidity 绝对湿度 absolute instability 绝对不稳定性 absolute maximum 绝对极大
G I S专业英语
第一课 Comprehensive:全面的,综合的,Intellectual:智力的,才智的Jargon:专业术语 Terminology:专业术语Geomatique:地理信息技术Geoscience:地球科学Derivative:派生物,衍生物Cartography:地图绘制学,地图绘制Architect:建筑师 Preliminary:初步的,起始的Enumerate:列举,枚举Resemble:像,与……相似Transformation:转换 第二课 Automated:自动化的Equivalent:a等价的Cartographer:绘制图表者,制图师Mylar:胶片 Electronic:电子的 Encode:编码Orthophotoquad:正射影像图Aerial:空中的,航空的Aggregation:集合,聚合,集合体Reproduction:再现,复制,繁殖Dissemination:传播,宣传,传染Counterpart:相似之物Compactness:致密性 Complexity:复杂,复杂性Hamper:阻碍,束缚 Retrieval:取回,恢复,修补Analog:模拟的 Planimeter:测面器,求积仪 Phenomena:现象Quantitative:数量的,定量的Histogram:直方图,柱状图Supplementally:追加,补充Modification:修改,变型Cartogram:统计地图,统计图Hand-drawn:手绘 Emergency:紧急事件Employe:雇佣,雇工
Clarify:澄清,阐明Taxonomy:分类学,分类法Bifurcation:分歧,分叉 Parcel:地块 Conservation:保存,保持Procurement:获得,取得,采购Wildlife:野生动植物Earthquake:地震 Landslide:泥石流,山崩Cadastral:地籍的,有关土地清册的Geodetic:大地测量学,最短线的Sophisticated:精致的,复杂的 第三课 Pervade:弥漫,遍及 Aspect:坡向,方向,面貌Inevitable:必然的,不可避免的Proprietary:所有的,专利的Mineral:矿物的,矿质的Military:军队,军人 Electricity:电力,电流Telecommunication:通讯,电信学Interconnect:使相互连接,相互联系Administrative:管制的,行政的Environmental:环境的,周围的Attribute:属性,特质Procedure:步骤,程序,手续Manipulation:操作,操纵,处理Historically:历史上地,Subsume:把…..归入,把…..包括在Eclipse:形成蚀,使黯然失色Visualization:可视化,Immense:巨大的,广大的Analogue:类似,相似物Conventional:常见的,惯例的Enquire:询问,打听Coniferous:松柏科的 Highlight:强调,突出, Stress:强调,加压力与 Derive:得到,源于 Discipline:纪律,学科,惩罚Algorithm:算法, Interpret:说明,口译,解释Artificial:人造的,仿造的,虚伪的 Geomatique:地理信息技术Cartography:地图绘制学,地图绘制Preliminary:初步的,起始的Cartographer:绘制图表者,制图师Encode:编码 Aggregation:集合,聚合,集合体Retrieval:取回,恢复,修补Analog:模拟的 Quantitative:数量的,定量的Histogram:直方图,柱状图Cartogram:统计地图,统计图Parcel:地块 Geodetic:大地测量学,最短线的Cadastral:地籍的,有关土地清册 的 Attribute:属性,特质 Procedure:步骤,程序,手续 Prime meridian:本初子午线 Algorithm:算法, Discipline:纪律,学科,惩罚Visualization:可视化, Globe;球体 Map projection地图投影 Planar projection;平面投影Azimuthal projection;方位投影Characteristic,特征,特性Reference globe;参考椭球体 Scale factor;比例因子 Principle scale;主比例尺Equivalent projection;等积投影Equidistant;等距投影 Mercator transverse;横轴莫卡托投影Gnomonic protection;中心切面投影Lambert‘s equal area projection 兰伯特等级方位投影
盛年不重来,一日难再晨。及时宜自勉,岁月不待人。 地理专业英语 geography 地理 geographer 地理学家 hemisphere 半球 meridian 子午线,经线 parallel 平行圈,纬线 latitude 经度 longitude 精度 elevation 海拔 altitude 高度 temperate latitudes 温带地区 horizon 地平线 equator 赤道 tropics 热带地区 Arctic 北极 Antarctic(Antarctica) 南极 expedition 探险 time zone 时区 topography 地形,地形学 plain 平原 plateau (highland) 高地 lowland 低地 basin 盆地 cavern (cave) 洞穴 terrain 地域 subterranean ( underground) 地底下 coastland 沿海地区 island 岛屿 continental island 大陆岛 volcanic island 火山岛 coral island 珊瑚岛 islet 小岛 peninsular 半岛 continent 大陆
continental shelf 大陆架 ranges 山脉 valley 峡谷 canyon 峡谷 channel (strait) 海峡 remote-sensing 遥感的 terrestrial 地球的,陆地的 terrestrial heat (geothermal) 地热terrestrial magnetism (geomagnetism) 地磁continental drift 大陆漂移学说 sea-floor spreading 海床扩展 evaporation 蒸发 salinity 含盐度 ocean bottom 海床 sediment 沉淀物,沉积物 tropical 热带的 temperate 温带的 frigid 寒带的 formation 形成 frost heaving 冻胀现象 fieldstone 卵石 physical geography 自然地理 economic geography 经济地理 geopolitics 地理政治论 ethnography 民族志 cosmography 宇宙志 cosmology 宇宙论 geology 地理学 toponymy 地名学 oceanography 海洋学 meteorology 气象学 orography 山志学 hydroaraphy 水文学 vegetation 植被 relief 地形,地貌
地理信息系统(GIS)词汇表accreditation 委派accuracy 准确度acquisition 获取activity patterns 活动模式 added value 附加值adjacency邻接Aeolian 伊奥利亚人的, 风的, 风蚀的 Age of Discovery 发现的年代aggregation聚合algorithm, definition算法,定义 ambiguity 不明确analytical cartography 分析制图 application programming interfaces(APIs) 应用编程接口 ARCGis 美国ESRI公司开发的世界先进的地理信息系统软件 ArcIMS 它是个强大的,基于标准的工具,让你快速设计和管理Internet地图服务 ArcInfo 在ArcGIS软件家族中,ArcInfo是GIS软件中功能最全面的。它包含ArcV iew和ArcEditor所有功能,并加上高级空间处理和数据转换 ArcNews 美国ESRI向用户终生免费赠送的ArcNews报刊 ArcSDE ArcSDE在ESRI GIS软件和DBMS之间提供通道,是一个空间数据引擎 ArcUser Magazine 为ESRI用户创建的报刊 ArcView 桌面GIS和制图软件,提供数据可视化,查询,分析和集成功能,以及创建和编辑地理数据的能力ARPANET ARPA计算机网(美国国防部高级研究计划局建立的计算机网) aspatial data 非空间数据Association of Geographic Information (AGI) 地理信息协会attribute data 属性数据attributes, types 属性,类型attributive geographic data 属性地理数据autocorrelation 自相关Autodesk MapGuide 美国Autodesk公司生产的Web GIS软件Automated mapping/facility management(AM/FM) systems 自动绘图/设备管理系统facilities 设备avatars 化身A VIRIS 机载可见光/红外成像光谱仪 azimuthal projections 方位投影batch vectorization 批量矢量化 beer consumption 啤酒消费benchmarking 基准Berry, Brian best fit line 最优线 binary counting system 二进制计算系统binomial distribution 二项式分布 bivariate Gaussian distribution 二元高斯分布block encoding 块编码 Bosnia, repartitioning 波斯尼亚,再分离成两个国家buffering 缓冲区分析 Borrough, Peter Business and service planning(retailing) application in petroleum and convenience shopping 石油和便利购物的业务和服务规划(零售)应用business drivers 业务驱动 business, GIS as 业务,地理信息系统作为Buttenfield, Barbara cadasters 土地清册Callingham, Martin cannibalizing 调拨 Cartesian coordinate system笛卡尔坐标系Cartograms 统计地图 cartographic generalization 制图综合cartographic modeling 地图建模 cartometric transformations 量图变换catalog view of database 数据库目录视图 census data人口普查数据Census of Population 人口普查 central Place Theory 中心区位论central point rule 中点规则 central tendency 中心倾向centroid 质心choropleth mapping分区制图 choosing a GIS 选择一个地理信息系统class 类别classification generalization 分类综合client 客户端client-server C/S结构客户端-服务器cluster analysis 聚类分析 clutter 混乱coastline weave 海岸线codified knowledge 编码知识 COGO data 坐标几何数据COGO editing tools 坐标几何编辑工具Collaboration 协作 Local level 地方级National level 国家级Collection-level metadata 获取级元数据Commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) systems 成熟的商业化系统chemas-microsoft-comfficeffice" />>>
地理专业词汇英语翻译(M) 地理专业词汇英语翻译(M) maar 低平火山口 macedonite 方假象橄玄岩 maceration 浸渍 machine proof 开印样 macro aggregate 大团聚体 macroclimate 大气候 macroclimatology 大气候学 macrometeorology 大气象学 macromolecule 大分子 macrophage 巨噬细胞 macrophyte 大型植物
macroplankton 大型浮游生物macroporosity 大孔隙度 macrorelief 大区地形 macrotherm 高温植物 maelstrom 大涡流 mafite 镁铁矿物 magazine 暗匣 magenta contact screen 品红接触网目片maghemite 磁赤铁矿 magma 岩浆 magma chamber 岩浆储源
magma reservoir 岩浆储源 magmatic assimilation 岩浆同化酌magmatic differentiation 岩浆分异酌magmatic evolution 岩桨进化magmatic migration 岩浆迁移magmatic rock 岩浆岩 magmatic segregation 岩浆分结酌magmatic water 岩浆水 magmatism 岩浆酌 magnesian limestone 含镁石灰岩magnesian skarn 镁质夕卡
magnesioferrite 镁铁矿magnesite 菱镁矿 magnesite deposit 菱镁矿床magnesium 镁 magic action 磁酌 magic amplifier 磁放大器magic anisotropy 磁力蛤异性magic anomaly 地磁异常magic attraction 磁吸引力magic axis 磁轴 magic azimuth 磁方位角
地理信息科学专业英 语
专业术语英译汉 affine 仿射 band 波段 cartography 制图学 clip 剪切 digitizer 数字化仪 DLG 数字线划图 dpi 每英寸点数edgematching 边缘匹配equator 赤道 equiarea 等积 geoid 大地水准面geospatial 地理空间 GPS 全球定位系统Habitat 栖息地 Interface 接口 Item 项目 Latitude 纬度 legend 图例 longitude 经度 median 中值 meridian 子午线 metadata 元数据 neatline 图廓线 Object-Based 基于对象的parcel 宗地photogrammetry 摄影测量precipitation 降水量 range 范围 raster 栅格 resample 重采样 resolution 分辨率 RMS 均方根 scanner 扫描仪 siting 选址 TIGER 拓扑统一地理编码topology 拓扑 tuple 数组 UTM 通用横轴墨卡托投影vector 矢量
专业术语汉译英 保护区protected area 比例尺Scale bar 标准差Standard deviation 标准图幅Standard picture frame 单精度Single precision 地理空间数据Geospatial data 点缓冲区Point buffer 动态分段Dynamic segmentation 度量标准Metrics 多项式变换Polynomial transformation 高程基准Elevation base 跟踪算法Tracking algorithm 规则格网Rules grid 过渡带Transition zone 基于位置服务Based on location service 畸形线Malformation line 几何变换Geometric transformation 检验图Inspection chart 解析几何Analytic geometry 空间要素Space element 平面坐标系统Planar coordinate system 曲流河Meandering river 人口普查地段Census Lot 上四分位数The upper quartile 矢量数据模型Vector data model 数据可视化data visualization 数据探查Data exploration 双精度Double precision 水文要素Hydrological elements 泰森多边型Tyson Polygons 统一建模语言Unified Modeling Language 投影坐标系统Projection coordinate system 线缓冲区Line buffer 遥感数据Remote sensing data 用材林Timber forest 晕渲法Halo rendering method 指北针Compass 属性表Property sheet 最短路径分析Shortest path analysis 最小二乘法Least squares method
法学 Law Study 英语 English 日语 Japanese 信息与计算科学 Information and Computation Science 应用物理学 Applied Physics 冶金工程 Metallurgical Engineering 金属材料工程 Metallic Materials Engineering 无机非金属材料 Inorganic Nonmetallic Materials 材料成型及控制工程 Material Formation and controlEngineering 高分子材料与工程 Multimolecular Materials and Engineering 工业设计 Industrial Disign 建筑学 Architecture 城市规划 City Planning 艺术设计 Artistical Disign 包装工程 Packaging Engineering 机械设计制造及自动化Machine Disign,Manufacturing,and Automation 热能与动力工程 Thermal and Power Engineering 水利水电工程 WaterConservance and Electro-power Engineering 测控技术与仪器 Technique and Instrumentation of Measurements 电气工程及其自动化 Electric Engineering and its Automation 自动化 Automation 通信工程 Communication Engineering 电子信息科学与技术 Sience and Technology of Electronic Information 计算机科学与技术 Computer Sience and Technology 土木工程 Civil Engineering
地理专业英语 geography 地理 geographer 地理学家 hemisphere 半球 meridian 子午线,经线 parallel 平行圈,纬线 latitude 经度 longitude 精度 elevation 海拔 altitude 高度 temperate latitudes 温带地区 horizon 地平线 equator 赤道 tropics 热带地区 Arctic 北极 Antarctic(Antarctica) 南极 expedition 探险 time zone 时区 topography 地形,地形学 plain 平原 plateau (highland) 高地 lowland 低地 basin 盆地 cavern (cave) 洞穴 terrain 地域subterranean ( underground) 地底下coastland 沿海地区 island 岛屿 continental island 大陆岛 volcanic island 火山岛 coral island 珊瑚岛 islet 小岛 peninsular 半岛 continent 大陆 continental shelf 大陆架 ranges 山脉
valley 峡谷 canyon 峡谷 channel (strait) 海峡 remote-sensing 遥感的 terrestrial 地球的,陆地的 terrestrial heat (geothermal) 地热terrestrial magnetism (geomagnetism) 地磁continental drift 大陆漂移学说 sea-floor spreading 海床扩展 evaporation 蒸发 salinity 含盐度 ocean bottom 海床 sediment 沉淀物,沉积物 tropical 热带的 temperate 温带的 frigid 寒带的 formation 形成 frost heaving 冻胀现象 fieldstone 卵石 physical geography 自然地理 economic geography 经济地理 geopolitics 地理政治论 ethnography 民族志 cosmography 宇宙志 cosmology 宇宙论 geology 地理学 toponymy 地名学 oceanography 海洋学 meteorology 气象学 orography 山志学 hydroaraphy 水文学 vegetation 植被 relief 地形,地貌 climate 气候 Earth 地球,大地 Universe, cosmos 宇宙